India PPT
advertisement

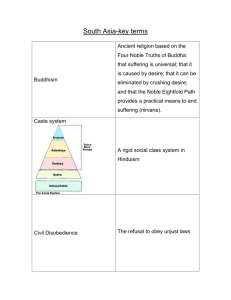
Classical India Chapter 3 Interactive Lecture Notes Politics 4 Corner Debate Geography is the most important factor in the development of a civilization. How might the geography of India influence its political development? •Mountains = full political unit different, decentralized govt. •Came into the orbit of other civilizations •Monsoons = drought to flood What sort of problems would this regionalism pose to India? Classical Dynasties Aryan Nomadic emigrants who eventually settled and began farming in India Mauryan Chandragupta Ashoka Gupta Golden Age of Classical India Achievements of the Gupta Rulers • Consolidation and unification • Taxes • Hinduism • Promoted Sanskrit, but no single language imposed • Uniform law codes Economy 4 Corner Debate Greed is good. Vigorous economy • • • • • Manufacturing Steel and iron Textiles Trade and merchant activity Firmly agricultural at its base, however Religion 4 Corner Debate Religion is a philosophy. The Aryans and Hinduism Vedic and Epic ages- Veda means “knowledge” and the RigVeda was the first epic dedicated to ryan gods Upanishads- epic poems of fe after death, divine force, sacred ghts and rituals The Vedas and Upanishads the basis of Hinduism Rig-Veda Hinduism • http://safari03.pisd.edu/SAFARI/montage/ play.php?keyindex=3355&location=local • Chapters 2,3,4 • Note- This video clip is from PISD database, but there are plenty clips to use as links Hinduism 101 • No single founder • No central holy figure • Encouraged political and economic goals • Pursuit of worldly pleasuresKarma • Tolerant of other religions • Monism • Brahma, the basic holy essence, formed every part of the world • Reincarnation • Dharma- attention to the moral consequences of action, and at the same time the need to act, stresses inner study and mediation Buddhism 101 • Siddhartha Gautama • What is unique about Buddhism? Similarities differences between Buddhism and Hinduism? • Meditative and natural • Rejected priests and caste system • Focused on a supreme divinity • Believed in the after life an ultimate goal was the destruction of the self and the union with the divine essence, a state called “nirvana” • Stress on self-control • Four Noble Truths • Eightfold Path Buddhism • http://safari03.pisd.edu/SAFARI/montage/ play.php?keyindex=244&location=local • Chapters 2,3 • -Note- This video clip is from PISD database, but there are plenty clips to use as links Theravada Buddhism Mahayana Buddhism Intense, dedicated and timeconsuming effort require for Nirvana Enlightenment achieved through normal life with spiritual involvement Wisdom is the highest virtue Compassion is the highest virtue Followed as a teaching or philosophy Followed as a religion with higher beings Politicaly conservative Political liberal Sri Lanka, Burma, Laos, Thailand, China, Japan, Singapore, Cambodia Vietnam, Tibet (Tantric) Social 4 Corner Debate A society must have a caste/ class system in order to function. Indian Caste System • Began as a way establish relationships between Aryan invaders and indigenous people whom they felt were inferior Gender Roles • Family life/ structure/ gender roles • Wife worshipped husband • Agricultural male dominance • Can women advance spiritually without being reincarnated as a man? • Arranged marriages Intellectual 4 Corner Debate The best evidence of highly intellectual civilization is their advancements in math and science. Advancements in Math and Science • Length of the solar year • Mathematics- Indian numbers, concept of zero, decimals, square root, pi, algebra • Astronomy • Gravity • Bone setting and plastic surgery • Inoculation against small pox • Hospitals Art 4 Corner Debate Art is religious at its core. Art • How was Indian culture expressed in writing? • • • • • • • Epic poetry Drama Advancements in art? Stupas Buddha statues Human form Nature Indi a Japa n Chin a Thailan d Sri Lanka Burma (Myanmar) Sri Lanka Thailand Burma (Myanmar) India China Japan