EXERCISES Exercise 16-1
advertisement

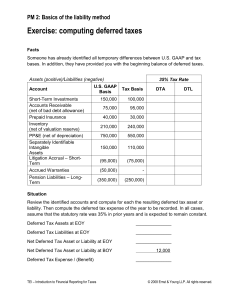
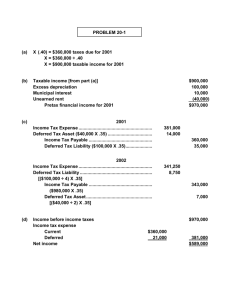
EXERCISES Exercise 16-1 Requirement 1 Since taxable income is less than pretax accounting income, a future taxable amount will occur when the temporary difference reverses. This means a deferred tax liability should be recorded to reflect the future tax consequences of the temporary difference. Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax liability ([$400,000 - 250,000] x 35%) Income tax payable ($250,000 x 35%) 140,000 52,500 87,500 As a result, net income is $260,000: Pretax accounting income Income tax expense Net income $400,000 140,000 $260,000 Requirement 2 In its balance sheet, Alvis will report the $52,500 deferred tax liability among either its current or long-term liabilities depending on the cause of the temporary difference and the $87,500 income tax payable as a current liability. Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-15 Exercise 16-2 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset ($300,000 x 40%) Income tax payable (given) 830,000 120,000 950,000 Exercise 16-3 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset ([$1 million x 40%] - $435,000) Income tax payable ($75 million x 40%) © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-16 30,035,000 35,000 30,000,000 Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-8 ($ in millions) December 31 2009 Depreciable asset (net): Accounting basis Tax basis TEMPORARY DIFFERENCE $80 (20) 80 (25) 5 Tax rate 2010 $60 (20) 55 (33) $ 5 13 40% DEFERRED TAX LIABILITY $ 2 ↑ ↑ originating differences © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-22 2011 $40 (20) 22 (15) $18 (5) 2012 $20 (20) $0 7 (7) 0 $13 (13) $0 40% 40% $7.2 $ 5.2 ↑ 40% $0 ↑ reversing differences Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-9 D 1. Accrual of loss contingency, tax-deductible when paid. D 2. Newspaper subscriptions; taxable when received, recognized for financial reporting when earned. T 3. Prepaid rent, tax-deductible when paid. D 4. Accrued bond interest expense; tax-deductible when paid. T 5. Prepaid insurance, tax-deductible when paid. D 6. Unrealized loss from recording investments available for sale at fair value (tax-deductible when investments are sold). D 7. Bad debt expense; allowance method for financial reporting; direct write-off for tax purposes. D 8. Advance rent receipts on an operating lease (as the lessor), taxable when received. T 9. Straight-line depreciation for depreciation for tax purposes. D financial reporting; accelerated 10. Accrued expense for employee postretirement benefits; tax-deductible when subsequent payments are made. Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-23 Exercise 16-10 1. Liability – loss contingency 2. Liability – subscriptions 3. Prepaid rent 4. Accrued bond interest payable 5. Prepaid insurance 6. Unrealized loss on investments (shareholders’ equity account) 7. Allowance for uncollectible accounts; and thus accounts receivable (net) 8. Liability – unearned rent 9. Accumulated depreciation; and thus depreciable assets (net) 10. Liability – postretirement benefits © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-24 Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-11 Requirement 1 ($ in thousands) Current Year 2009 Pretax accounting income Non-temporary difference: Municipal bond interest Temporary difference: Depreciation 300 Taxable income (income tax return) 250 Enacted tax rate Tax payable currently Deferred tax liability 40% 100 Future Taxable Amounts (40) (10) 10 40% 4 ↓ Deferred tax liability: Ending balance (balance currently needed) Less: beginning balance Change needed to achieve desired balance Journal entry at the end of 2009 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax liability (determined above) Income tax payable (determined above) $4 0 $4 104 4 100 Requirement 2 ($ in thousands) Pretax income Income tax expense Net income Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 $300 (104) $196 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-25 Exercise 16-17 Requirement 1 ($ in millions) Income tax expense (to balance)................................................ Deferred tax asset ($25 million x 40%) ....................................... Deferred tax liability ($80 million x 40%) .............................. Income tax payable ($145 million x 40%)............................... 80 10 32 58 Requirement 2 ($ in millions) Pretax income Income tax expense Net income © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-32 $200 (80) $120 Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-20 Requirement 1 ($ in thousands) Current Year 2009 Pretax accounting income Non-temporary difference: Municipal bond interest Temporary differences: Depreciation Warranty expense 977 Taxable income (income tax return) 900 Enacted tax rate Tax payable currently Deferred tax liability Deferred tax asset 40% 360 Future Taxable Amounts Future Deductible Amounts (32) (55) 10 85 (10) 40% 40% 34 (4) ↓ ↓ Deferred tax liability Ending balances (balances currently needed): Less: beginning balances: Change needed to achieve desired balances Journal entry at the end of 2009 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset (determined above) Deferred tax liability (determined above) Income tax payable (determined above) $34 (12) $22 Deferred tax asset $ 4 (0) $4 378 4 22 360 Requirement 2 ($ in thousands) Pretax income Income tax expense Net income Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 $ 977 (378) $599 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-35