Periodic Table_Trends Student_NOTES

Name:_______________________________________________Period:________Date:________
_________________________________________________:
•
Published his first periodic table in 1869
•
Arranged the elements by ______________________________
•
Grouped elements with similar properties together
•
Left _____________spaces for “missing” elements that were later discovered (predicted the chemical and physical properties of these elements)
_________________________________ (1913)-
•
Arranged elements by _________________________________________
•
Today we organize the periodic table by increasing atomic number
________________________= the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers
•
When elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties reoccur at regular intervals
__________________= vertical column on the periodic table o Numbered left to right and ranges from ___________ o Elements in the same ____________have _____________but not identical characteristics
____________________= horizontal row on the periodic table o Ranges from _________ o Elements in a period are ___________alike in properties
*KEY IDEA: the periodic table is an arrangement of the elements in order of their ________________so that elements with similar properties fall in the same
______________(column).
The first element in a period is usually an active __________and the last element is a period is always in inactive_____________.
1
A. METALS:
•
Most of the Periodic Table consists of_____________.
•
88 elements to the _______________of the zigzag line (_________________) are metals EXCEPT
_____________ and the ____________________.
⇒
Physical Properties:
•
Luster (______________appearance)
•
Good __________________________of heat and electricity
•
High melting point
•
______________________(most metals can be drawn into thin wires)
•
___________________________(most metals can be hammered into thin sheets)
•
__________________under ordinary conditions; except ______________is a __________
⇒ Chemical Properties:
•
Easily ____________________________
•
___________________________easily (Example: silver tarnishing & iron rusting)
Special Metal Groups:
1.
__________________________ (found in _______________;EXCEPT for_______________)
•
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr
•
Are very reactive
•
__________________________with water
2.
____________________________________ (found in________________)
•
Be, Mg, Ca, Sr, Ba, Ra
•
Are very reactive, but ____________as reactive as the Alkali
Metals
3.
________________________
•
Elements ________________the main part of the periodic table.
•
Also called the “________________________” and “_________________________”
4.
_____________________________ (38 elements found in___________________________)
2
√
B. NONMETALS:
•
___________________________ plus all elements to the RIGHT of the zigzag line (metalloid line) are nonmetals (_______________________); EXCEPT for the_______________________.
⇒
Physical Properties:
•
No Luster (dull appearance)
•
Poor conductors of heat and electricity
•
__________________(breaks easily)
•
Not ductile
•
Not malleable
•
__________density
•
__________melting point
•
______________________________and the __________________are gases under ordinary conditions
•
_____________________(Br) is a _________________under ordinary conditions
•
All other nonmetals are _____________under normal conditions
⇒ Chemical Properties: o Tend to _____________electrons
Since ___________tend to_________ electrons and ______________tend to_________ electrons, metals and nonmetals like to form __________________with each other!
Special Nonmetal Groups:
1.
_______________________: (5 non-metallic elements found in__________________) o F, Cl, Br, I, At o Halogen means “salt former” and compounds containing halogens are called
“______________”
2.
____________________________: (6 non-metallic elements found in______________) o He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Xe, Rn o All have _____________________electron configurations consisting of a full outer energy level of ________electrons, which has a lower potential energy than other electron arrangements. o Noble gases b/c of their stable configurations (see below) seldom form __________ o Ne =1s
2
2s
2
2p
6 o Ar =1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6 o Kr =1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
4s
2
3d
10
4p
6 o Xe =1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
4s
2
3d
10
4p
6
5s
2
4d
10
5p
6 o Rn =1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
4s
2
3d
10
4p
6
5s
2
4d
10
5p
6
6s
2
4f
14
5d
10
6p
6 o Exception: He = 1s
2
(this is the stable configuration)
3
C. METALLOIDS:
•
Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of BOTH ______________and
__________________________
•
B, Si, As, Te, Po, Sb, Ge
⇒
Physical Properties: o _____________________under ordinary conditions o Can be shiny or dull o Conduct heat and electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals
_____________
-
____________________________
_____________________
4
1) _____________= atom or group of bonded atoms with a positive or negative charge
(electrons were either lost or gained)
If protons are gained or lost the identity of the atom will change! a) __________________= ion formed from a single atom o Ex: S -2 and Fe +2 o Any monatomic ion that is _______________ends in
–ide
Ex: oxide and bromide b) _____________________= a group of bonded atoms with a charge
Ex: NH
4
+ and NO
3
− c) _________________ = negative ion
(electron(s) were gained) o Ex: O
–2
Oxide ion has 8 protons
Oxide ion gained 2 electrons so now it has
_________ for an overall -2 charge d) _____________= positive ion (electron(s) were lost) o Ex: Al
+3
Al has 13 protons
Al lost 3 electrons so now it has
_________ for an overall +3 charge
What happens when a K atom forms a K
+1
ion? (Hint:
How many protons and electrons does a K +1 ion contain?)
Chlorine atom:
What happens when a S atom forms a S
−
2 ion? (Hint: How many protons and electrons does a S
−
2 ion contain?)
5
1) ______________________= the tendency of atoms to gain or lose electrons so that they acquire eight electrons in their outer energy level in order to acquire the stable electron configuration.
2) The electron configuration of filled “s” and “p” orbitals of the same energy level
(consisting of 8 electrons in the outermost energy level) is unusually______________
• H and He are exceptions and are stable with 2 electrons in their outermost energy level
3) The octet rule is useful for determining the type of ions likely to form.
• Elements on the right side (_______________________) of the Periodic Table tend to gain electrons and form
negative ions
• Elements on the left side (___________________) of the Periodic Table tend to lose electrons and form
positive ions
4) Ex: When a sodium atom loses its single electron in the ___________________ energy level to form a +1 ion, its electron configuration changes: o Sodium ATOM = 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 1 o Sodium ION = 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
5) Ex: When a chlorine atom gains a single electron in the_____________________ energy level to form a -1 ion, its electron configuration changes: o chlorine ATOM = 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
4s
2
3d
10
4p
5 o chloride ION = 1s
2
2s
2
2p
6
3s
2
3p
6
4s
2
3d
10
4p
6
6) The following are group trends of elements and the ions that they tend to form:
• Group 1 elements produce ______ions
• Group 2 elements produce ______ ions
• Group 18 elements (Noble Gases)–
__________ are produced since they contain 8 electrons in their outer energy level
• Group 17 elements produce _____ ions
• Group 16 elements produce _____ ions
• Group 15 elements produce
mostly
____ions (except Bi Bi +3 and Bi +5 )
• Group 14 elements produce
mostly _____
ions (except Pb +2 and Sn +2 )
• Group 13 elements produce _____ ions
• Transition elements:
almost
all produce ______ o Zn
+2 and Cd
+2
and Ag
+1
and Cu
+1
6
• Roman Numerals: o Sometimes an atom is able to give away a various number of electrons and be stable o The Roman numerals tell how many _____________ have been given away and that will be the _____________________________
Ex: iron (II) and iron (III)
_________________________________
1.
_____________________________= one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms joined in a molecule
• PERIOD trend : _______________in atomic radius across periods (left to right) o
Explanation
= nuclear charge increases across periods, pulling electrons closer to the nucleus
______________________ (number of protons) is increasing
• GROUP trend : _________________in atomic radius down groups (top to bottom) o
Explanation
= electrons added to higher main energy levels and are therefore farther from nucleus
Nuclear charge (_____________________) is also increasing, but this factor is offset by other factors
2.
__________________________________ (F.I.E.) = Energy required to remove one electron from an atom of an element
• PERIOD trend : __________________in first ionization energy across periods
(left to right)
Explanation
= nuclear charge increases across periods, which more strongly attracts electrons so electrons are harder to remove (requires more energy)
• GROUP trend : ______________ in first ionization energy down groups (top to bottom)
Explanation
= electrons added to higher main energy levels, are therefore farther from nucleus and are more easily removed (requires less energy)
__________________occurs because more and more electrons lie between the nucleus and outer electrons, causing the outer electrons to be shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus
7
3. __________________________= a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons. o
PERIOD trend : ____________in electronegativity across periods (left to right)
___________________is the
most
electronegative element o GROUP trend : _________________in electronegativity down group (top to bottom)
* TREND DIAGRAM - all periodic trends are shown in the direction that they________________________ !
8
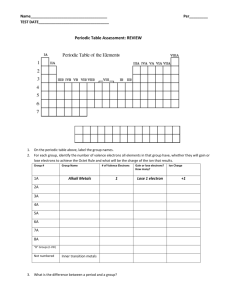
Periodic Table Worksheet
1.
How did Dmitri Mendeleev arrange elements on the Periodic Table?
2.
How did Henry Moseley arrange elements on the Periodic Table?
3.
How are the elements arranged on the Periodic Table today?
4.
What is the difference between a group and a period? List the number of groups and period.
5.
Circle where you would find elements with similar properties? Group or Period
6.
What is the name given to each of the following groups of elements on the Periodic Table? a) Group 1 ___________________ b) Group 2 ___________________ c) Group 3-12 ___________________ d) Group 17 ___________________ e) Group 18 ___________________
7.
From the groups listed in question #6, what group of elements are considered the most stable?_________________
8.
What is a metalloid?
9.
List 4 properties of metals. a) ___________________________________________ b) ___________________________________________ c) ___________________________________________ d) ___________________________________________
10.
List 4 properties of nonmetals a) ___________________________________________ b) ___________________________________________ c) ___________________________________________ d) ___________________________________________
9
Finding Your Way Around the Periodic Table Worksheet
1.
What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________
2.
What is the atomic number of osmium? __________
3.
What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________
4.
What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________
5.
What element is in group 6 and period 4? __________
6.
What element is in group 12 and period 6? __________
7.
What element is in group 13 and period 3? __________
8.
What element is in group 17 and period 5? __________
9.
What element is in group 18 and period 1? __________
10.
What element is in group 4 and period 7? __________
11.
Use the following list of elements to answer the questions below. Each element may be used more than once. Each question may have one or more correct answers.
Li, Ca, Y, Mn, Hg, Ga, Pb, Ge, P, S, Cl, I, He, Xe, U a) Which of the above elements is in group 3? ________________________ b) Which of the above elements is in period 4? ________________________ c) Which of the above elements is a metal? ________________________ d) Which of the above elements is a non-metal? ________________________ e) Which of the above elements is a metalloid? ________________________ f) Which of the above elements is a transition metal? ________________________ g) Which of the above elements is a alkaline earth metal?______________________ h) Which of the above elements is a noble gas? ________________________ i) Which of the above elements is a halogen? ________________________ j) Which of the following is a rare earth metal?_______________________ k) Which of the above elements is an alkali metal? ________________________
10
Atomic Radius Worksheet
1.
Define “atomic radius”.
2.
State the period trend (moving left to right across the periods) for atomic radius.
3.
State the group trend (moving top to bottom down the groups) for atomic radius.
Directions: Place each of the following groups of elements in order of
DECREASING
atomic radius.
4.
Li, Rb, K, Na __________________________
5.
O, Se, S, Po __________________________
6.
Mg, Cl, Na, P __________________________
7.
Li, O, C, F, N __________________________
8.
Br, At, F, I , Cl __________________________
9.
Na, K, P __________________________
10.
Li, B, Cs, N, C __________________________
11.
Li, C, O
12.
Mg, Ba, Ca
__________________________
__________________________
13.
In, Al, Tl, B __________________________
Ionization Energy Worksheet
Define “first ionization energy”. 1.
2.
State the period trend (moving left to right across the periods) for first ionization energy.
3.
State the group trend (moving top to bottom down the groups) for first ionization energy.
11
4.
Which of the following will have the highest and lowest first ionization energy?
HIGHEST LOWEST a) Na, Al, S _______ b) Si, Cl, Ar _______ c) Ba, Ca, Br _______
_______
_______
_______ d) Li, K, Rb _______ e) Cl, I, Br _______
_______
_______
5. Arrange the following elements in order of DECREASING first ionization energy: a) Li, O, C, K, Ne, F _____________________________________ b) Li, B, Rb, F, C ______________________________________ c) Mg, Ba, Be ______________________________________ d) Cl, Al, Ar, Tl ______________________________________
6. Among the elements Mg, P, Cl, Na which would be expected to have the highest first ionization energy: _________
Electronegativity Energy Worksheet
1.
Define “electronegativity”.
2.
State the period trend (moving left to right across the periods) for electronegativity.
3.
State the group trend (moving top to bottom down the groups) for electronegativity.
4.
Place each of the following groups of elements in order of DECREASING electronegativity. a) Po, Se, O __________________________ b) Ga, Br, Ra, Ca __________________________ c) F, Sr, Be, B __________________________ d) K, Br, As __________________________ e) Li, Rb, Na, B __________________________
12
f) Li, B, Rb, O, C, Cs __________________________ g) Li, C, Fr, O __________________________
5.
For each of the pairs of elements, which will have the higher electronegativity? a) Be or N _____ b) F or N _____ c) Rb or Li _____ d) C or Sn _____ e) I or Cl ______
6.
What is the difference between anions and cations? Explain.
7.
Suppose calcium formed an ion. How many electrons and protons does a calcium ion have?
Hint: what is the charge of a calcium ion?
8.
Suppose bromine formed an ion. How many electrons and protons does a bromide ion have?
Hint: what is the charge of a bromide ion?
9.
Place the ionic charges for the following groups on the Periodic Table: group 1, group 2, group 3-12, group 13, group 14, group 15, group 16, group 17 and group 18
10.
What is the difference between a monatomic ion and a polyatomic ion?
11.
What is the ending of all monatomic anions?
13
1. Where are the most active metals located? _______________________________
2. Where are the most active nonmetals located? ____________________________
3. As you go from left to right across the period, the atomic radii (decreases / increases).
4. As you travel down a group, the atomic radii (decreases / increases)
5. A negative ion is (larger / smaller) than its parent atom. a. Why? __________________________________________
6. A positive ion is (larger / smaller) than its parent atom. a. Why? __________________________________________
7. As you go from left to right across a period, the first ionization energy generally
(decreases / increases).
8. As you go down a group, the first ionization energy generally (decreases / increases).
9. Where is the highest electronegativity found? _____________________________
10. Where is the lowest electronegativity found? _____________________________
11. Elements of Group 1 are called ________________________________________
12. Elements of Group 2 are called ________________________________________
13. Elements of Group 3-12 are called _____________________________________
14. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, the elements go from
(metals / nonmetals) to (metals / nonmetals).
15. Group 17 elements are called __________________________________________
16. Compounds that contain elements from group 17 are commonly called _______________.
17. The most active element in Group 17 is _________________________________
18. Group 18 elements are called _________________________________________ a. Why? __________________________________________
19. The majority of elements in the periodic table are (metals / nonmetals).
20. Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their ________________________
14
21. An element with both metallic and nonmetallic properties is called a __________________
22. Metals are usually solids under ordinary conditions. List one exception.
___________________
23. Nonmetals can be solids, a liquid or 11 are gases under ordinary conditions. a. List the gases:_____________________________________________________ b. List the liquid:__________________
24. The noble gases contain _______ electrons in their outer energy level.
25. Suppose oxygen formed an ion. a) What is the charge of the O ion? _________ b) How many electrons does an O ion have?________ c) How many protons does an O ion have?_________ d) Write the name for the O ion.__________
26. Use the following list of elements to answer the questions below. You may have more than one correct answer per questions.
Rb, Ca, Co, Mn, Hg, Ga, Pb, Sb, P, S, F, I, He, Kr, U a) Which of the above elements is in group 9? ________________________ b) Which of the above elements is in period 6? ________________________ c) Which of the above elements is a metal? ________________________ d) Which of the above elements is a non-metal? ________________________ e) Which of the above elements is a metalloid? ________________________ f) Which of the above elements is a transition metal? ________________________ g) Which of the above elements is a alkaline earth metal?______________________ h) Which of the above elements is a noble gas? ________________________ i) Which of the above elements is a halogen? ________________________ j) Which of the following is a rare earth metal?_______________________ k) Which of the above elements is an alkali metal? ________________________
27. What is the charge of the following ion, copper II? ________
15
Unit Learning Map (6 days) :
Periodic Table
Class
: Academic Chemistry A - Grade 11
Unit Essential Question(s):
How are elements on
Concept
Ions
Concept
Organization of the
Periodic Table
Mrs. Hostetter
Optional
Instructional Tools:
Guided Notes
Lab Materials: Inquiry lab
Coloring lab
P.T trends lab
Concept
Trends of the Periodic
Table
Concept
Lesson Essential Questions: Lesson Essential Questions: Lesson Essential Questions: Lesson Essential Questions:
What is an ion? How is the periodic table organized?
How can the trends of the periodic table be used to predict properties of elements?
Vocabulary:
Octet Rule
Ions
Anion
Cation
Monatomic ion
Polyatomic ion
Vocabulary:
Dmitri Mendeleev
Henry Moseley
Periodic law
Group
Period
Alkali metals
Alkaline earth metals
Rare earth metals
Transition metals
Halogens
Noble gases
Metalloids
Vocabulary:
Atomic radius
First Ionization Energy
Shielding effect
Electronegativity
Vocabulary:
16
Peri odic Table Vocabulary:
1) Octet Rule = the tendency of atoms to gain or lose electrons so that they acquire eight electrons in their outer energy level in order to acquire the stable electron configuration.
2) Ion = atom or group of bonded atoms with a positive or negative charge (electrons were either lost or gained)
3) Monatomic ion = ion formed from a single atom; Ex: S
-2
and Fe
+2
4) Polyatomic ion = a group of bonded atoms with a charge; Ex: NH
4
+
and NO
3
−
5) Cation = positive ion b/c the parent atom lost electron(s)
6) Anion= negative ion b/c the parent atom gained electron(s)
7) Dmitri Mendeleev’s Periodic Table = Published his first periodic table in 1869, Arranged the elements by increasing atomic MASS, Grouped elements with similar properties together, Left blank spaces for “missing” elements that were later discovered (predicted the chemical and physical properties of these elements)
8) Henry Moseley = Arranged elements by increasing atomic NUMBER, Today we organize the periodic table by increasing atomic number
9) Periodic Law = the physical and chemical properties of the elements are periodic functions of their atomic numbers
10) Group = vertical column on the periodic table (#1-18)
11) Period = horizontal row on the periodic table (#1-7)
12) Alkali metals = found in group 1, except for hydrogen, very reactive and explosive with water
13) Alkaline earth metals = found in group 2, Are very reactive, but not as reactive as the Alkali Metals
14) Rare earth metals = elements below the main part of the periodic table
15) Transition metals = 38 elements (groups 3-12)
16) Halogens = 5 non-metallic elements found in group 17; Halogen means “salt formers”
17) Noble gases = 6 non-metallic elements found in group 18; stable b/c of having 8 electrons in their outer energy level
18) Metalloids = solids under ordinary conditions, can be shiny or dull, conduct heat and electricity better than nonmetals but not as well as metals
19) Atomic radius = one-half the distance between the nuclei of identical atoms joined in a molecule
20) First Ionization Energy = Energy required to remove one electron from an atom of an element
21) Shielding effect = occurs because more and more electrons lie between the nucleus and outer electrons, causing the outer electrons to be shielded from the positive charge of the nucleus
22) Electronegativity = a measure of the ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons
17