Population Pyramids
advertisement

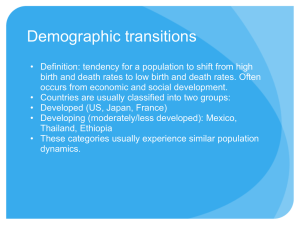
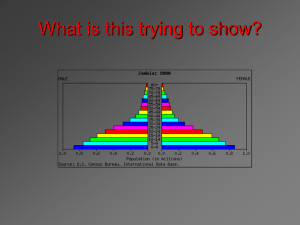
Population Pyramids Population Pyramids Population Pyramids A graphical representation of the age and gender structure of a population. Consists of 2 horizontal bar diagrams -- one for the male and the other one for female. Placed side by side according to the various age groups (usually in a 5 year period). Example Population Pyramid Population Pyramids INFORMATION POSSIBLE FROM A POPULATION PYRAMID: 1. Age Structure • young: < 16 years • mature: 16 - 64 • aged: > 64 Population Pyramids INFORMATION POSSIBLE FROM A POPULATION PYRAMID: 2. Sex Ratio – female : male 3. Dependency Ratio: young + aged ------------------------mature Population Pyramids INFORMATION POSSIBLE FROM A POPULATION PYRAMID: 4. Birthrate from the base of the pyramid. 5. Life expectancy can be inferred. 6. Can infer economic status (for example, agriculture or industrialized type of nation). Population Pyramids YOUNG POPULATION M F Population Pyramids CHARACTERISTICS OF YOUNG POPULATION: 1. High birthrate. 2. High proportion of dependent population to working population. Therefore, expect low standard of living. Population Pyramids CHARACTERISTICS OF YOUNG POPULATION: 3. Agricultural economy. 4. Problems associated with overpopulation. Population Pyramids MATURE POPULATION M F Population Pyramids MATURE POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS OF MATURE POPULATION: 1. Birthrate and death rate low -- about 1% population growth. 2. High proportion working. Population Pyramids MATURE POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS OF MATURE POPULATION: 3. industrialized nation = high living standard Population Pyramids AGING POPULATION M F Population Pyramids AGING POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AGING POPULATION: 1. Very low birthrate, so a low or zero population growth. 2. Many aged dependents. Population Pyramids AGING POPULATION CHARACTERISTICS OF AGING POPULATION: 3. Advanced industrialized country (for example, UK, Germany, Sweden, and Japan). Importance of Population Pyramids 1. Enable comparisons to be made between countries. 2. Can help to plan for future service needs such as old folk’s home if it has an aging population or build fewer schools. Importance of Population Pyramids A BROAD BASE POPULATION PYRAMID MEANS: 1. Increase food production. 2. Build more homes and schools. Importance of Population Pyramids A BROAD BASE POPULATION PYRAMID MEANS: 3. Plan for more job opportunities for the young in future. 4. Implement birth control campaigns. Importance of Population Pyramids A NARROW BASED POPULATION PYRAMID MEANS: 1. Work out incentives to encourage more births. 2. Hiring foreign labor. 3. Proper medical services and health care for the aged. Some Population Pyramids Some Population Pyramids Some Population Pyramids Some Population Pyramids Population Pyramid of a Less Developed Nation Population Pyramid of Nigeria (1995) Population Pyramid of a Developed Nation Population Pyramid of Sweden (1995) POPULATION STRUCTURE The population pyramid displays the age and sex structure of a country or given area. OLD DEPENDENTS Population in Five Year Age bands MALES To the left ECONOMICALLY ACTIVE YOUNG DEPENDENTS FEMALES To the right What Population Pyramids Show Us Economically More Developed Country Economically Less Developed Country KEY slope of pyramid indicate the death rate width of the base is related to birth rate/fertility rate proportions of men and women can suggest male or female migrations height of graph can indicate life expectancy (ignore the very thin end of the wedge as occurs on graph B as these people are a definite minority) "kinks" indicate dramatic reductions in birth rate or increases in death rate in the past area of graph indicates total population - compare areas of different population age groups or different sex on one graph The overall shape of the population pyramid can indicate whether it is an Economically More Developed Country or Economically Less Developed Country. Population Pyramids Related to the Demographic Transition Model Stage 1 Stage 2 Stage 3 Stage 4 IMPLICATIONS IMPLICATIONS IMPLICATIONS IMPLICATIONS Both birth rates and death rates are high, so population growth rates are slow but population is usually restored due to high birth rate. Short life expectancy. Population starts to grow at an exponential rate due to fall in death rate. More living In middle age. Life expectancy rises. Infant mortality rate falls. Population continues to grow but at slower rate. Low death rate. Dramatically declining birth rate. Low birth rate and death rate. Higher dependency ratio and longer life expectancy. Death rate does rise slightly because of the aging population.