Understanding Fixed Income Concepts
advertisement

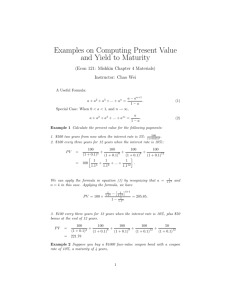
Understanding Fixed Income Concepts Basic structure of a bond The institution that ‘issues’ a bond, or ‘borrows’ from the public YEAR 1 ISSUER YEAR 2 @ x% @ x% YEAR 3 The year in which the bond ‘matures’ – the lender receives the last coupon and the principal YEAR 4 @ x% YEAR 5 @ x% @ x% COUPON Tenor COUPON COUPON – number of years the bond has toCOUPON pay all returns COUPON + Regular pre-specified payments, based on the interest rate Rate at which the coupon is generated PAR The amount on which interest is paid, and what the bond holder receives when the bond matures. Also called the ‘face value’ of the bond. Par value, premium and discount PREMIUM 108 If the bond trades at a premium, the investor pays more than the face value of the bond Par 100 Value If the bond trades at a discount, the investor pays less than the face value of the bond DISCOUNT 95 What is a bond rating? Bonds are rated on the basis of their risk of default Default: the risk that the lender may not get his money back The ratings do not convey other risks: change in liquidity, or interest rates Bond ratings are carried out by agencies What goes into a bond rating? Capacity Character The Four C’s of Corporate Credit Capital Conditions What are bond ratings? High Risk Low Risk CRISIL Source: Crisil Long Term Ratings Short Term Ratings AAA AA A BB B C D P-1 P-2 P-3 P-4 P-5 What are bond ratings? High Risk Low Risk ICRA Source: ICRA Long Term Ratings Medium Term Ratings Short Term Ratings LAAA LAA LA LBBB LBB LB LC LD MAAA MAA MA MBBB MBB MB MC MD A1 A2 A3 A4 A5 Understanding yield to maturity What the investor gets if bond is held to maturity Yield to Maturity Assumes all cash flows reinvested at the YTM Bond price is the sum of all cash flows discounted at YTM Math Check Individual cash flows CPN Bond Price CPN + 1 = 1+r Present value of the bond Discount rate: Yield to Maturity 1+r Terminal cash flow: coupon + par value of bond …+ + 2 CPN + PAR n 1+r Number of times discount occurs: based on time period The term structure – normal yield curve Economy stable. No inflationary shocks expected. Longer maturities generate higher risk expectation. Greater risk demands greater yield. Yield 1. 2. 3. 4. 10 Yr 5 Yr 3 Yr 1 Yr Maturity The term structure – steep yield curve 1. 2. 3. Economy about to boom. Inflation expected to rise. Long term investors demand higher returns to avoid getting locked into lower rates. 10 Yr Yield 5 Yr 3 Yr 1 Yr Maturity The term structure – flat yield curve 1. Yield 2. Flat yield curves mark a transition between economic cycles. Flatness occurs through a combination of rising short term rates and falling long terms rates. 1 Yr 5 Yr 3 Yr Maturity 10 Yr The term structure – inverted yield curve 1. Yield 2. An inverted curve means that the market expects interest rates to fall in future. This could signal an economic slowdown, as interest rates are lowered to stimulate growth. 1 Yr 3 Yr 5 Yr Maturity 10 Yr The concept of yield spread In a positive economic environment, the spread between corporates and g-secs contract, reflecting lower longterm default possibility in a lower interest rate environment. The high yield, or speculative grade, bond market is not yet prevalent in India. High - yield Yield AAA Corporate Gilts Yield spreads are a function of credit. Investment grade corporates have lower credit than G-secs, so other things being equal, G-secs will have lower yields than corporates at every maturity. Maturity Risks associated with fixed income investment Credit Risk Default Risk Issuer could fail to meet debt obligations in a timely manner. Credit Spread Risk Risk premium required for particular corporate bond (or bond class, sector, industry, or economy) increases, leading to price reduction in existing bonds Downgrade Risk Rating agency could lower rating on a bond after conducting analysis, increasing the credit spread, causing yields to go up and prices to go down Interest Rate Risk Prices and yields have inverse relationships Yields are influenced by interest rates PRICE AT DISCOUNT YIELD ABOVE COUPON YIELD = COUPON PRICE = PAR PAR VALUE YIELD BELOW COUPON PRICE AT PREMIUM When rates change, yields move to track the new rate Prices move in the opposite direction to reflect the new yield If yield = coupon rate, the bond will sell at par Duration Duration measures interest rate sensitivity In other words, how much does the price of a bond change with a change in interest rates? Duration +VE RELATIONSHIP -VE RELATIONSHIP Term to maturity Yield to maturity Coupon Math Check: Approximate price change using duration The delta sign denotes ‘change’. This means change in yield. - Duration x The negative sign is because of the inverse relationship between price change and yield change Δy x 100 = Approx. percentage price change Math Check: Approximate price change using duration - 3.33 x 0.015 x 100 = - 5% Practical application: Portfolio duration Interest rate scenario Portfolio manager action Lower Duration Higher Duration Portfolio managers often change the duration of their securities to manage changing interest rates Reinvestment Risk 8% 7.5% 7% 6.5% 10% 10% 10% 10% 6.5% EXISTING BOND 6.5% 6.5% NEW BOND ROLLOVER 6.5% Liquidity Risk The greater the bid – ask spread, the less certain the fair value of the price Liquidity risk is not important for hold-to-maturity investors It is an issue for those seeking to profit from bond price movements Liquidity risk is a function of the following factors Expectation of interest rate changes Number of market makers Comfort level with security Securitisation – What is it all about ? Loan Pmt Originator Obligors Issues loan Sale of assets Proceeds of rated securities Fees SPV Credit Enhancement Issuance of rated securities Credit Enhancement Payment for rated securities Underwriter Issuance of rated securities Payment for rated securities Investors Key Macro-economic indicators for fixed income Liquidity indicators Liquidity Indicators 25 100000 80000 Net LAF amount (LHS) Call (RHS) 60000 20 40000 20000 Rs. crore 15 0 -20000 10 -40000 -60000 5 -80000 -100000 -120000 01/01/2008 12/02/2008 28/03/2008 Source: Bloomberg, Fidelity. 20th November 2008 15/05/2008 30/06/2008 12/08/2008 26/09/2008 0 18/11/2008 Source: Bloomberg, Fidelity. 20th November 2008 04/10/2008 16/08/2008 28/06/2008 10/05/2008 22/03/2008 CRR 02/02/2008 10-yr G-Sec 15/12/2007 27/10/2007 08/09/2007 WPI 21/07/2007 02/06/2007 14/04/2007 24/02/2007 06/01/07 Key rates Key rates 14 12 Repo 10 8 6 4 2 0 Other key macro indicators Fiscal deficit Government borrowings Credit growth Deposit growth GDP Rupee QUESTIONS ?? Thank You.