EXERCISES
advertisement

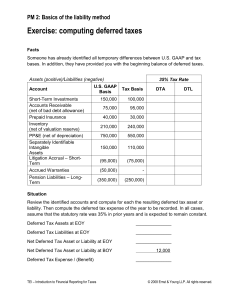
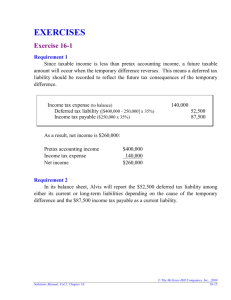
EXERCISES Exercise 16-1 Requirement 1 Since taxable income is less than pretax accounting income, a future taxable amount will occur when the temporary difference reverses. This means a deferred tax liability should be recorded to reflect the future tax consequences of the temporary difference. Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax liability ([$400,000 - 250,000] x 35%) Income tax payable ($250,000 x 35%) 140,000 52,500 87,500 As a result, net income is $260,000: Pretax accounting income Income tax expense Net income $400,000 140,000 $260,000 Requirement 2 In its balance sheet, Alvis will report the $52,500 deferred tax liability among either its current or long-term liabilities depending on the cause of the temporary difference and the $87,500 income tax payable as a current liability. Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-15 Exercise 16-2 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset ($300,000 x 40%) Income tax payable (given) 830,000 120,000 950,000 Exercise 16-3 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset ([$1 million x 40%] - $435,000) Income tax payable ($75 million x 40%) © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-16 30,035,000 35,000 30,000,000 Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-4 Requirement 1 ($ in millions) Current Future Year Deductible 2009 Amounts Temporary difference: Taxable income Enacted tax rate Tax payable currently Deferred tax asset (70) 180 40% 72 40% (28) ↓ Deferred tax asset: Ending balance (balance currently needed) Less: beginning balance ($75 x 40%) Change needed to achieve desired balance $ 28 (30) $( 2) Journal entry at the end of 2009 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset (determined above) Income tax payable (determined above) 74 2 72 Requirement 2 ($ in millions) Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset (determined above) Income tax payable (determined above) 74 Income tax expense Valuation allowance – deferred tax asset (1/2 x $28) 14 2 72 14 Of course, these two entries can be combined. Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-17 Exercise 16-8 ($ in millions) December 31 2009 Depreciable asset (net): Accounting basis Tax basis TEMPORARY DIFFERENCE $80 (20) 80 (25) 5 Tax rate 2010 $60 (20) 55 (33) $ 5 13 40% DEFERRED TAX LIABILITY $ 2 ↑ ↑ originating differences © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-22 2011 $40 (20) 22 (15) $18 (5) 2012 $20 (20) $0 7 (7) 0 $13 (13) $0 40% 40% $7.2 $ 5.2 ↑ 40% $0 ↑ reversing differences Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-15 A deferred tax liability is established using the currently enacted tax rate for the year(s) a temporary difference is expected to reverse. In this case that rate was 40%. The change in the tax law in 2010 constitutes a change in estimate. The deferred tax liability is simply revised to reflect the new rate. ($ in millions) Income tax expense (to balance) ................................................ Deferred tax liability ($20 million x [40% – 30%]) ...................... Income tax payable ($30 million x 40%) ................................. 10 2 12 When a company revises a previous estimate, prior financial statements are not revised. No adjustment is made to existing accounts. A disclosure note should describe the effect of a change in estimate on income before extraordinary items, net income, and related per-share amounts for the current period. Exercise 16-16 Income tax expense (to balance) ................................................ 32,000 Deferred tax asset ($12,000 x 40%) ............................................ 4,800 Deferred tax liability ($77,000 x 40%) ................................... 30,800 Income tax payable ($15,000 x 40%)...................................... 6,000 Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-31 Exercise 16-17 Requirement 1 ($ in millions) Income tax expense (to balance)................................................ Deferred tax asset ($25 million x 40%) ....................................... Deferred tax liability ($80 million x 40%) .............................. Income tax payable ($145 million x 40%)............................... 80 10 32 58 Requirement 2 ($ in millions) Pretax income Income tax expense Net income © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-32 $200 (80) $120 Intermediate Accounting, 5e Exercise 16-20 Requirement 1 ($ in thousands) Current Year 2009 Pretax accounting income Non-temporary difference: Municipal bond interest Temporary differences: Depreciation Warranty expense 977 Taxable income (income tax return) 900 Enacted tax rate Tax payable currently Deferred tax liability Deferred tax asset 40% 360 Future Taxable Amounts Future Deductible Amounts (32) (55) 10 85 (10) 40% 40% 34 (4) ↓ ↓ Deferred tax liability Ending balances (balances currently needed): Less: beginning balances: Change needed to achieve desired balances Journal entry at the end of 2009 Income tax expense (to balance) Deferred tax asset (determined above) Deferred tax liability (determined above) Income tax payable (determined above) $34 (12) $22 Deferred tax asset $ 4 (0) $4 378 4 22 360 Requirement 2 ($ in thousands) Pretax income Income tax expense Net income Solutions Manual, Vol.2, Chapter 16 $ 977 (378) $599 © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., 2009 16-35