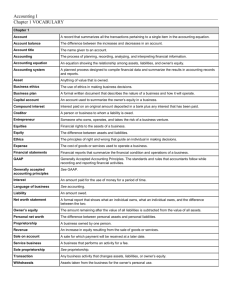
Topic Description Formula Range Your Store Net Profit Net profit
advertisement

Topic Formula Range Net Profit = Net Income ÷ Net Sales 0.88% to 1.91% EBITDA EBITDA stands for Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, & Amortization. Some companies consider this a truer measure of operating performance than net profit. It closely reflects cash flow (relative to sales). EBITDA = (Net Sales - Cost of Goods Sold) ÷ Net Sales 4.20% to 5.33% Capital Expenditures Capital expenditures (as a percentage of sales) is a measure of the company's investment level. Capital Expenditures = Total Capital Expenditures ÷ Total Sales 2.22% to 2.79% Return on Assets Return on total assets (ROA) measures the ability of a company's combined equity capital and debt securities to generate profits. ROA reflects the profit generated from a firm's asset base regardless of how it is financed. ROA = Net Income after Taxes ÷ Total Assets 3.04% to 5.85% Return on Equity Return on equity (ROE) relates the company earnings specifically to the resources provided by its owners. It reflects how well the firm employs leverage (i.e., funds acquired from outside sources by issuing debt securities). ROE = Net Income after Taxes ÷ Owner's Equity 9.38% to 16.79% Asset Turnover Asset Turnover is used to measure the company's ability to use its assets to generate sales. Asset Turnover = Net Sales ÷ Total Assets 3.12 to 3.37 Debt-to-Equity Ratio The debt-to-equity ratio indicates the degree of dependence on creditors, rather than owners, in providing funds to operate the business -- in short, the amount of trading on the equity. Total Liabilities = Current Liabilities + Loans from Banks + Mortgages + Notes and Bonds Payable in one year or more + Capitalized Lease Obligations + Other Non-Current Liabilities Net Profit Description Net profit margin measures the portion of the company's sales dollar remaining after it pays all expenses (including product costs) and realizes any extraordinary gains or losses. Total Equity = Capital Stocks (common and preferred) + Paid-in Surplus + Retained Earnings minus the Cost of Treasury Stocks Debt-to-Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities ÷ Total Equity 1.95 to 2.60 Your Store Topic Formula Range Times Interest Earned The times interest earned ratio suggests the firm's ability to cover long-term debt. If the times interest earned value is sufficient, the firm should be able to fulfill its interest obligations. Times Interest Earned = (Net Income + Income Taxes + Interest Paid) ÷ Interest Paid 2.31 to 4.65 Current Ratio The current ration indicates the ability of a company to meet its current (short-term) obligations with its current assets. This important measure of liquidity is the ratio of current assets to current liabilities. Current assets include cash, accounts receivable, total inventory, investment in marketable securities, and other assets. Current liabilities include accounts payable, mortgages, notes and bonds payable in less than one year, income taxes payable, and other liabilities. Current Ratio = Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities 1.05 to 1.28 Quick Ratio = (Current Assets minus Inventory) ÷ Total Assets 0.41 to 0.56 GMROI = Gross Margin ÷ Average Inventory 349% to 453% Quick Ratio Gross Margin Return on Investment Description The quick ratio measures the relationship between cash, current receivables, and marketable securities to current liabilities. It indicates a company's ability to discharge its current obligations without the need to sell off inventories. The GMROI combines the gross margin percentage and inventory turns into one number (it is the product of those two ratios). Inventories are valued on a first-in, first-out basis at cost. For this report, fiscal year-end inventories were assumed to a reasonable measure of average inventory levels during the year. Your Store