PDF of PPT
advertisement

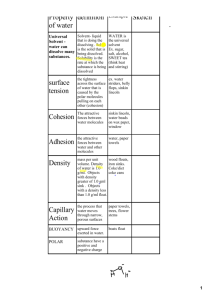
Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Important Word Roots Water • Old English w æterian "moisten” www.ces.fau.edu Polar • Latin polus "an end of an axis +/-­‐ www.personal.psu.edu Hydrogen Bonding • Hydro = w ater • Joined • *gen = a combining form meaning “that which produces” Polar, Non Polar and Amphipathic • Polar • Non-­‐Polar • Amphipathic • Combining Form • Experience www.marin.edu www.york.ac.uk Water ’s Life Supporting Properties The S heer Awesomeness that are Hydrogen Bonds 1. Water m olecules stick together. 2. Water has a strong resistance to change in temperature. 3. Frozen water floats. 4. Water is a common solvent for life. Proff. Zannie Dallara 1 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Water as the Solvent of Life – A solution is a liquid consisting of a homogeneous mixture of two or more substances. • The dissolving agent is the solvent. • The dissolved substance is the solute. – When water is the solvent, the result is an aqueous Salt crystal Sodium solution. ion in solution Na+ Na + Cl– Cl– Chloride ion in solution © 2 0 1 3 P earso n Ed u catio n , In c. How do A mphipathic Molecules Work in a world full of water? How about cell membranes? Important Word Roots Adhesion Cohesion Capillary Action • French adhésion = • French cohésion • Capillaris "of hair” = sticking sticking t o • Action = Move together Add to another Water sticking to substance water http://water.usgs.gov/edu/adhesion.html springtolife.weebly.com Proff. Zannie Dallara 2 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Important Word Roots Hydro • Water *Phylic • Loving *Phobic • Fearing A charge is what makes something hydrophilic Water’s Life-­‐S upporting Properties • The polarity (charge) of water molecules and the hydrogen bonding that results explain most of water’s life-­‐supporting properties. 1. Water molecules stick together. 2. Water has a strong resistance to c hange in temperature. 3. Frozen water floats. 4. Water is a common solvent for life www.ces.fau.edu Why do you care about water? www.kidsworldfun.com Proff. Zannie Dallara 3 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Water’s Life-­‐S upporting Properties – The polarity ( charge) of water molecules and the hydrogen b onding that results explain most of water’s life-­‐supporting p roperties. 1) Water molecules stick together. –AKA Cohesion http://water.usgs.gov/edu/adhesion.html 1) Water molecules stick together. Surface tension is the measure of how difficult i t i s to stretch or break the surface of a liquid. • Hydrogen b onds give water an u nusually h igh surface tension. Water’s Life-­‐S upporting Properties – The polarity ( charge) of water molecules and the hydrogen b onding that results explain most of water’s life-­‐supporting p roperties. 2) Water has a s trong resistance to change in temperature. –Hydrogen bonds build and reform easily Proff. Zannie Dallara 4 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Water’s Life-­‐S upporting Properties – The polarity (charge) of w ater molecules and the hydrogen bonding t hat results explain most of water’s life-­‐supporting properties. 3) Frozen water floats. • Cold = Moves slower = all hydrogen bonds met = each molecule is farther apart = less dense = floats Water’s Life-­‐S upporting Properties – The polarity (charge) of w ater molecules and the hydrogen bonding t hat results explain most of water’s life-­‐supporting properties. 4) Water is a common solvent for life. Water as the Solvent of Life – A solution is a liquid consisting of a homogeneous (looks the same throughout) mixture of two or more substances. • The dissolving agent is the solvent. • The dissolved substance is the solute. – When water is t he solvent, t he result is an aqueous solution. Salt crystal Sodium ion in solution Na + Na + – Cl Cl– Chloride ion in solution Proff. Zannie Dallara 5 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Other Molecules Detergent -­‐ ßHydrophilic ßHydrophobic www.york.ac.uk Other Molecules Oil ßHydrophilic ßHydrophobic wps.prenhall.com www.emec.com.eg Start W ith A ctivity 4 It needs to get in the freezer so we start it • Each group: 1. 1 t est t ube rack 2. 2 t est t ubes 3. Measure 10mls of ice cold water into each of your t est t ube 4. Label test t ubes (tape) 1. 2. 3. Label 1: Room Temp Label the Other: Freezer Label both with team name/symbol 5. Measure/record the height of the w ater in each t ube (in mm) 6. Put t hem in t he group rack • 1 will go in the freezer, 1 wont Proff. Zannie Dallara 6 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Build 3 Marshmallow W ater Molecule • Build 3 water molecules: – 3 Large M arshmallow = Oxygen • Label w ith atom and charge Oxygen -­‐ – 6 s mall marshmallows = H ydrogen – Label with atom and charge • • 6 t oothpicks = polar covalent bonds 3 strings = H bonds – D rop them and add their interactions – Get signed off www.science-­‐sparks.com Balloon • • • • • Beaker full of water Cork with tube Blow up balloon Tie it off Rub it on your head (20-­‐30 www.dailymail.co.uk sec) • Remember where the spot it rubbed was • Move close to stream of poring water Race! • Oil • Water • Strip of paper • Dip and race up the paper • Observe and t ry t o figure out w hat is happening Proff. Zannie Dallara 7 Bio 1 1 Lab#3: Water Lab Cutouts and lay out like it would look • Get me to sign off before gluing down Soda • Try to figure out the: – Solvent – Solute – Solution Capillary Action • Skinny tube • Touch tube to drop of water on desk • Shake out the water • Do that a couple times • Record observations • Answer questions Proff. Zannie Dallara 8