Population Pyramids
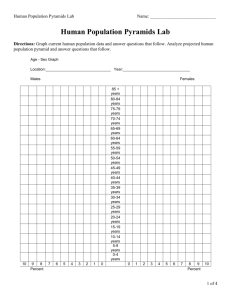
How to read a population pyramid
• Imagine 2 sideways bar
graphs
• Males – left
• Females – right
• Vertical axis
– age
– year of birth
• Horizontal axis
– Thousands
– Millions
– Percent
• Year
• 3 types of pyramids…
Expansive type
•
•
•
•
•
•
Triangle/pyramid
Base – widest part
Birth rate – high or low? Note the concave sides
Death rate – high or low?
Rate of Natural Increase – high or low?
Which stage of Demographic Transition Model?
Stationary type
•
•
•
•
•
•
Half ellipse shape
Base – about the same width as middle
Birth rate – high or low?
Death rate – high or low? Note the convex sides
Rate of Natural Increase – high or low?
Which stage of Demographic Transition Model?
Constrictive type
•
•
•
•
•
•
Base – narrower than middle
In extreme cases, upside-down pyramid
Birth rate – high or low?
Death rate – high or low?
Rate of Natural Increase – high or low?
Which stage of Demographic Transition
Model?
Asymmetry in Pyramids
• typically, most pyramids show symmetry. Any
asymmetry means . . .
a.) there is something that happened/happens
that accounts for a difference in female and
male population – examples: war, restrictive
population policies, migrant workforce
b.) there was a baby boom
Population
Pyramids for
Several US Cities
& Towns
(Upper left
corner is the
whole US.)
Dependency Ratio
• Compares population of
dependents (children and
elderly) to working-age
population
• 0-14
• 15-64
• 65+
• Why do we use these ages?
• What might be some
problems with using these
ages?
Percent of population under age 15
(darker color means higher percent)
Goldilocks Moment
• Too hot! Too cold! Just right.
• Too young! Too old! Just right.
• Low dependency ratio
• Not too many children or elderly
• Good for economy – why?
More pyramids to explore
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Immigrants to US from various countries http://www.migrationinformation.org/DataHub/pyramids.cfm
US 1850-2000 http://vis.stanford.edu/jheer/d3/pyramid/shift.html - but link doesn’t work
Canada 1921-2009 http://strategy.sauder.ubc.ca/antweiler/edutainment/pyramid.pdf
Several major countries 1950-2050 http://visualization.geblogs.com/visualization/aging/
Australia 1971-2056
http://www.abs.gov.au/websitedbs/d3310114.nsf/4a256353001af3ed4b2562bb00121564/ca0b3137794a
766bca256f6c0078cb0b!OpenDocument
World 1950-2100 http://populationpyramid.net/
Various, including some historical US, and WWII Germany
http://gero.usc.edu/AgeWorks/core_courses/gero500_core/demographics_lect/index_a.htm
UK vs. Mozambique
http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/geography/population/population_change_structure_rev5.sht
ml
UK 1971-2085 http://www.neighbourhood.statistics.gov.uk/HTMLDocs/dvc1/UKPyramid.html
China 1950-2050 http://www.china-europe-usa.com/level_4_data/hum/011_7a.htm
India http://populationcommission.nic.in/facts1.htm
Japan 1950-2050 http://econviews.wordpress.com/2011/03/19/japans-demographic-crisis-part-2/
Connecting to your project
•
Think about the country that you are researching for your Status of Development
Project.
– If you’ve already looked at your country’s population pyramid, use what you remember
about it.
– If you haven’t looked at it yet, make an educated guess based on what you know about
the country.
•
Questions to consider:
–
–
–
–
How can you use what we learned today in your project?
What shape is your country’s population pyramid? Why?
What can you tell about your country from its pyramid?
Is there anything distinctive in your country’s pyramid? Why? What does it mean?
• Examples - Very high or very low numbers of people in certain age groups? A sex imbalance?
Etc.