Cell Membrane Structure and Function Worksheet
advertisement

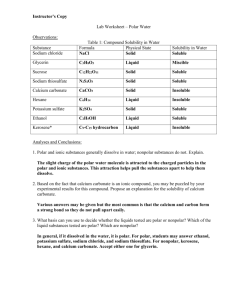
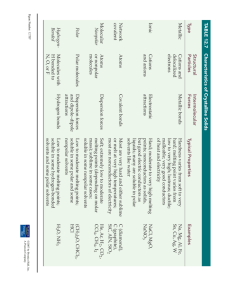
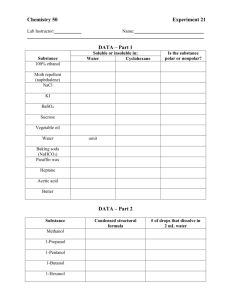
Name________________________________________ Date_______ Over the years, scientists have collected the following data about cell membranes (listed in chronological order). Lipid soluble substances enter cells faster than water soluble substances (lipids are nonpolar). Lipids are unstable in water because they repel water (think of oil in water). o If you don't have a mental picture, take some drops of oil and put them in a glass of water at home and see for yourself what happens. From the chemical analysis of cell membranes, it was discovered that cell membranes are composed of phospholipids. o Phospohlipids look a lot like clothespins with a polar(attracted to water) head and 2 nonpolar (repels water) tails. polar head nonpolar tails 1) When phospholipids are put in water, could you think of a way that they might arrange themselves so that like is near like (i.e. polar is near polar, and nonpolar is near nonpolar). Sketch your arrangement and then provide a justification. Sketch: Justification for sketch (Based on evidence above and evidence from our lab activities): Name________________________________________ Date_______ 3) When you placed cells in high concentrations of salt, what did you observe about the responses of the cell wall and the cell membrane? How were they similar and how were they different? Be specific. 4) What might that tell you about the structure of the cell wall versus the cell membrane? Explain. 5) Not all molecules that a cell needs are going to be able to enter a cell by diffusion through the cell membrane. Give two examples of molecules that a cell might need and explain why they can't enter by diffusion. 6) Think of two mechanisms by which these molecules might be able to enter the cell. (Hint: Think of how animals take food into their bodies or how humans get water where it is needed.) Name________________________________________ Date_______ 7) Based on our lab activities, list the properties of the following molecules. Molecule Example Charge (0 for (if neutral, ++ for applicable) highly charged, + for slight charge) Size (+ for small, ++ for medium, +++ for large) soluble, ++ Solubility in oil (0 for not soluble, + for slightly soluble, ++ for highly soluble) Solubility in water(0 for not soluble, + for slightly for highly soluble) Carbohydrate Glucose Protein Fat* Salt Water Oxygen* Carbon dioxide* *Cannot measure conductivity of this substance. 8) Based on our discussion, which of these molecules will be able to cross the cell membrane by diffusion? a. Which won't? 9) What characteristics of the molecules can you use to determine whether they will cross the cell membrane or not? Explain your answer.