A Brief Review
advertisement

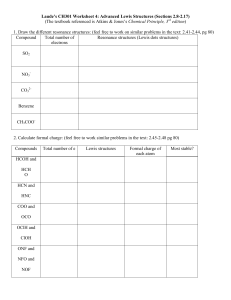
A Brief Review Organic Chemistry – study of • Bonds with • > million compounds Bonding -- 2 ways to achieve 1. Ionic bond Na Ex: + Cl Æ H Æ 2. Covalent bond H Ex: + Lewis Structures (molecules/ions): dots = lines = Common Bonding Patterns Bonds Lone prs. Patterns Ex: Carbon 4 0 Nitrogen 3 1 Oxygen 2 2 Hydrogen 1 0 Halogen 1 3 Draw the Lewis structure for CH3CN Formal charge: to determine charge on atom or polyatomic ion F.C. = # valence e- in neutral atom – (all unshared e- + ½ shared e-) Ex: Determine which atom bears the charge on H3O+ Summer Notes CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 1 Nonpolar Covalent Bonds Polar Electronegativity -- Measure of See Figure 1-6 ∆EN = 0.5 – 1.9 Æ Dipole moment – ( ) defined as C—H Ex: O—H C — Cl Note: Polarity of Molecule depends on Resonance -- when single • Valence e- Ex: Acetate ion (CH3CO2-) Æ 2 possible Lewis Structures Contributing structuresÆ Major Minor Resonance hybridÆ Summer Notes CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 2 Writing Organic Compounds Compound Lewis Condensed Line-angle ethane pentane acetone cyclohexanol Acids & Bases Bronsted-Lowry: Acids Æ Bases Æ HCl + NaOH Æ Strong Weak Strength measured by: HA Summer Notes + H2O CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 3 Ka = pKa = pKa acid strength **Stronger acid Æ **Acid-base reactions Æ What about bases? Acidity of Organic Acids Æ 4 main factors: 1. Electronegativity of atom bonded to acidic H • More EN Æ Ex: H3C—H HO—H 2. Size of atom bonded to acidic H • Bigger Æ Ex: HI HF 3. Resonance • Is conjugate base Ex: CH3CH2OH (ethanol) pKa = 15.9 Summer Notes CH3COOH (acetic acid) pKa = 4.76 CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 4 4. Inductive Effect • Positive charge withdraws e- from H—A bond Æ O H3C C O H Acids & Bases Take 2 Acid Æ Base Æ Lewis: + A A B B H H N H + H+ H H N H H Curved arrows Æ End of Chpt. 1 Shapes of Molecules Æ Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion Theory (VSEPR) • Valence e- repel ∴ • Unshared e- repel H Ex: CH4 (methane) H C H C H H H H Summer Notes CHE 261 H Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 5 Ex: H NH3 N H N H H H H Lewis Structures only predict shape Æ Bonding: Sharing e- by Sigma (σ) bond – H – overlap along bonding axis + H 1s Æ 1s H H sigma bond C, N, O Æ also use p Hybridization: sp3, sp2, sp Hybridization s+p+p+pÆ Hybridized orbital Example CH4 s+p+pÆ CH2CH2 s+pÆ C2H2 Pi (π) bond Æ sharing of e- by Æ double bond Æ *Bond length: triple< Summer Notes CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 6 Summary Hybridization # bonding “areas” 4 3 Hybridization Bond Types Angles* 4 – sigma 3 – sigma 1 – pi 2 – sigma 2 – pi 109.5° 120° 2 180° * Ex: Determine the hybridization and bond angles and label the bond types for hydrogen cyanide (HCN). Single bonds – allow Æ lots of Double bonds – Æ results in Isomer Constitutional Isomer Stereoisomer Geometric Def: Summer Notes Others CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 7 Ex: C4H10 2-butene Molecular dipole moment Æ is the molecule Must consider & Ex: CCl4 CHCl3 Why important? Types of Intermolecular Interations: 1. dipole-dipole Ex: 2. CH4 b. pt. = CH3OH b. pt. = London dispersion ( Ex: Summer Notes ) CHCl3 b. pt. = CCl4 b. pt. = CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 8 3. Hydrogen bonding Ex: CH3OCH3 b. pt. = CH3CH2OH b. pt. = Solubility Æ “ Ex: “ Salt + water Salt + gasoline Wax + gasoline Wax + water Functional Groups Æ Have specific Æ Gives compound H H H C C H H H Alkane (not true F.G.) C C C Alkene C Alkyne OH C Arene Summer Notes Phenol CHE 261 O Alcohol Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 9 H C C S H C Thiol N C O Ether Amine These groups contain a Carbonyl Group (not a functional group): O O C C O C C C OH H Aldehyde Ketone O C Carboxylic Acid O O O O C C C C N O Ester Amide Acetic Anhydride Examples: O OH OH O NH2 O Summer Notes CHE 261 Chpt. 1,2 – pg. 10