Liquidity,Risk and Profitability Analysis : A case Study of Maruti India
advertisement

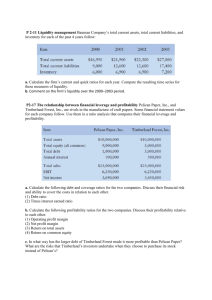
Search & Research Vol-II No. 2 (191-193) : (2011) Liquidity, Risk and Profitability Analysis : A Case Study of Maruti India Ltd. Dr. Vivek Sharma Director, C. Rajagopalachari Institute of Management, U.T.D. Barkatullah University, Bhopal (M.P.) India MS Received : 23 June 2010 MS Accepted : 06 Aug 2010 Abstract : Liquidity risk and return both are very important aspects to be considered while making any decisions regarding company’s finance. It affects the liquidity and profitability in any ways. This paper attempts to study these three elements in company’s existence and their relationship. Key words : Liquidity, Risk, Profitability Introduction : Liquidity management has been taken as an important tool to analyze the sustainability and liquidity position of any enterprise that may also help any organization to derive maximum profits at minimum cost. A company must maintain its ability to pay off its current obligations and have a sound base of working capital to stay for a long in the competitive market. The management of working capital is an important aspect to be considered for attaining sound liquidity position. Profitability, in this reference may be the return earned on the total assets of the company. Every firm aims to dig up maximum profits out of the invested capital pool. The success of the company usually depends on its returns earned, keeping the liquidity prospects in view. Usually, it is a difficult task to trade off between the liquidity and profitability, as the conservative policy of working capital may ensure sound liquidity but endangers the profitability. On the other hand, aggressive policy helps in making profits but the liquidity is in not promised. Before deciding on an appropriate level of working capital investment, a firm’s management has to evaluate the trade off between expected profitability and the risk that it may be unable to meet its financial obligations.1 Finance deals with creating a proper framework to maximize profits at a given level of risk. In pursuing this balance, the firm must develop controls over the flows of funds while allowing sufficient flexibility to Oct-2010-Jan-2011 respond to changes in the operating environment.2 Thus, the firms must attain a level of adequate liquidity at a minimum risk so as to achieve maximum profitability. Company Snapshot: Maruti Suzuki India Limited (MSIL) is a passenger car company. The Company is engaged in the business of manufacturing, purchase and sale of motor vehicles and spare parts (automobiles). The other activities of the Company include facilitation of pre-owned car sales, fleet management and car financing. The Company is a subsidiary of Suzuki Motor Corporation, Japan. The Company has a portfolio of 13 brands and over 150 variants across India and abroad. The Company's two manufacturing facilities are located at Gurgaon and Manesar, south of New Delhi. The Company's subsidiaries include Maruti Insurance Business Agency Limited, Maruti Insurance Distribution Services Limited, Maruti Insurance Agency Solutions Limited, Maruti Insurance Agency Network Limited and Maruti Insurance Agency Services Limited. Objectives of the Study : The study is being done with the following objectives:1. To examine the association between liquidity and risk. 2. To test the correlation between profitability and risk. 191 Search & Research Hypothesis of the Study : The above stated objectives are to be achieved by testing the following hypothesis: 1. There is negative association between liquidity and risk. 2. Profitability and risk of the firm are negatively correlated. Research Methodology : The study is concerned with the ten years data of Maruti Suzuki India Ltd. for a period of (2001 2010).The data is of secondary nature and is obtained from the published annual reports of Maruti Suzuki India Ltd. The collected data has been analyzed through various liquidity and profitability ratios and drawing out the risk factor. Further, t test has been applied to test the hypothesis and draw conclusions. Results and Discussions : Tables given forward show the liquidity and profitability position of the company along with the risk factor has been calculated to study the inter relation ship. Liquidity Position of Maruti India Ltd. assets viz. cash in hand and at bank and market securities with current liabilities. This ratio helps in examining the absolute liquid position. The ratio at highest in year 2008 at 0.10 and thus ranked as 1 and the lowest ratio is in year 2003, 2004 & 2006.In these years the company struggled with shortfall of cash balances to meet their short term obligations. Further, the ultimate ranks denote that in year 2001 and 2005, the company was having highest liquidity and the poorest performed year in reference of liquidity was 2010. Profitability Position of Maruti Suzuki India Ltd. Table No 2 exhibits the profitability position of the company by using three very basic ratios of profitability. The return on assets (ROA) percentage shows how profitable a company's assets are in generating revenue. Table 2 reveals an increasing trend in spite of the first year to give a negative percentage at -7.18%.This shows that the company is managing to get good returns out of their assets pool. Return on capital employed is the indicator of the operational efficiency of the company. The resulting ratio represents the efficiency with which capital is being utilized to generate revenue. Table 2 shows that the ratio is at negative value in year 2001 at -9.88% and is showing a fluctuating trend till 2010. Table No.1 exhibits the three basic ratios of test of liquidity, viz. Current Ratio, Quick Ratio and Absolute Ratio. The ratios are ranked in the order of their influence on liquidity. The higher is the ratio, the greater is the liquidity. Further, ultimate rank has been calculated form the total of the ranks of ratios. Ultimate ranking has been done on the principle that the lower the aggregate of the individual ranks, the more profitable is the liquidity position and vice versa. Current ratio is a relationship between the current assets and current liabilities and thus is used as measure of general liquidity. It can be noted form Table No.1 that the current ratio in year 2001 and 2006 is the highest at 1.77 times. The rule of thumb is 2:1 but it can vary from firm to firm. The least value of the current ratio is 1.02 in year 2010. Quick ratio is an indicator of the liquidity in sense of the relationship between the quick assets and current liabilities. Again, the higher ratio is an indicator of higher liquidity. Years 2003 and 2005 are the period of the highest quick ratio at 1.32.The ratio was at least value in year 2010 at 0.68 which is very low and that’s why ranked as 10. Where, Rk = Risk factor, Ej = Equity + Retained Earnings, Lj = Long term Loans, Aj = Fixed Assets, Cj = Current Assets Absolute ratio shows the relation of absolute liquid The above formula helps to know about the Oct-2010-Jan-2011 Return on net worth is the relationship between the net profit and the shareholder’s funds of the company. Table 2 reveals that the ratio is showing a negative percentage in year 2001 and showing a increasing trend till 2007, but is showing some fluctuations till the end of the period. Trade off between risk and profitability: Trade off between risk and profitability can be made by calculating the risk factor. The analysis can be done through which it can be said about the policies adopted while managing the working capital of the company. Risk factor has been calculated & shown in Table no 3. Risk factor can be calculated through the following formula:A1 Rk = (Ej + Lj ) - Aj Cj 192 Search & Research financing of the current assets through long term funds after fixed assets are financed in full. Based on the above formula, following inferences can be drawn: ! Value of Rk is zero or less would mean that the firm is using the aggressive policy and normally the profitability would be high. ! Value of Rk is 1 or close to 1 would mean that the firm is using a conservative policy and the profitability would be low. Under aggressive policy the firm opts for a lower level of working capital thereby investing in current assets at lower proportion to total assets. When a firm adopts this policy, the profitability is high but at higher risk of liquidity. In case of conservative policy, the firm adopts a conservative approach of having high proportion of working capital. The profitability is relatively low as the return on current assets is normally less. But ensuring good liquidity as the risk of meeting current obligations is reduced. Table no 3 discloses the risk factor that has been ranked and is indicating the policy adopted by the company in various periods. Conclusion: Maruti Suzuki India Ltd being an established company from past few decades is satisfactorily giving out profits and maintaining its liquidity position but at increased risk factor. The liquidity position of the company is fluctuating but is acceptable. The risk factor calculated is a needle of the working capital management and the policy adopted. The company is timely changing its policies for better results but at higher risk. The profitability is increasing at good pace showing the efficiency of the company. Thus, it can be concluded that the company is earning good profit with moderate liquidity and at higher risk. References : 1. Bhalla V.K.1 (1997), Financial Management and Policy, Anmol Publications Pvt. Ltd pp 200. 2. Hampton John J.2 ( 1990), Financial Decision Making, Prentice- Hall of India Pvt. Ltd. pp 9. 3. Gupta S.P. (2004) Management Accounting, Sahitya Bhawan Publications. 4. Luther C.T. Sam (2007) The Management accountant, Liquidity, Risk and Profitability Analysis, A Case Study of Madras Cements Ltd. 5. The null hypothesis stated that there is negative association between liquidity and risk. Sur Debasis,(2001),”Liquidity Management: an overview of four companies in Indian power sector”, The Management Accountant, pp 407412 6. Calculated Value of ‘t’=1.43 and Critical value of ‘t’= 2.31 Sharma R.K. and Gupta Shashi K. (2008), Financial Management, Kalyani Publishers. 7. Annual reports of Maruti Suzuki India Ltd. 8. www.moneycontrol.com 9. www.economic times.com The hypothesis drawn are tested by using student’s’ test for confirming the association between the risk, liquidity and profitability. Table no 4 exhibits that there is low degree of association between liquidity and risk, further, this association is tested. Conclusion: As the calculated value is less than the critical value, thus, the null hypothesis is accepted. Thus, it can be said that there is no significant association between liquidity and risk of this company. The table shows that the profitability and risk are negatively associated but again, it has to be tested using‘t’ test. 10. www.google.com Corresponding Author Dr. Vivek Sharma The null hypothesis states that profitability and risk of the firm are negatively correlated. Calculated value of ‘t’ = -3.63 & Table value of ‘t’ = 2.31 As the calculated value is less than the table value, the null hypothesis is accepted. Hence, it can be said that the profitability and risk are negatively correlated. Oct-2010-Jan-2011 193