Lewis Structures: Drawing & Rules Handout
advertisement

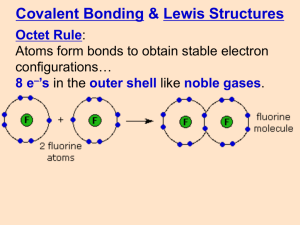
Lewis Structures Handout 4.7 (5.6) Drawing Lewis Structures Rules for Writing Lewis Dot Structures for Molecules 1. Add up valence electrons from all atoms It does not matter which atom they come from. Add 1 e- for each (-) charge Subtract 1 e- for each (+) charge 2. Identify the central and terminal atoms and write the skeletal structure The central atom will usually be one of the lowest electronegativity (least electron loving) (H excepted) This may take some trial and error (or be given). H is always terminal O usually terminal except for peroxides and hydroxides OH C is always a central atom, it always has 4 bonds 3. Draw a bond between each pair of atoms. Each bond uses up 2 of the available e-. 4. Assign remaining e to terminal elements first to fill octet (duet for H) 5. If there are leftover e-, If there are additional e- still left, place them on central atoms that have empty d orbitals (period 3 and below). 6. If all e- are used up and the central atoms do not have completed octets, move one or more lone pairs to form a multiple bond. Usually for C, N, O, X (halogen) and H – C forms covalent bonds and lone pairs. – N forms covalent bonds and lone pairs. – O forms covalent bonds and lone pairs. – X forms covalent bonds and lone pairs. – H forms covalent bond Lewis Structures Handout Examples for Rows 1 + 2 (Octet rule never exceeded) H2 O NH3 HCN Problem: Draw the Lewis structure for N2H4 and CO2 Lewis Structures Handout Exceptions to Octet Rule Boron & Al have fewer than a full octet (3 bonds) Period 3 & below elements can exceed the octet rule (have 10-12 electrons) The octet rule is sometimes broken because of unfilled d orbitals that are available. Examples SeF6 BrF3 Problem: Draw the Lewis Structure for SF4.