Nomenclature Notes
advertisement

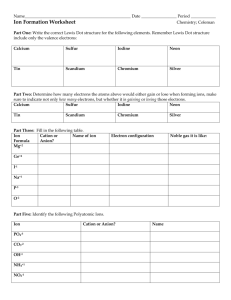
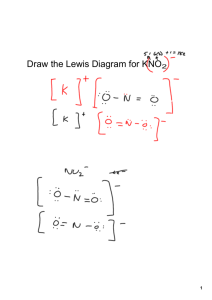
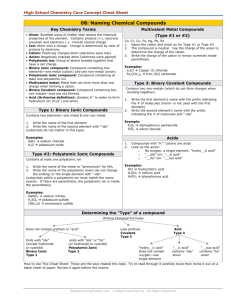
Unit Five Nomenclature Nomenclature Introduction Ionic bonds are formed when electrons are transferred between one metal and one non-metal element. Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared between two non-metal elements. Because each bond is different, scientists must have a specific way to name ionic compounds, and a different way to name covalent or metallic compounds. Today we will go through some examples of how we name ionic and covalent compounds and practice what we learn from the sample problems. Review 1.) Ions that have a positive charge are called 2.) Ions that have a negative charge are called 3.) Metals tend to 4.) Non-metals tend to become electrons to become electrons to Determine which naming system to use FIRST A. Stock System (Ionic Bonds) Molecules involved are metals and non metals. B. Molecular System (Covalent Bonds) Molecules involved are only nonmetals. A. Stock System (Ionic Bonds) If the compound is Binary – contains only 2 types of atoms. Ionic Compounds Write the full name of the 1st element. Write the name of the 2nd element, but change the ending to “ide” Put the two together and you have the correct name for the compound. Example: NaFSodium Fluoride Example One Write the proper name for NaCl. Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first: Step 3: Write the name of the element that is the anion second but change the ending to “ide” Step 4: Put step 2 and step 3 together and you have the correct name for the compound. Example Two Write the proper name for CaS. Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first: Step 3: Write the name of the element that is the anion second but change the ending to “ide” Step 4: Put step 2 and step 3 together and you have the correct name for the compound. Example Three Write the proper name for LiF. Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first: Step 3: Write the name of the element that is the anion second but change the ending to “ide” Step 4: Put step 2 and step 3 together and you have the correct name for the compound. Example Four Write the proper name for BeO. Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first: Step 3: Write the name of the element that is the anion second but change the ending to “ide” Step 4: Put step 2 and step 3 together and you have the correct name for the compound. Review Stock System (Ionic Bonds) Look over the flowchart to review the steps of forming an ionic bond. Use the notes and the flowchart to name the following ionic compounds. 1. AgCl 6. Cr2O3 2. NaO 7. CuO 3. PbO 8. K3N 4. CoCl2 9. NiS 5. SnF2 10. SrBr2 Review Stock System (Ionic Bonds) Look over the flowchart to review the steps of forming an ionic bond. Use the notes and the flowchart to name the following ionic compounds. 11. MgI2 16. NaI 12. BaCl2 17. CrF 13. BaS 18. BaO 14. VP 19. CaF2 15. HgS 20. NaCl 21. Ag2S A. Stock System If the compound contains a polyatomic ion. Steps for naming compounds with a polyatomic ion. 1.) Find the polyatomic ion on your list. Remember that most polyatomic ions are (-) so chances are it’s the second thing written. 2.) Name the first element or polyatomic ion, and then name the second element or polyatomic ion. 3.) If the second ion is not the polyatomic atom then be sure to add –ide. Examples: Na3PO4 – Sodium Phosphate NH4Cl- Ammonium Chloride Example One Write the proper name for Be(OH)2 1.) Find the polyatomic ion on your list. Remember that most polyatomic ions are (-) so chances are it’s the second thing written 2.) Name the first element or polyatomic ion, and then name the second element or polyatomic ion. If the second ion is not the polyatomic atom then be sure to add –ide. Example Two Write the proper name for Ca3(PO4)2 1.) Find the polyatomic ion on your list. Remember that most polyatomic ions are (-) so chances are it’s the second thing written 2.) Name the first element or polyatomic ion, and then name the second element or polyatomic ion. If the second ion is not the polyatomic atom then be sure to add –ide. Forming Ionic Compounds Ionic compounds always have an overall charge of zero Potassium + Oxygen= Criss-cross method Magnesium + Sulfur= Write the formula unit for when magnesium and nitrogen combine: Beryllium + Carbon= Aluminum + Phosphate= Potassium + Hydroxide= A. Stock System If the compound contains a transition metal (D-Block) You must include a Roman numeral that denotes the charge on the transition metal. For instance, Fe2+ is iron (II). Fe3+ is iron (III) Example: FeBr2 Iron (II) Bromide Example One Write the proper name for FeO. Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first : Step 3: Determine the charge of the cation- remember that the charges of the cation and the anion must balance out (equal zero). Write the charge of the cation in roman numerals in parenthesis after the cation’s symbol. Step 4: Write the name of the element that is the anion second. If the second ion is not a polyatomic ion then be sure to change the ending to “ide” Step 5: Put step 3 and step 4 together and you have the correct name for the compound. Example Two Write the proper name for CuSO3. Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first : Step 3: Determine the charge of the cation- remember that the charges of the cation and the anion must balance out (equal zero). Write the charge of the cation in roman numerals in parenthesis after the cation’s symbol. Step 4: Write the name of the element that is the anion second. If the second ion is not a polyatomic ion then be sure to change the ending to “ide” Step 5: Put step 3 and step 4 together and you have the correct name for the compound. Example Three Write the proper name for Pb(SO3)2 . Step 1: Determine the charge of the cation and anion in the compound. Which element has a positive charge and is a cation? Which element has a negative charge and is a anion? Step 2: Write the name of the element that is the cation first : Step 3: Determine the charge of the cation- remember that the charges of the cation and the anion must balance out (equal zero). Write the charge of the cation in roman numerals in parenthesis after the cation’s symbol. Step 4: Write the name of the element that is the anion second. If the second ion is not a polyatomic ion then be sure to change the ending to “ide” Step 5: Put step 3 and step 4 together and you have the correct name for the compound. B. Molecular System (Covalent Bonds) In order to name covalent or metallic compounds, you have to know the prefixes used to describe the numbers scientists use in Chemistry. 1.) Use prefixes to state how many atoms are present. 1=mono 6= hexa 2=di 7=hepts 3=tri 8=octa 4=tetra 9=nona 5=penta 10=deca * Mono is never used on the first atom written, only the second atom. 2.) Add the prefix to the name of the first element (unless there is only one atom). 3.) Add the prefix to the name of the second element. Drop the ending of the second atom written and add – IDE. Example One Write the proper name for CO2 Step 1: Determine how many atoms are in the first element in the compound Step 2: Determine what prefix this number represents Step 3: Add the prefix onto the front part of the elements name: Step 4: Determine how many atoms are in the second element in the compound: Step 5: Determine what prefix this number represents: Step 6: Add the prefix onto the front part of the elements name and add “ide” on to the end: Step 7: Add Step 3 and Step 6 together and you get: Example Two Write the proper name for Li2Be Step 1: Determine how many atoms are in the first element in the compound Step 2: Determine what prefix this number represents Step 3: Add the prefix onto the front part of the elements name: Step 4: Determine how many atoms are in the second element in the compound: Step 5: Determine what prefix this number represents: Step 6: Add the prefix onto the front part of the elements name and add “ide” on to the end: Step 7: Add Step 3 and Step 6 together and you get: Example Three Write the proper name for P2S3 Step 1: Determine how many atoms are in the first element in the compound Step 2: Determine what prefix this number represents Step 3: Add the prefix onto the front part of the elements name: NOTE: IF there is only ONE atom of the first element- you DO NOT add the prefix mono to it. This is the ONLY exception to the rule. Step 4: Determine how many atoms are in the second element in the compound: Step 5: Determine what prefix this number represents: Step 6: Add the prefix onto the front part of the elements name and add “ide” on to the end: Step 7: Add Step 3 and Step 6 together and you get: Review Stock System (Ionic Bonds) and Molecular System (Covalent Bonds) Look over the flowchart to review the steps of forming an ionic bond. Use the notes and the flowchart to name the following ionic compounds. How do you know which naming system to use? 1. P4O10 6. SF8 2. SeCl2 7. BCl3 3. NO 8. CoCO3 4. N2O 5. NO2 9. FePO4 10.Cu2S