Course Syllabus
advertisement

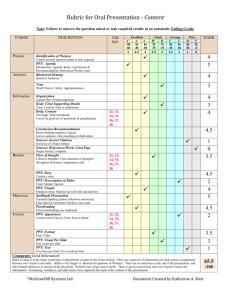
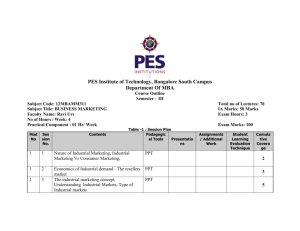
Syllabus BA 5702 Marketing Management METU Department of Business Administration Instructor: Office: Office Hours: Phone: Course Materials: Cengiz Yılmaz H106 Monday-Wednesday 10:00-11:00 3066 yilmazcourses (yahoo group) http://uk.groups.yahoo.com/group/yilmazcourses/ Course Description: This is a graduate level marketing course that focuses specifically on the key terms, frameworks, and approaches that constitute the contemporary marketing theory as well as its applications in practical business circles. The purpose of the course is to provide the students with a keen understanding of the marketing function in business firms and of the methods of using this knowledge in developing and implementing successful marketing strategies. Classroom discussions will begin with fundamental issues and theories, but shall progress fast into more sophisticated and deeper, graduate-level topics. Students are therefore expected to read the relevant chapters and articles before coming to class and contribute in an active and constructive manner to classroom discussions. Upon completing this course, students are expected to (1) know basic marketing philosophy and its key terms and theories, (2 ) effectively use this knowledge in an integrated manner for the purpose of making strategic marketing decisions regarding practical business life problems, and (3) communicate this knowledge in a clear and organized manner. Grading will be based on two midterm exams, classroom participation, and most importantly on a course project whereby students are expected to prepare an annual marketing plan as a group and present their work to the class. A simplified marketing plan outline that lists major components of a marketing plan is provided with this syllabus. There will be no final exam for this course. Text: Philip Kotler Marketing Management, 11th or later edition, Prentice Hall International, Inc. Further Reading: McDaniel, Lamb, and Hair, Introduction to Marketing, 12th Edition, South-Western, Cengage Learning. Method: Formal Lectures + Discussion Sessions + Group Presentations Grading: Participation and Quizzes 5%; Midterm1 25%; Midterm2 30 %; Course Project 40 % Topics: WEEK1. Introduction and Key Terms What is Marketing? History of the Thought of Marketing ppt.: What is marketing WEEK2. Modern Marketing Philosophy Marketing and Micro Environment Marketing and Macro Environment ppt. What is marketing WEEK3. Competitive Analyses Corporate Strategy and Marketing Key Elements of the Marketing Strategy Buyer Decision Process (Overview) Market Segmentation, Target Marketing, and Positioning. ppt: Segmentation and Positioning & Competitive Advantage WEEK4. Market Segmentation, Target Marketing, and Positioning Continued ppt: Segmentation and Positioning WEEK5. Product & Branding Strategies Key Terms and Classifications Branding and Brand Equity Management ppt. Product and brand Management WEEK6. Integrated Marketing Communications ppt. Promotions WEEK7. Integrated Marketing Communications Continued ppt. Promotions WEEK8. Pricing Methods and Tactics Demand Estimation & Mathematical Pricing Catching Up, Overview, & Midterm. ppt: Pricing WEEK 9. Management of Marketing Channels Structural & Administrative Issues ppt: Management of Marketing Channels WEEK10. Understanding the Consumer ppt: Understanding Buyers WEEK11. Business to Business Markets Services WEEK12. Business Strategy WEEK 13 Marketing Research Applications WEEK 14 Sustainability and Marketing Ethics Plagiarism: Plagiarism is simply stealing someone else’s academic work and presenting as if it is your own. Even using two consecutive sentences from another author’s work without providing appropriate citation is going to be considered plagiarism for all assignments and project reports in this class. A submission with direct quotations exceeding 5 percent of the total body of the text will also be considered plagiarism regardless of the citations and references provided. It is a crime, and anyone caught committing this crime will not only get a direct F from the course but also be reported to Faculty Administration for further disciplinary action. READING LIST 1. Conceptualizing, measuring, and managing customer-based brand equity Keller, Kevin Lane Journal of Marketing; Jan 1993; 57, 1; pg. 1 2. "The Commitment-Trust Theory of Relationship Marketing," Morgan, Robert M. and Shelby D. Hunt (1994), Journal of Marketing, 58 (3), 20-38. 3. Frontiers of the marketing paradigm in the third millennium. Ravi S. Achrol & Philip Kotler, J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. (2012) 40:35–52. 4. Marketing and business performance Neil A. Morgan J. of the Acad. Mark. Sci. (2012) 40:102–119 5. “The Nature and Scope of Marketing” Shelby Hunt, Journal of Marketing (40) July 1976 SIMPLIFIED MARKETING PLAN OUTLINE I. SITUATION ANALYSES A. Market (Current and projections) Size, scope, shares and category sales history of all competitors, customer perceptions and positioning approaches. Product features, pricing, distribution, promotions, and other strategic approaches of all competitors. B. Customers (Current and projections) Purchasing habits, preferences, purchasing patterns, purchasing power, segments and profiles of each segment, etc. C. Competitive Primary competitors, secondary competitors. Nature and degree of competition, competitive dynamics, new product entry prospects, rivalry, power of suppliers and buyers. Strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats of and to the company as well as of and to the core product. D. Product (Current and projections) Features, attributes, expectations, rooms for improvement. II. OBJECTIVES (quantity, direction, time frame, rationale). A. Corporate objectives, divisional objectives, marketing objectives. B. Program objectives and rationales. Positioning Pricing Advertising/Promotions Sales/Distribution Product Service III. STRATEGY AND PROGRAMS (How the objectives will be achieved) A. Strategic alternatives and the core strategy B. Marketing Programs Pricing Advertising/Promotion Copy Media Trade versus consumer promotion Sales/Distribution Product development Service Market Research IV. MONITORS AND CONTROLS Specific research information to be used Methods through which the plan will be evaluated V. CONTINGENCY PLANS VI. BUDGETS