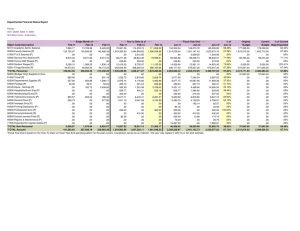
Four Pillars of Free Enterprise
advertisement

Free Enterprise Economic system where people exchange goods & svcs. free of most government intervention • Also known as: o Economics Chapter Two Free Enterprise in the U.S. private enterprise, market economy, Capitalism, or free market • • • • Four Pillars of Free Enterprise: (basic foundation of our econ system) 1. Four Pillars of Free Enterprise (cond.) Price System: as people make voluntary exchanges, they establish the prices of goods & svcs. 2. Private Property: individuals own their own biz, not the govt. Therefore, the indv. owner must maintain capital resources the price one is willing to sell @ price one is willing to buy @ prices indicate the value consumers place on items/products, as well as the opportunity cost of using resources: the •Prices also provide incentives price goes up, people look for bargains •when prices go down, they buy more of the desired items •when Price doesn’t always create these situations: •more •one expensive = better might choose location to live for a job loyalty is very strong •product Four Pillars of Free Enterprise (cond.) 3. o Market Competition: people engage in a competition to consume scarce resources. 2 kinds of competition in markets: Four Pillars of Free Enterprise (cond.) Entrepreneurship: seeing the opportunity to make money by taking chances, introducing new products, methods of production, management into the market 4. oFor Resources: buyers compete for productive resources (workers, oil, machinery, etc.), while sellers compete to find these buyers •the more educated you are, the more likely you'll be paid more oFor Products: buyers compete for goods & svcs. (steak, tacos, pizza). When people want more tacos, they are willing to pay more for them, and the price goes up. You might in turn, buy less • • entrepreneurs follow through w/ their ideas…even the unpopular ones free enterprise encourages entrepreneurs •sellers compete to attract these buyers by pricing @ their wants 1 FREE ENTERPRISE IN ACTION The Circular Flow in the Production of Shoes Cow Grower Consumer must buy goods & svcs for the Free Enterprise system to work $$ Cow Killer $$ $$ Cow “Pulper” Leather Tanner •Consumer ("Household") consume goods and svcs. to keep biz. going •They also provide resources to the production of goods (i.e., labor) $$ $$ Shoe Maker Feed for Other Cows $$ (kid in 3rd world) $$ YOU & ME Shoe Store (SBE = Bad) $$ Ideas, Terms & People You Should Know. Ya Know? The Circular Flow in Action Markets for Goods & Services Goods & Svcs. Medium of Exchange: trading goods & svcs for money o Store of Value: you can store the medium (money) for future use Measure of Prices: measures price & relative value of products & resources • Goods & Scvs. $$ $$ Businesses Producing Goods & Services Households/Consumers $$ Labor & Other Resources $$ Markets for Resources Labor & Other Resources o $ is the medium (means) we value ** Money helps us put a value on the goods & svcs we want, and those we produce oAdam Smith: Scottish-born Economist (founded the study of equal exchanges). Asked how we could care about well-being of others while looking out for ourselves 2