A Holistic Approach to Basic Enzymes
advertisement

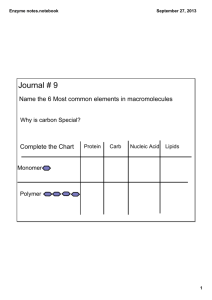
Basic Enzyme Therapy Karla S. Anderson RN, BSN, CHPN, LDHS, LMT, CNC, CTH Food enzymes are a natural and important component in our food supply, yet they are removed to extend shelf-life. While shelf-life is necessary in our modern society, enzymes must be replaced, just as vitamins and minerals are. For example, when milk is pasteurized it depletes the vitamin A and D content as well as enzymes. The vitamins are added back in, but the enzymes are not. Enzymes are the construction workers of the body. Protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals are simply the building materials. The best sources of nutrients are not concentrated chemical compounds but whole foods with contents that act synergistically when properly digested and assimilated. All digestion in the body is affected by the way we prepare our foods. Any food cooked over 102 degrees is rendered “dead food” meaning there is no enzyme activity. Without enzymes, the body cannot maintain a balanced pH. Fat (olives, avocados, etc) Digestion Process Fat is broken down into lipid droplets by bile. Bile is an emulsifier that is produced in the liver and stored in the gallbladder. Fresh lemon juice is also an emulsifier and helps assist a weakened biliary system. Fats Lipid droplets are then converted by Proteins Lipase (enzyme) into fatty acid and Glycerol. Fats are a source of energy and used in growth e Vitamins and repair in the human body. The body must have dietary intake of Omega 3 & Omega 6 as they are essential to our health and well-being. Protein (meats, beans, etc.) Digestion Process Protein fibers are broken down in the stomach with the assistance of HCL. Protease (enzyme) then converts proteins into peptides and Peptidase (enzyme) converts peptides into amino acids. Amino acids are used as a source of energy, for growth and repair and for the regulation of body processes. Digestive and Metabolic enzymes are also built from amino acids. Carbohydrate (potatoes, pasta, etc) and Cellulose (celery, carrots, etc) Digestion Process Polysaccharides/Starch are converted into disaccharides by Amylase/Cellulase (enzymes). Then a enzyme specific for each carbohydrate, Lactase (milk sugar), Sucrase (refined sugar), Maltase (malt sugar), Invertase, Glyucoamylase, Alpha-Galactosidase, etc., convert the disaccharides to glucose and monosaccharides which are used as a source of energy. POOR PROTEIN ASSIMILATION Increased body secretions: Saliva, Urine, Sweat, and Sinuses. Muscle cramps at night. Menstrual cramps and irregularity. Hot flashes. Bleeding gums and frequent nosebleeds. Cold hands and feet. Edema, swelling of hands and feet. Does not tolerate exercise. Inability to digest protein (Functional Hypoglycemia) o Hydrochloric acid deficiency Five Steps of Digestion o Biliary dysfunction o Low protein levels in the blood o Low calcium levels Food enzymes o Iron deficiency Chewin g POOR CARBOHYDRATE ASSIMILATION skin. Decreased body secretions, such as dry mouth and Saliva enzymes dry Dehydration. Stomach acid Muscle weakness. Startle easily. Endogen ous enzymes Unable to concentrate and think clearly. Increased sensitivity to light. Difficulty swallowing. Voice affected by stress. Muscle cramps during exercise. Loss of energy and fatigue. Inability to digest carbohydrates (Reactive Hypoglycemia) o Low blood glucose levels o Inability to release glycogen from the liver o Adrenal insufficiency o An alcoholic hangover o o Those with headache present with loss of kyphosis Acute attacks of gastritis or ulcers can be relieved immediately with spinal manipulation POOR LIPID ASSIMILATION Dry Skin Hair loss Tremors Slow morning starter Muscle cramps Muscle weakness Menstrual cramps & irregularity Startle easily POOR PROSTAGLADIN ASSIMILATION Inability to control blood pressure Inability to induce labor Inability to conceive Inability to carry fetus to term / Spontaneous abortion 17 Enzymes Outline Not digesting protein, look for: Constipation, Arthritis, Anxiety Attacks, Premenstrual Syndrome Not digesting carbohydrates, look for: Diarrhea, Fibromyalgia, Attention Deficit Disorder Not digesting fats, look for: Constipation, Gallbladder Problems, Heart Disease Fat Digestion Process Fat Bile Emulsification (lemon or lime juice closest to human bile) Lipid Droplets Lipase Fatty Acid + Glycerol Protein Digestion Process Protein Proteases Peptides Peptidase Amino Acids Carbohydrate Digestion Polysaccharides/Starch Amylase/Cellulase Disaccharides Malt Diastase, Alpha-Galactosidase, Lactase, Invertase, Glucoamylase Glucose/Monosaccharides 3 Types of Enzymes: 1. Food Enzymes = contained in all raw food 2. Digestive Enzymes = which are secreted by the body to digest food 3. Metabolic Enzymes = which run other biochemical processes Food Enzymes = 4 Main Types Proteases = break down protein (meats, beans, etc.) Amylases = break down carbohydrates (potatoes, pasta, cookies, etc.) Lipases = break down fats (olives, avocados, etc.) Cellulases = break down fiber (celery, carrots, etc.) 3 Enzymes Essential for Digestion of Carbohydrates Lactase = breaks down lactose (milk sugar) Sucrase = breaks down sucrose (refined sugar) Maltase = breaks down maltose (malt sugar)