PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS PPT Review
advertisement

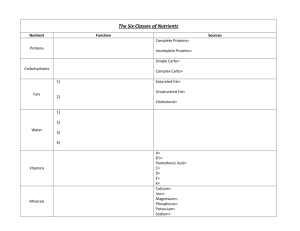
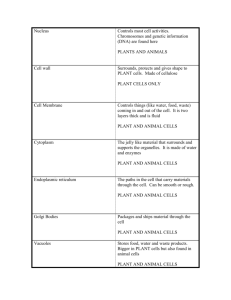
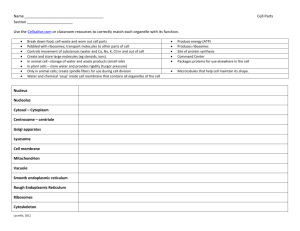
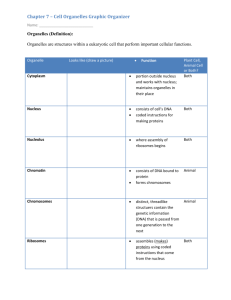
PLANT AND ANIMAL CELLS PPT Review 1. 2. • Gives the cell most of its support and structure CELL WALL: PLANT • Semi permeable, allowing some substances to pass into the cell and blocking others. CELL MEMBRANE • Photosynthesis takes place in the Chloroplast • The jellylike material outside the cell nucleus in which the organelles are located. Cytoplasm • Act as tunnels and transports materials although the cell Endoplasmic Reticulum • Are stacks of membranecovered sacs that package and move proteins to the outside of the cell. Golgi Bodies • Where the digestion of cell nutrients takes place Lysosome • Where energy is released. Mitochondria • Controls many of the functions of the cell Nucleus:The Manager • Small structures in the cytoplasm that create proteins. Ribosome's • Like your suitcase, this is a temporary storage space for the cell. Vacuole Plant Cell: Cross Section Plant Cell: Cross Section Students Will: • Summarize the contributions scientists have made toward the cell theory • State the cell theory. Anton van Leeuwenhoek • First compound light microscope Robert Hooke • Coined the term “cell” Matthias Schlieden • All plants are made of cells Theodor Schwann • All animals are made of cells Rudolf Virchow • Cells can only arise from pre-existing cells Cell Theory 1. All organisms are made up of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of organization of all organisms. 3. All cells come from other cells all ready in existence. Questions... • Who used the first microscope? • Who said that plants were made of cells • Who coined the term “cell”? • Who said that all animals were made of cells? • Who said that cells must come from existing cells? State the cell theory... The cell is the basic unit of structure. The cell is the basic unit of function. All cells arise from pre-existing cells. From largest to smallest place in the proper order: • • • • • • • • • • • Populations Organs/Tissues Organelles Ecosystems Proteins, Fats & Carbs Quarks Biosphere Cells Atoms Communities Individual Answer from Large to Small: Biosphere Ecosystem Communities Population Individual Organs/Tissues Cells Organelles Proteins/fats/carbs Atoms Quarks