ELECTRONICS-I Field Effect Transistors (FET) • Yrd. Doç. Dr. Nihan
advertisement

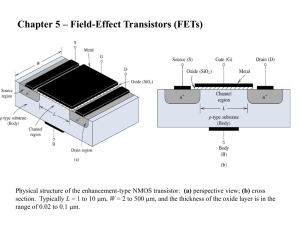
ELECTRONICS-I Field Effect Transistors (FET) Metal Oxide Semiconductor Field Effect Transistor (MOSFET) • Yrd. Doç. Dr. Nihan Kosku Perkgöz Field Effect Transistor -FET • FETs are majority-charge-carrier -UNIPOLAR devices (only electrons or holes carry current). • Much smaller than BJTs. • Most of the manufactured transistors are FETs. • High input resistance to the signal source, drawing little input power, • Low resistance to the output circuit, so it supplies a large current to drive the circuit load. http://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/transistor/tran_6.html The gate turns the transistor (inversion layer) on and off with an electric field through the oxide. Field Effect Transistor -FET • Different types: – – – – – – MOSFET (Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor), JFET (Junction field-effect transistor), MESFET (Metal–Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor), MODFET (Modulation-Doped Field Effect Transistor), HEMT (High electron mobility transistor) … MESFET MOSFET JFET (Junction field-effect transistor) Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock Jaeger «Microelectronic Circuit Design» CMOS –complementary MOS • -The CMOS (complementary metal oxide semiconductor) process technology is the basis for modern digital integrated circuits. This process technology uses an arrangement where the ("enhancement-mode") p-channel MOSFET and nchannel MOSFET are connected in series such that when one is on, the other is off. p-channel MOSFET n-channel MOSFET n-channel enhancement-mode MOSFET http://www.utdallas.edu/~torlak/courses/ee3311/lectures/ Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor (MOS) Capacitor http://www.utdallas.edu/~torlak/courses/ee3311/lectures/ Formation of Channel http://www.utdallas.edu/~torlak/courses/ee3311/lectures/ Characteristics of MOSFETs Donald A. Neaman «Electronic Circuit Analysis and Design» Characteristics of MOSFET For small values of VDS: When VGS< VTH, the drain current is zero. When VGS> VTH, inversion charge layer is formed and the drain current increases with VDS. For VDS > VGS-VTH : When VGS< VTH, the drain current is zero. http://www.utdallas.edu/~torlak/courses/ee3311/lectures/ When VGS> VTH, the drain current increases with VDS until saturation point (until the potential difference across the oxide at the drain terminal is equal to VTH). Channel Pinch-off Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock Jaeger «Microelectronic Circuit Design» n-channel & p-channel D G D G S S I-V Characteristics Operation in the Triode (Linear) Region Operation in the Saturation Region Richard C. Jaeger Travis N. Blalock Jaeger «Microelectronic Circuit Design»