LCL
advertisement

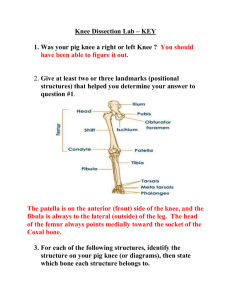
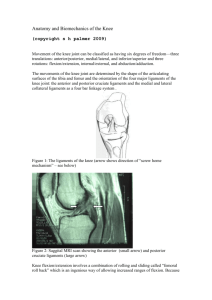
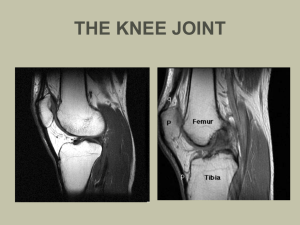
Knee Boney Anatomy Femur Patellar surface femur Lateral condyle & epicondyle Medial condyle & epicondyle Medial condyle of tibia Head fibula Tibial tuberosity Fibula Medial Collateral Ligament MCL Mechanism of Injury Valgus Stress MCL Sprain 1st Degree 2nd Degree 3rd Degree Valgus Stress Test Stresses MCL Valgus Stress at 0 - 5º Valgus Stress at 25 - 30 º Lateral Collateral Ligament LCL- MOI of LCL Injury Varus Stress Test Stresses lateral structures Varus Stress Varus Stress at 0 º and 25 º to 30º of flexion Anterior Cruciate Ligament ACL Tear • Anterior instability • Mechanism – Deceleration injury – IR of femur with knee flexed and foot planted – Hyperextension of knee • Swelling • Pop at time of injury • Pain with Signs and Symptoms – AROM – PROM • Anterior instability • Decreased strength • Giving way or buckling Anterior Drawer Test Grading Anterior Instability Medial view Right knee • • • • • Stabilize Foot Check for hamstrings relaxation Thumbs either side patellar tendon Apply anterior force Grade amount of translation Lachman’s Test • • • • • Better test than Anterior Drawer Takes opposition of hamstrings out of play Knee flexed 15 º - 30º Stabilize femur Apply anterior force to tibia Pivot Shift Test • • • • Gold standard test for ACL Leg is externally rotated Valgus force is applied as leg is flexed Positive test indicated by clunk sensation Posterior Cruciate Ligament Posterior cruciate Posterior Sag Test • • • • Posterior Cruciate vs Anterior Cruciate Athlete supine Both knees flexed 90’ Observe laterally Posterior Drawer Test PCL • • • • • • ACL Athlete supine Knee flexed 90’ Foot neutral Sit on foot to stabilize it Posterior force applied at tibial plateau Positive test indicates PCL injury Medial and Lateral Meniscus Medial meniscus “C” shaped Lateral meniscus more circular shaped • Mechanism of Injury – Squat with rotation – Internal rotation of femur – on fixed tibia Joint Space Orientation Lateral Meniscus Lateral Joint Space Medial Meniscus Medial Joint Space Mc Murray Test • • • • Flex knee fully Palpate medial & lateral joint spaces with one hand Rotate tibia opposite to femur as knee is extended Palpable pop and/or pain indicate a positive test Apley’s Compression Test External rotation of tibia tests medial meniscus Internal rotation of tibia tests lateral meniscus Apley’s Distraction Test Unloads the meniscus Stressess MCL and LCL