Lower Limb Muscles: Origin, Insertion, Action, Innervation
advertisement
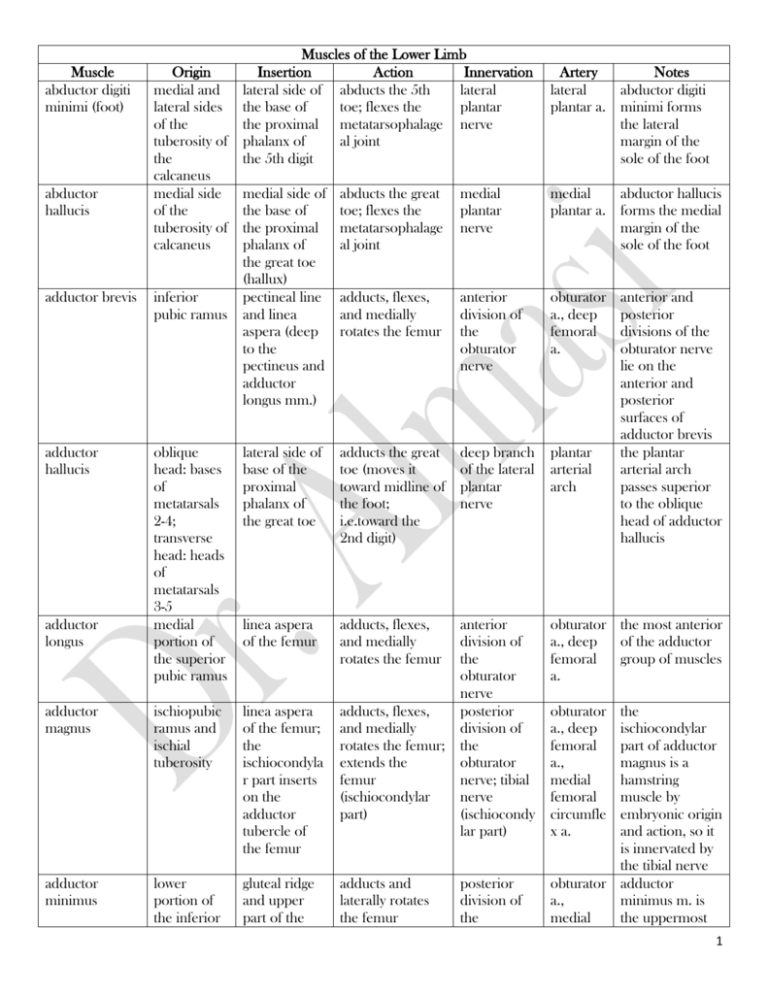
Muscle abductor digiti minimi (foot) abductor hallucis adductor brevis adductor hallucis Muscles of the Lower Limb Origin Insertion Action Innervation medial and lateral side of abducts the 5th lateral lateral sides the base of toe; flexes the plantar of the the proximal metatarsophalage nerve tuberosity of phalanx of al joint the the 5th digit calcaneus medial side medial side of abducts the great medial of the the base of toe; flexes the plantar tuberosity of the proximal metatarsophalage nerve calcaneus phalanx of al joint the great toe (hallux) inferior pectineal line adducts, flexes, anterior pubic ramus and linea and medially division of aspera (deep rotates the femur the to the obturator pectineus and nerve adductor longus mm.) Artery Notes lateral abductor digiti plantar a. minimi forms the lateral margin of the sole of the foot medial abductor hallucis plantar a. forms the medial margin of the sole of the foot obturator a., deep femoral a. anterior and posterior divisions of the obturator nerve lie on the anterior and posterior surfaces of adductor brevis the plantar arterial arch passes superior to the oblique head of adductor hallucis oblique head: bases of metatarsals 2-4; transverse head: heads of metatarsals 3-5 medial portion of the superior pubic ramus lateral side of base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe adducts the great toe (moves it toward midline of the foot; i.e.toward the 2nd digit) deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve plantar arterial arch linea aspera of the femur adducts, flexes, and medially rotates the femur obturator the most anterior a., deep of the adductor femoral group of muscles a. adductor magnus ischiopubic ramus and ischial tuberosity linea aspera of the femur; the ischiocondyla r part inserts on the adductor tubercle of the femur adducts, flexes, and medially rotates the femur; extends the femur (ischiocondylar part) anterior division of the obturator nerve posterior division of the obturator nerve; tibial nerve (ischiocondy lar part) adductor minimus lower portion of the inferior gluteal ridge and upper part of the adducts and laterally rotates the femur adductor longus posterior division of the obturator a., deep femoral a., medial femoral circumfle x a. the ischiocondylar part of adductor magnus is a hamstring muscle by embryonic origin and action, so it is innervated by the tibial nerve obturator adductor a., minimus m. is medial the uppermost 1 pubic ramus linea aspera of the femur obturator nerve anterior surface of the femur above the patellar surface long head: ischial tuberosity; short head: lateral lip of the linea aspera shafts of adjacent metatarsal bones articular elevates the capsule of the articular capsule knee of the knee joint femoral nerve extensor digitorum brevis superolatera l surface of the calcaneus extensor expansion of toes 1-4 extensor digitorum longus lateral condyle of the tibia, anterior surface of the fibula, lateral portion of the interosseous dorsum of the lateral 4 toes via extensor expansions (central slip inserts on base of middle phalanx, articularis genu biceps femoris dorsal interosseous (foot) head of fibula and lateral condyle of the tibia bases of the proximal phalanges for digit 2 (both sides) & digits 3,4 (lateral side) extends the thigh, flexes the leg femoral circumfle x a., deep femoral a. descendi ng genicular a. long head: tibial nerve; short head: common fibular (peroneal) nerve abduct digits 2-4 deep branch (move these digits of the lateral away from plantar midline as nerve defined by a plane passing through the 2nd digit); flex the metatarsophalang eal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints of those digits extends toes 1-4 deep fibular (peroneal) nerve perforati ng branches of the deep femoral a. dorsal metatars al aa. extends the metatarsophalang eal, proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints of the lateral 4 toes anterior tibial a. deep fibular (peroneal) nerve dorsalis pedis a. fibers of the adductor magnus m. articularis genu is formed by muscle fascicles deep to the vastus intermedius m. one of the "hamstring" muscles four in number; remember DAB (Dorsal interossei ABduct) and PAD (Plantar interossei ADduct), then logic can tell you where these muscles insert the part of the extensor digitorum brevis that goes to the great toe is called the extensor hallucis brevis m. one of the muscles involved in anterior compartment syndrome 2 membrane extensor hallucis brevis superolatera l surface of the calcaneus extensor hallucis longus middle half of the anterior surface of the fibula and the interosseous membrane lower one third of the lateral surface of the fibula fibularis (peroneus) longus upper two/thirds of the lateral surface of the fibula fibularis (peroneus) tertius distal part of the anterior surface of the fibula flexor digiti minimi brevis (foot) base of 5th metatarsal bone fibularis (peroneus) brevis lateral slips on base of distal phalanx) dorsum of base of proximal phalanx of the great toe extends the great toe deep fibular (peroneal) nerve dorsalis pedis a. base of the distal phalanx of the great toe extends the metatarsophalang eal interphalangeal joints of the great toe deep fibular (peroneal) nerve anterior tibial a. tuberosity of the base of the 5th metatarsal extends (plantar flexes) and everts the foot superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve fibular (peronea l) a. after crossing the plantar surface of the foot deep to the intrinsic muscles, it inserts on the medial cuneiform and the base of the 1st metatarsal bone dorsum of the shaft of the 5th metatarsal bone extends (plantar flexes) and everts the foot superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve fibular (peronea l) a. everts the foot deep fibular (peroneal) nerve anterior tibial a. lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of flexes the metatarsophalang eal joint of the 5th digit lateral plantar nerve lateral plantar a. usually considered to be the medial-most part of the extensor digitorum brevis m. one of the muscles involved in anterior compartment syndrome stress fracture of the base of the 5th metatarsal bone is a common runner's injury fibularis longus lies superficial to the fibularis brevis m. in the lateral compartment of the leg fibularis tertius is in the anterior compartment of the leg, not the lateral compartment (which contains fibularis longus and brevis) none 3 flexor digitorum brevis flexor digitorum longus 5th digit tuberosity of base of the the middle calcaneus, phalanx of plantar digits 2-5 after aponeurosis, splitting to intermuscul allow passage ar septae of the flexor digitorum longus tendons middle half bases of the of the distal posterior phalanges of surface of digits 2-5 the tibia flexes the metatarsophalang eal, proximal interphalangeal and distal interphalangeal joints of digits 25; plantar flexes the foot medial belly: flexes the medial side of metatarsophalang proximal eal joint of the phalanx of great toe the great toe; lateral belly: lateral side of the proximal phalanx of the great toe flexor hallucis brevis cuboid, lateral cuneiform, medial side of the first metatarsal flexor hallucis longus lower 2/3 of the posterior surface of the fibula base of the distal phalanx of the great toe gastrocnemius femur; medial head: above the medial femoral condyle; lateral head: above the lateral femoral condyle ischial tuberosity dorsum of the calcaneus via the calcaneal (Achilles') tendon gemellus, inferior flexes the metatarsophalang eal & proximal interphalangeal joints of digits 2-5 obturator internus flexes the metatarsophalang eal and proximal interphalangeal joints of the great toe; plantar flexes the foot flexes leg; plantar flexes foot laterally rotates the femur medial plantar nerve medial and lateral plantar aa. flexor digitorum brevis in the foot is equivalent to the flexor digitorum superficialis m. of the arm tibial nerve tibial a. flexor digitorum longus in the leg is equivalent to the flexor digitorum profundus m. of the arm medial plantar nerve (lateral belly occasionally receives innervation from the lateral plantar nerve) tibial nerve medial each tendon of plantar a. insertion contains a sesamoid bone fibular (peronea l) a. and tibial a. flexor hallucis longus is very important in the "push off" part of the normal gait tibial nerve sural aa. (from the popliteal a.), posterior tibial a. the calcaneal tendon of the gastrocnemius and soleus is the thickest and strongest tendon in the body nerve to the quadratus inferior gluteal a. gemellus is a Latin word that 4 tendon femoris m. gemellus, superior ischial spine obturator internus tendon laterally rotates the femur nerve to the obturator internus m. inferior gluteal a. gluteus maximus posterior gluteal line, posterior surface of sacrum and coccyx, sacrotubero us ligament external surface of the ilium between the posterior and anterior gluteal lines upper fibers: iliotibial tract; lowermost fibers: gluteal tuberosity of the femur extends the thigh; laterally rotates the femur inferior gluteal nerve superior and inferior gluteal aa. greater trochanter of the femur abducts the femur; medially rotates the thigh superior gluteal nerve superior gluteal a. gluteus minimus external surface of the ilium between the anterior and inferior gluteal lines greater trochanter of the femur abducts the femur; medially rotates the thigh superior gluteal nerve gracilis pubic symphysis and the inferior pubic ramus medial surface of the tibia (via pes anserinus) adducts the thigh, flexes and medially rotates the thigh, flexes the leg anterior division of the obturator nerve iliacus iliac fossa and iliac crest; ala of sacrum lesser trochanter of the femur flexes the thigh; if the thigh is fixed it flexes the pelvis on the thigh femoral nerve iliopsoas iliac fossa; lesser flexes the thigh; branches of gluteus medius means "little twin" gemellus is a Latin word that means "little twin" gluteus maximus is a site of intramuscular injection the angle at which the gluteus medius tendon approaches the greater trochanter of the femur is anterior to the axis of rotation of the thigh, resulting in medial rotation superior the angle at gluteal a. which the gluteus minimus tendon approaches the greater trochanter of the femur is anterior to the axis of rotation of the thigh, resulting in medial rotation obturator the pes anserinus a. is the common insertion of the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus mm. iliolumba inserts in r a. company with the psoas major m. via the iliopsoas tendon iliolumba a combination of 5 bodies and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae trochanter of the femur flexes and laterally bends the lumbar vertebral column inferior gemellus ischial tuberosity obturator internus tendon laterally rotates the femur interosseous, dorsal (foot) shafts of adjacent metatarsal bones bases of the proximal phalanges for digit 2 (both sides) & digits 3,4 (lateral side) interosseous, plantar base and medial side of metatarsals 3-5 lumbricals (foot) tendons of the flexor digitorum longus obturator externus the external surface of abduct digits 2-4 (move these digits away from midline as defined by a plane passing through the 2nd digit); flex the metatarsophalang eal joints and extend the interphalangeal joints of those digits bases of adduct digits 3-5 proximal (move these digits phalanges toward the and extensor midline of the expansions of foot as defined by digits 3-5 a plane through the second digit); flex the metacarpophalan geal and extend interphalangeal joints of digits 3-5 medial side of flex the the extensor metatarsophalang expansion of eal joint, extend digits 2-5 the proximal interphalangeal & distal interphalangeal joints of digits 2-5 trochanteric fossa of the laterally rotates the thigh the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves L2L4; branches of the femoral nerve nerve to the quadratus femoris m. r a. the iliacus and psoas major mm. inferior gluteal a. deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve dorsal metatars al aa. gemellus is a Latin word that means "little twin" four in number; remember DAB (Dorsal interossei ABduct) and PAD (Plantar interossei ADduct), then logic can tell you where these muscles insert deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve plantar metatars al aa. remember PAD (Plantar interossei ADduct) and DAB (Dorsal interossei ABduct), and logic will tell you where these muscles must insert medial (1st) lumbrical: medial plantar nerve; lateral three lumbricals: lateral plantar nerve obturator nerve medial and lateral plantar aa. the lumbricals of the foot have the same action on the toes that the lumbricals in the hand have on the fingers obturator the tendon of a. the obturator 6 obturator internus pectineus the obturator membrane and the superior and inferior pubic rami the internal surface of the obturator membrane and margin of the obturator foramen femur externus m. passes inferior to the neck of the femur to reach its insertion site greater trochanter on its medial surface above the trochanteric fossa laterally rotates and abducts the thigh nerve to the obturator internus m. pecten of the pubis pectineal line of the femur adducts, flexes, and medially rotates the thigh femoral nerve and possibly the anterior division of the obturator nerve obturator the obturator a. internus m. leaves the pelvis by passing through the lesser sciatic foramen; the superior and inferior gemellus mm. insert on the obturator internus tendon medial pectineus often femoral has a dual circumfle innervation x a. peroneus mm. (SEE fibularis mm.) piriformis anterior surface of sacrum upper border of greater trochanter of femur laterally rotates and abducts thigh ventral rami of S1-S2 plantar interosseous base and medial side of metatarsals 3-5 bases of proximal phalanges and extensor expansions of digits 3-5 deep branch of the lateral plantar nerve plantar metatars al aa. plantaris above the lateral femoral dorsum of the calcaneus medial to the adduct digits 3-5 (move these digits toward the midline of the foot as defined by a plane through the second digit); flex the metacarpophalan geal and extend interphalangeal joints of digits 3-5 flexes the leg; plantar flexes the foot tibial nerve popliteal a. peroneus is the old terminology used for the fibularis mm. piriformis leaves the pelvis by passing through the greater sciatic foramen remember PAD (Plantar interossei ADduct) and DAB (Dorsal interossei ABduct), and logic will tell you where these muscles must insert plantaris has a long slender tendon that is 7 condyle (above the lateral head of gastrocnemi us) calcaneal tendon popliteus lateral condyle of the femur posterior surface of the tibia above soleal line flexes and rotates tibial nerve the leg medially (with the foot planted, it rotates the thigh laterally) popliteal a. psoas major bodies and transverse processes of lumbar vertebrae lesser trochanter of femur (with iliacus) via iliopsoas tendon flexes the thigh; flexes & laterally bends the lumbar vertebral column subcostal a., lumbar aa. psoas minor bodies of the T12 & L1 vertebrae flexes & laterally bends the lumbar vertebral column quadratus femoris lateral border of the ischial tuberosity iliopubic eminence at the line of junction of the ilium and the superior pubic ramus quadrate line of the femur below the intertrochante ric crest quadratus plantae anterior portion of the calcaneus and the long plantar ligament tendons of the flexor digitorum longus m. assists the flexor digitorum longus in flexing the toes lateral plantar nerve quadriceps femoris anterior surface of the femur and the tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament extends the knee; rectus femoris flexes the thigh femoral nerve laterally rotates the thigh branches of the ventral primary rami of spinal nerves L2L4 branches of the ventral primary rams of spinal nerves L1L2 nerve to the quadratus femoris m. lumbar aa. equivalent to the tendon of the palmaris longus m. of the arm; its tendon is often called the "freshman nerve" because it is often misidentified by the freshman medical student has a round tendon of origin; popliteus unlocks the knee joint to initiate flexion of the leg the genitofemoral nerve pierces the anterior surface of the psoas major m. absent in 40% of cases inferior gluteal a. the nerve to the quadratus femoris m. also innervates the inferior gemellus m. lateral the quadratus plantar a. plantae m. changes the line of force of the flexor digitorum longus m. to bring it in line with the long axis of the foot lateral composed of 4 circumfle muscles: rectus x femoris, vastus femoral lateralis, vastus 8 rectus femoris anterior side of the medial and lateral intermuscul ar septa straight head: anterior inferior iliac spine; reflected head: above the superior rim of the acetabulum anterior superior iliac spine a., deep femoral a. intermedius and vastus medialis patella and extends the leg, tibial flexes the thigh tuberosity (via the patellar ligament) femoral nerve lateral circumfle x femoral a. rectus femoris is part of the quadriceps femoris muscle medial surface of the tibia (pes anserinus) flexes, abducts and laterally rotates the thigh; flexes leg femoral nerve lateral femoral circumfle x a., sapheno us a. semimembrano upper, outer medial sus surface of condyle of the ischial the tibia tuberosity extends the thigh, flexes the leg tibial nerve semitendinosus medial surface of tibia (via pes anserinus) extends the thigh, flexes the leg tibial nerve perforati ng branches of the deep femoral a. perforati ng branches of the deep femoral a. sartorius means "tailor"; its actions put the lower limb in the traditional crosslegged seated position of a tailor one of the "hamstring" muscles dorsum of the calcaneus via the calcaneal (Achilles') tendon plantar flexes the foot tibial nerve posterior tibial a. obturator internus tendon laterally rotates the femur nerve to the obturator internus m. inferior gluteal a. sartorius soleus superior gemellus lower, medial surface of ischial tuberosity (common tendon with biceps femoris m.) posterior surface of head and upper shaft of the fibula, soleal line of the tibia ischial spine pes anserinus is the common insertion for the gracilis, sartorius, and semitendinosus mm. soleus, gastrocnemius, and plantaris mm. are sometimes called the triceps surae muscle gemellus is a Latin word that means "little twin" 9 tensor fasciae latae anterior part of the iliac crest, anterior superior iliac spine lateral tibial condyle and the upper lateral surface of the tibia iliotibial tract flexes, abducts, and medially rotates the thigh superior gluteal nerve medial surface of the medial cuneiform and the 1st metatarsal dorsiflexes and inverts the foot deep fibular (peroneal) nerve interosseous membrane, posteromedi al surface of the fibula, posterolater al surface of the tibia anterior and lateral surface of the femur tuberosity of the navicular and medial cuneiform, metatarsals 24 plantar flexes the foot; inverts the foot tibial nerve patella extends the leg femoral nerve vastus lateralis lateral intermuscul ar septum, lateral lip of the linea aspera and the gluteal tuberosity patella and medial patellar retinaculum extends leg femoral nerve vastus medialis medial intermuscul ar septum, medial lip of the linea aspera patella and medial patellar retinaculum extends leg femoral nerve tibialis anterior tibialis posterior vastus intermedius superior gluteal a. tensor fascia latae redirects the rotational forces of the gluteus maximus m. anterior acts as both an tibial a. antagonist (dorsiflexion/pla ntar flexion) and a synergist (inversion) of the tibialis posterior m. fibular acts as both an (peronea antagonist l) a. and (dorsiflexion/pla tibial a. ntar flexion) and a synergist (inversion) of the tibialis anterior m. lateral vastus femoral intermedius is circumfle part of the x a. quadriceps femoris muscle lateral vastus lateralis is femoral part of the circumfle quadriceps x a., femoris muscle perforati ng branches of the deep femoral a. lateral vastus medialis is femoral part of the circumfle quadriceps x a. femoris muscle 10