Literary Terms and Figurative Language Terms Flashcards
advertisement

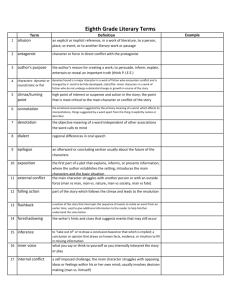
Name: _______________________________ Hour: ______ DUE DATE: WED NOV 12 Literary Terms and Figurative Language Terms Flashcards Assignment Elements of Fiction/Story Vocabulary/Memoir - 7th grade Each underlined word should be a flash card. *We will work on in class on Thursday, November 12. No other class time will be planned, however students may work on flash cards if they finish classwork early. author’s purpose why the author wrote the story - three main categories: persuade inform entertain setting where and when a story takes place (may be general or specific - understand the time period in history and the location in the world to help comprehend the story mood the emotion/feeling the writer want the READER to feel in different parts of the story tone the attitude the WRITER shows toward the topic or subject of the story character one of the people (or animals) in a story protagonist - the main character in the story, often a “good” or heroic type antagonist - the character or force that works AGAINST the hero of the story dynamic character - changes throughout the text as a result of events static character - stays the same throughout the text characterization the ways in which an author develops a character, making him or her seem believable methods of characterization 1. description - the author describes the character’s physical and personality traits 2. actions - what the character does 3. thoughts - what the character thinks - if the author gives us the internal dialogue 4. speech - what the character says 5. reaction of others - how other characters act or what they do/say in response character trait qualities that a character shows MOST of the time (ex:: cautious, intellectual, sentimental) point of view the place of the person telling the story (within the story, outside the story, etc.) st 1person the story is told from the point of view of ONE character in the story (I, my, we, ours...) rd 3person the story is told from someone OUTSIDE the story 3rd person LIMITED - the narrator does not know or tell the other characters’ feelings 3rd person OMNISCIENT - the narrator knows/shares the characters’ feelings 2nd person - the speaker is talking directly to the reader narrator : who is “telling” the story perspectivethe narrator’s background knowledge, attitude, and values that influence the way he or she tells the story dialogue: when characters speak conflict a problem or struggle between two forces 2 categories of conflict: internal and external internal conflict - person vs self the antagonist is the struggle within the character’s mind the character struggles with a decision, belief, fate, faith external conflict - the main character struggles against an outside (external) force TYPES OF EXTERNAL CONFLICT - person vs. person (between characters) -person vs. society (school, the law, tradition) - person vs. nature (blizzard, hurricane, mountain climb) - person vs. fate (character/person struggles against his or her destiny) plot the series of events in a story: ELEMENTS OF PLOT : exposition, rising action, climax, falling action, resolution exposition the beginning of the story when characters and setting are Introduced and background information is given rising action events from the beginning of the story up to the climax climax- the turning point of the story -near the END of the story -involves one of these: - an important event -an important decision or choice -an important discovery -AND that affects the outcome or ending of the story. falling action the events that happen AFTER the climax up to the end of the story resolution how the conflict is wrapped up but NOT necessarily solved foreshadowing the author gives the reader a hint of what is to come flashback the author gives information about a previous experience; a character’s memory back to an earlier time - usually not part of the main story author’s message what the author wants you to “learn” from reading the story theme a message or lesson about life, a statement/sentence, it is true throughout life situations, not just in the specific story FIGURATIVE LANGUAGE YOU NEED TO KNOW *imagery *simile *metaphor *personification *onomatopoeia *hyperbole *alliteration *literal language *idiom *figurative language *allusion *symbol/symbolism Additional terms/concepts for memoir: characteristics of memoir (there are 7 on your unit sheet!) author’s reflection significance word choice sentence variety snapshot thoughtshot explode a moment shrink a century leads paragraph