objectives unit 2
advertisement

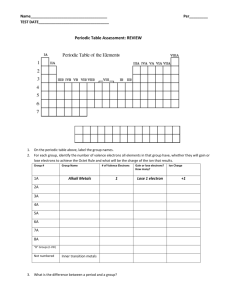
Honors Chemistry: Unit 2 (Book Chapter 8) Objectives: The student will be able to Models of the Atom 1. Define the term atom. 2. Discuss how Democritus first proposed the atom, what he called it and how it translates. 3. Explain the Law of Constant Composition by Joseph Louis Proust 4. List the 4 postulates of John Dalton’s Atomic Theory of Matter. 5. Know the contributions of each of the people in the “Atom History Song” refrain. 6. Describe how a cathode ray tube (CRT) is made and works and the location of cathode and anode. 7. Describe the cloud model of the atom and its deficiencies The Atom 8. Name and describe the properties of the three subatomic particles and their locations in an atom. 9. Define isotopes and ion 10. Be able to determine the number of protons, neutrons, and electrons in any atom or ion or isotope. 11. Explain how the isotopes of the same element differ. 12 Describe the relative masses of electrons, protons and neutrons. 13. Explain why an atom is electrically neutral. 14. Explain how we use symbols to represent the 100 plus symbols on the periodic table. 15. Be able to draw an element or ion’s arrow diagram 16. Be able to describe the path of any electron in the first three levels and explain the meaning of "electron clouds". 17. Be able to write an elements, or ion’s electron configuration 18. Be able to draw the Lewis dot diagram of any atom or ion using the octet rule 19. Be able to show the chemical symbols for ions and isotopes (isotope form of a chemical symbol) 20. Be able to explain a quanta and construct position of electrons using: Quantum Numbers-- principal quantum number, angular momentum (azimuthal quantum number), magnetic quantum number, spin 21. Distinguish between ground state, excited state, level, sublevel and orbital. 22. Be able to determine the allowable shapes, number of orbitals, number of electrons and number of lobes of the orbitals on any level 23. Be able to explain the wave-particle duality of nature. 24. Be able to explain what an atomic emission spectrum is and how it is obtained. The periodic table 25. Be able to use the periodic table to find the following information about and element: number of protons, neutrons and electrons; atomic number, atomic mass number; atomic mass and mass per mole (g.a.w.)and electron configuration. 26. Be able to predict the common ions for each “family”. 27. Describe at what point on the periodic table, elements are considered radioactive. 28. Describe the trend on the periodic table for metals and nonmetals. 1 29. Use the periodic table to determine electron configuration, knowing the s-p-d-f orbitals and their shapes (electron orbitals) 30. 31. 32. 33. 34. Identify metals, nonmetals, metalloids on the periodic table. Identify Alkali Earth Metals, Alkaline Metals, Transition Metals, Halogens, Nobel Gasses. Identify the “boot elements” and what they have in common. Identify the common ions for the main group elements Describe why all nuclei with the atomic numbers greater than 83 are radioactive Bonding 35 List physical properties of metals and non metals. 36. Describe metal quenching, tempering, annealing 37. Define Electronegativity 38. Describe and identify and code Ionic, Polar Covalent, Covalent (nonpolar covalent) bonds using Electronegativity. 39. Define Polarity 40. Determine if a solution is Polar or Nonpolar (Molecular) both through experiment a using Electronegativity. 41. Draw a diagram of the water molecule showing polarity and dipoles. 42. Be able to explain the difference between an ionic and a covalent bond on the basis of electron configuration. Naming/Formulas 43. Determine Oxidation numbers for molecules using the rules given 44. Write formulas for acids and their salts 45. Write formulas and names using the yellow card.(ic/ous and common cations and anions) 46. Name acids and their salts using the acid naming chart 47. Name ionic compounds 2