Crystalline solid classification
advertisement

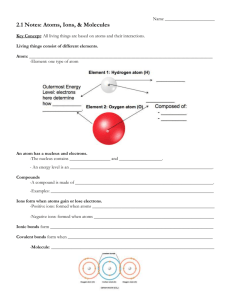
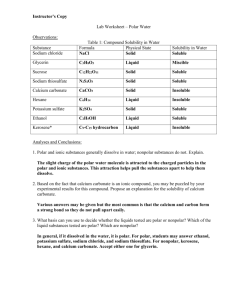
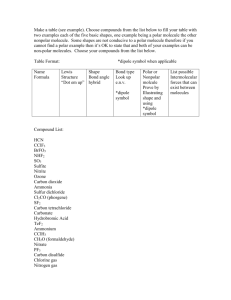
Type TABLE 12.7 Structural Particles Dispersion forces Covalent bonds Electrostatic attractions Metallic bonds Intermolecular Forces Characteristics of Crystalline Solids Low to moderate melting points; soluble in some polar and some nonpolar solvents Soft; extremely low to moderate melting points (depending on molar mass); sublime in some cases; soluble in some nonpolar solvents Most are very hard and either sublime or melt at very high temperatures; most are nonconductors of electricity Hard; moderate to very high melting points; nonconductors as solids, but good electric conductors as liquids; many are soluble in polar solvents like water Hardness varies from soft to very hard; melting point varies from low to very high; lustrous; ductile; malleable; very good conductors of heat and electricity Typical Properties (CH 3)2O, CHCl3 , HCl He, Ar, H 2 , CO2 , CCl4 , CH 4 , I 2 C (diamond), C (graphite), SiC, AlN, SiO2 NaCl, MgO, NaNO3 Na, Mg, Al, Fe, Sn, Cu, Ag, W Examples Polar Molecular Nonpolar Network covalent Ionic Metallic Cations and delocalized electrons Dispersion forces and dipole–dipole attractions H 2O, NH 3 Polar molecules Atoms or nonpolar molecules Atoms Cations and anions Hydrogen bonds HydrogenBonded Molecules with H bonded to N, O, or F AABJSWV0 ©2007 by Prentice Hall, Inc. A Pearson Company Low to moderate melting points; soluble in some hydrogen-bonded solvents and some polar solvents Figure Number: 12 T07