1- Participants will be able to understand the basics of food safety. 2
advertisement
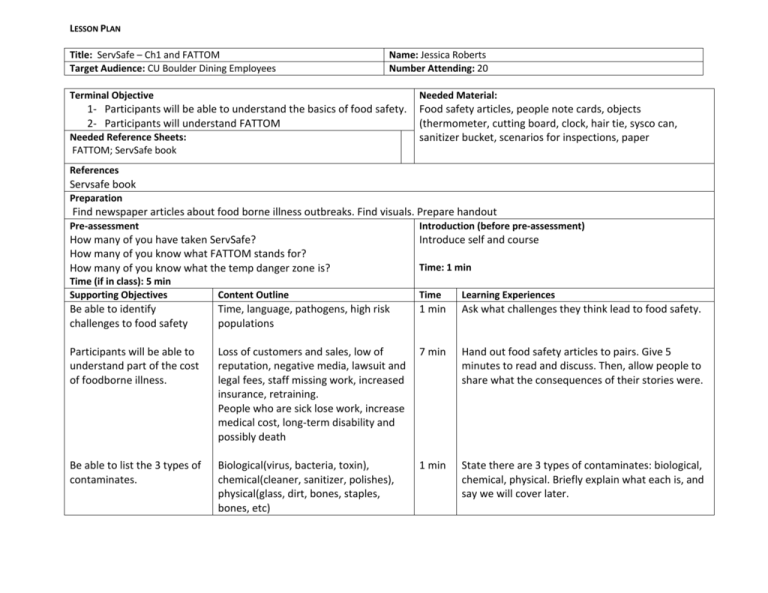
LESSON PLAN Title: ServSafe – Ch1 and FATTOM Target Audience: CU Boulder Dining Employees Name: Jessica Roberts Number Attending: 20 Terminal Objective Needed Material: 1- Participants will be able to understand the basics of food safety. 2- Participants will understand FATTOM Needed Reference Sheets: FATTOM; ServSafe book Food safety articles, people note cards, objects (thermometer, cutting board, clock, hair tie, sysco can, sanitizer bucket, scenarios for inspections, paper References Servsafe book Preparation Find newspaper articles about food borne illness outbreaks. Find visuals. Prepare handout Pre-assessment Introduction (before pre-assessment) How many of you have taken ServSafe? How many of you know what FATTOM stands for? How many of you know what the temp danger zone is? Introduce self and course Time: 1 min Time (if in class): 5 min Supporting Objectives Content Outline Time Learning Experiences Be able to identify challenges to food safety Time, language, pathogens, high risk populations 1 min Ask what challenges they think lead to food safety. Participants will be able to understand part of the cost of foodborne illness. Loss of customers and sales, low of reputation, negative media, lawsuit and legal fees, staff missing work, increased insurance, retraining. People who are sick lose work, increase medical cost, long-term disability and possibly death 7 min Hand out food safety articles to pairs. Give 5 minutes to read and discuss. Then, allow people to share what the consequences of their stories were. Be able to list the 3 types of contaminates. Biological(virus, bacteria, toxin), chemical(cleaner, sanitizer, polishes), physical(glass, dirt, bones, staples, bones, etc) 1 min State there are 3 types of contaminates: biological, chemical, physical. Briefly explain what each is, and say we will cover later. Be able to repeat 5 most common mistakes that lead to foodborne illness Purchase from unsafe, fail to cook correctly, hold foods wrong temp, use contaminated equipment, practicing poor personal hygiene. 1 min List/ask Be able to list four main factors that lead to foodborne illness Time temperature abuse, cross contamination, poor personal hygiene, poor cleaning and sanitizing 1 min List/ask Be able to identify which foods are most likely to become unsafe TCS foods & ready to eat. - Milk and dairy - Meat - Fish, shellfish, crustaceans - Poultry - Baked potatoes - Tofu - Sliced melon - Cut tomatoes - Cut leafy greens - Shell eggs - Heat-treated rice, beans, and vegetables - Sprouts - Untreated oil and garlic mix 2 min Ask which they think. Make sure have entire list. Be able to identify populations at high risk for foodborne illness and identify why Elderly: immune system weakens Preschool-aged children: not build up strong immune Compromised Immune: cancer/chemo, HIV/AIDS, transplant recipients, certain medications 8 min Pass out note cards. Have them go to two opposite sides of the room, one at high risk, one not. Summarize those at high risk. Have them move if they think they need to. Then discuss if people think it is correct. Correct any misconceptions. List what basic steps there are for keeping food safe. 1- control time and temperature, 2prevent cross-contamination, 3-practice 3 min Have visual aids for each item. (clokc, and thermometer, different color boards, soap and hair personal hygiene, 4-purchase from approved, reputable suppliers, 5cleaning and sanitizing tie, sysco something, sanitize bucket/rag) hold each up as we go over each, then have them repeat when seeing the object what it stands for Participants will be able to list why training and monitoring is important for keeping food safe Train staff on hire and regular basis. Train everyone on basics, then go to job specifics. Retrain and remind regularly. Document training. 30 sec State that training should be done and documented, as well as feel free to give reminders Be able to match government agencies to what they are responsible for FDA: inspect all food except meat, poultry eggs; create model food code for city, county, state and tribal agencies, though not require it USDA: inspect meat, poultry, egg; regulate food that crosses state boundaries or involve more than one state CDC(center for disease control and prevention) and PHS(US public health services): research, investigate outbreaks State& local: inspect, enforce, investigate complaints, issues license and permits, approve construction, review and approve HACCP 5 min List. Then give scenarios and have them determine which agency would be in charge of the scenario. Participants will be able to state what FATTOM stands for and what it means FATTOM – bacteria’s best friend Food – esp TCS Acidity- neut to slightly acidic Temperature – 41-135 Time – get food under 70 within 2 hrs, 41 within 6 Oxygen- some need oxygen, except botulism Moisture-grows well with moisture 2 min Explain the acronym FATTOM. They are the things that can cause bacteria to grow. Remember the acronym. Give them paper to write down (on drawn hand) and double-check that they remember. Closure Introduce next presentor.