The Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues
advertisement

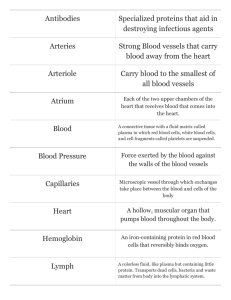
Chapter 20: The Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues M.C. Shamier BSc Shenzhou University Subjects Lymphatic Vessels Lymphoid Cells and Tissues Lymph Nodes Other Lymphoid Organs Developmental Aspects of the Lymphatic System and Lymphoid Organs and Tissues The Lymphatic System Lymph Lymphatic Vessels Lymph Nodes Lymphatic Vessels Function Return excess tissue fluid to the bloodstream Return leaked proteins to the blood Carry absorbed fat from the intestine to the blood Lymphatic Vessels Nutrients, wastes and gases are exchanged between blood and interstitial fluid Fluid that remains in tissue spaces (3L/day) becomes part of the interstitial fluid To prevent a loss of volume, this fluid must find a way back to the heart and the blood circulation Once interstitial fluid enters lymphatic vessels it is called lymph Lymphatic Vessels One way system towards the heart System begins in blind ended lymphatic capillaries Lymphatic Vessels Lymphatic Vessels Capillaries are very permeable (allowing passage of substances) Endothelial cells are not joined, but overlap loosely forming minivalves Collagen filaments anchor endothelial cells to surrounding structures so that any increase in interstitial fluid volume opens the minivalves So valves open when interstitial pressure > lymphatic pressure and vice versa Lymphatic Vessels Take up proteins, but even larger particles when tissue is inflamed Cell debris, bacteria, viruses, cancer cells In lymph nodes the immune system ‘examines’ and cleanses the lymph Lymphatic Vessels Duct (right lymphatic duct and thoracic duct) Trunk (lumbar, bronchomediastinal, subclavian, jugular, intestinal) Collecting vessel Capillaries Successively larger and thicker walled channels Right lymphatic duct: right upper limb, right side of head and thorax Thoracic duct: left upper limb, left side of head and thorax and rest of the body Thoracic Duct Lymph transport Slow and sporadic Skeletal muscle activity Pressure changes in thorax during breathing Valves to prevent backflow Smooth muscle contractions in lymphatic ducts and trunks Immobilization of an inflamed body part can prevent spread of infection Lymphedema results from blockage of the lymphatics Lymphedema Lymphoid Cells Lymphocytes (B and T), macrophages, dendritic cells, reticular (fibroblast-like) cells Lymphoid Tissue Houses and provides a proliferation site for lymphocytes Ideal surveillance point for lymphocytes and macrophages Loose connective tissue: reticular connective tissue Diffuse lymphatic tissue: scattered reticular tissue elements, found in virtually every organ Lymphoid follicles: spherical bodies of tightly packed reticular elements and cells Lymphoid Follicle Lymphoid Organs Lymph Nodes Lymph Nodes Cluster along lymphatic vessels of the body Functions Lymph filter: macrophages destroy microorganisms and debris Activation of the immune system Lymph Nodes Dense fibrous capsule Trabeculae extend inward dividing it in compartments Two distinct regions: Cortex Medulla Lymph Nodes Lymph Nodes Lymph Nodes Lymph enters at the convex side Through the subcapsular sinus into smaller sinuses through the cortex into the medulla Exits the node at the hilum on the concave side Afferent vessel (to the organ) Efferent vessel (away from the organ) More afferent than efferent vessels lowering the speed of flow, allowing time for cleansing. Lymph always passes through several nodes. Homeostatic Imbalance Swollen lymph nodes An overwhelming amount of microorganisms can lead to inflammation and swelling of lymph nodes (99%) Lymphoma is lymph cell cancer Metastasizing of cancer Spleen Spleen Largest lymphoid organ Splenic vein and artery enter/exit the hilum Function Site for lymphocyte proliferation, immune surveillance and response Blood-cleansing (defective blood cells and platelets, debris, foreign matter Storing breakdown products for reuse Storing platelets Site of erythrocyte production in the fetus Spleen Structure Surrounded by a capsule Trabeculae extending inward Huge number of erythrocytes White pulp: lymphocytes around a central artery, immune functions Red pulp: all remaining splenic tissue, disposing red blood cells and bloodborne pathogens Spleen Spleen Thymus Thymus Macroscopic Anatomy Inferior in the neck, extending into thorax, partially overlies the heart Atrophy after puberty, prominent in newborns and children Microscopic Anatomy Thymic lobules each containing a medulla and a cortex Consists mostly of T-cells, no B-cells. Hassal’s corposcules: keratinized epithelial cells, site of regulatory T-cell production? Thymus Function Thymus is where T-cells mature Only lymphoid organ not directly involved in immune response Blood-thymus barrier keeps bloodborne antigens out to prevent activation of immature lymphocytes Stroma consists of epithelial cells rather than reticular cells Destruction of autoreactive T-cells and T-cells with a weak or too strong antigen binding affinity. Tonsils Tonsils A ring of lymphatic tissue around the entrance of the throat (pharynx) Gather and remove pathogens from food or inhaled air Follicles with germinal centers and scattered lymphocytes Not fully encapsulated Tonsillar crypts are the entrance for bacteria They are ‘invited in’ and information is stored in the immunologic memory: known intrudors can more easily be fought than unknown intrudors. Aggregates of Lymphoid Follicles Digestive Tract Peyer’s patches: structurally similar to tonsils, located in the wall of the intestine Lymphoid follicles in the appendix Destroy bacteria before they can enter the internal environment Generate memory lymphocytes for longterm immunity Respiratory Tract and Urogenital Tract Mucosa Associated Lymphoid Tissue: MALT Protect open passages End of Chapter 20