Clinical Problems Lower limb Cullen – Lower Limb Neurovascular +

Clinical Problems Lower limb
Cullen – Lower Limb Neurovascular + Medial & Anterior Thigh
Tight piriformis can put pressure on sciatic nerve
Varicose veins form when valves fail causing dilation and pooling of blood
Can trace lymph for the spread of infection & cancer
Deep Inguinal nodes: deep leg
Horizontal Inguinal nodes: perineum, abdominal wall, gluteal
Vertical Inguinal nodes: medial leg, foot, thigh
Popliteal nodes: leg, plantar foot
Femoral artery: emergency blood control, pulse, compression = ischemia, heart
catheterization
Femoral hernia: intestines pass through the femoral canal and saphenous opening through the fascia
Cullen – Anterior & Lateral Leg & Foot
Anastomoses between superior lateral genicular & descending branch of lateral circumflex femoral a. important when squatting
Compartment syndrome: Increased pressure in confined anatomical space adversely affects the circulation and threatens the function and viability of tissue within or distally
Perform fasciotomy to relieve pressure (must be quick or else can lose leg)
Shin splints: related to Tibialis anterior
Fractures
Greenstick/Stress: bones don’t separate (greenstick = children)
Compound: all the way through the bone & pierces the skin, most dangerous (high risk of infection)
Avulsion: tendon or ligament pulls off a piece of the bone
Comminuted: 3+ pieces
Compression: crushed bone
Foot Drop: injury to Deep fibular n. or Tibialis anterior m. foot stuck in plantar flexion, problems with gait or balance
Plantar fasciitis: tightening of the plantar aponeurosis & binding of adjacent fascia which limits movement due to overuse
Release fascia with stretches
Morton’s neuroma: painful swelling of nerve between heads of metatarsal
Remove pressure with rest, inserts and proper shoes, last choice is surgery
Cullen – Lower Limb Posterior
Gluteal injection: Between digits 2-3 with palm on greater trochanter with 2 nd digit on ASIS and 3 rd digit on tubercle of iliac crest
Trendelenburg Sign: injury to superior gluteal n. causes weakness in hip abductors gluteus medius atrophies
Unable to maintain pelvis in a level position causing a hip drop of the opposite side with each step
Strain: muscle injury
1 = minor tearing 2 = major tearing 3 = avulsion (tendon pulls part of bone away)
Sprain: ligament injury
Cullen – Joints of the Lower Limb
Most common to disarticulate hip posteriorly (weak ischiofemoral l.) during a car accident with hip flexed & knees on dashboard
Osteoarthritis: wear and tear on cartilage leading to a narrowed joint space
Most common reason for a hip replacement
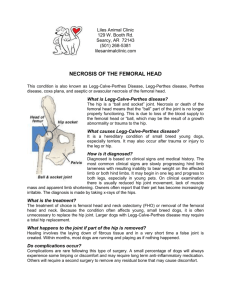
Osteoporosis: low bone mass lower weight bearing capacity of bones easier to fracture femur (especially at intertrochanteric region or femoral neck)
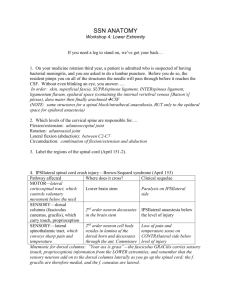
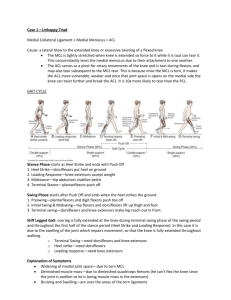
MCL injured from blow to lateral knee that abducts knee
LCL injured from blow to medial knee or by planting foot + twisting hips
Unhappy Triad: MCL, ACL, Meniscus
If ACL injured, the tibia will slide anteriorly on the femur (+ drawer test)
Torn meniscus: knee catches in flexion & extension, “joint mice”
High ankle sprain: tibiofibular l.
Inversion injury (lateral): anterior talofibular calcaneofibular posterior talofibular
More vulnerable to sprain than medial side
Calcaneofibular l. injury is most likely to create an avulsion fracture of fibula
Eversion injury (medial): deltoid l.