Study Guide for Content Mastery - Teacher Edition
advertisement
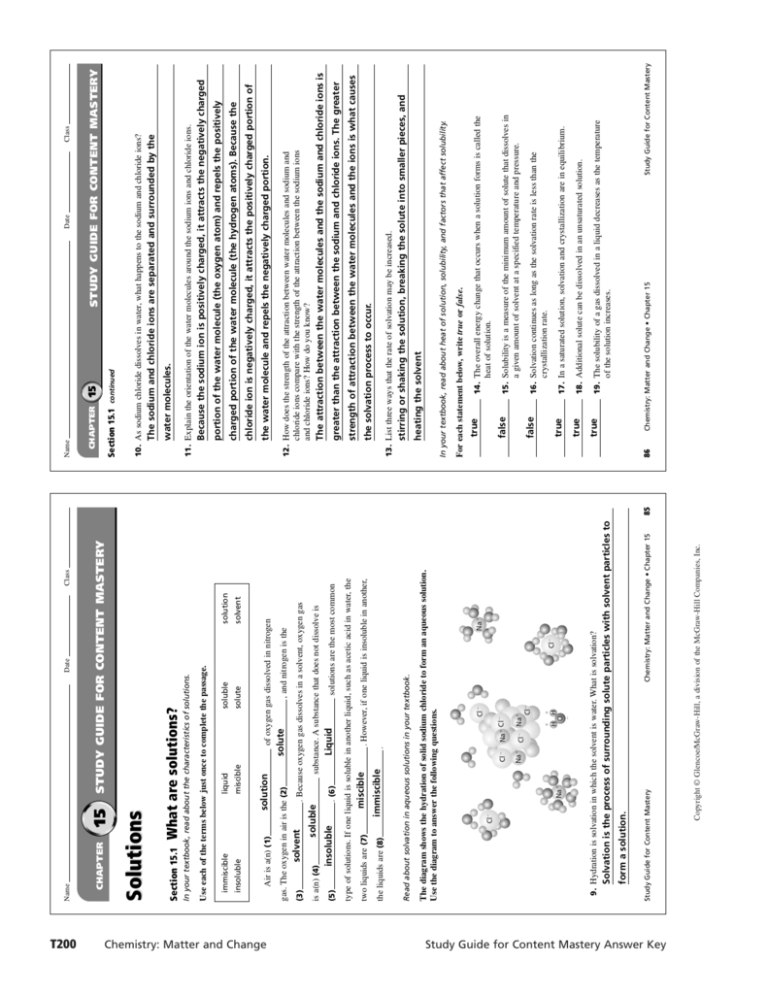
T200 Chemistry: Matter and Change Study Guide for Content Mastery Answer Key 15 Date What are solutions? miscible insoluble insoluble soluble solvent solvent solution , and nitrogen is the . (6) Liquid solutions are the most common substance. A substance that does not dissolve is . Because oxygen gas dissolves in a solvent, oxygen gas solute of oxygen gas dissolved in nitrogen solute soluble immiscible miscible . . However, if one liquid is insoluble in another, Na Na Cl H H O Na Cl Na Cl Cl Cl Na Chemistry: Matter and Change • Chapter 15 Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Study Guide for Content Mastery form a solution. Solvation is the process of surrounding solute particles with solvent particles to 9. Hydration is solvation in which the solvent is water. What is solvation? Cl Cl The diagram shows the hydration of solid sodium chloride to form an aqueous solution. Use the diagram to answer the following questions. Read about solvation in aqueous solutions in your textbook. the liquids are (8) two liquids are (7) type of solutions. If one liquid is soluble in another liquid, such as acetic acid in water, the (5) is a(n) (4) (3) gas. The oxygen in air is the (2) solution liquid immiscible Use each of the terms below just once to complete the passage. Air is a(n) (1) Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY In your textbook, read about the characteristics of solutions. Section 15.1 Solutions CHAPTER Name 85 15 Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY Date 86 of the solution increases. Study Guide for Content Mastery 19. The solubility of a gas dissolved in a liquid decreases as the temperature 18. Additional solute can be dissolved in an unsaturated solution. 17. In a saturated solution, solvation and crystallization are in equilibrium. crystallization rate. 16. Solvation continues as long as the solvation rate is less than the a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature and pressure. 15. Solubility is a measure of the minimum amount of solute that dissolves in heat of solution. 14. The overall energy change that occurs when a solution forms is called the Chemistry: Matter and Change • Chapter 15 true true true false false true For each statement below, write true or false. In your textbook, read about heat of solution, solubility, and factors that affect solubility. heating the solvent stirring or shaking the solution, breaking the solute into smaller pieces, and 13. List three ways that the rate of solvation may be increased. the solvation process to occur. strength of attraction between the water molecules and the ions is what causes greater than the attraction between the sodium and chloride ions. The greater The attraction between the water molecules and the sodium and chloride ions is chloride ions compare with the strength of the attraction between the sodium ions and chloride ions? How do you know? 12. How does the strength of the attraction between water molecules and sodium and the water molecule and repels the negatively charged portion. chloride ion is negatively charged, it attracts the positively charged portion of charged portion of the water molecule (the hydrogen atoms). Because the portion of the water molecule (the oxygen atom) and repels the positively Because the sodium ion is positively charged, it attracts the negatively charged 11. Explain the orientation of the water molecules around the sodium ions and chloride ions. water molecules. The sodium and chloride ions are separated and surrounded by the 10. As sodium chloride dissolves in water, what happens to the sodium and chloride ions? Section 15.1 continued CHAPTER Name Study Guide for Content Mastery Answer Key Chemistry: Matter and Change T201 Class 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.0 1 2 3 4 Mass (g) 400.0 300.0 200.0 100.0 H2O 8 7 6 5 Solution b. 2.9% b. Solution 2 c. Solution 3 c. 3.0% 15.0 9.0 5.0 2.0 b. 1.9% c. 2.0% b. Solution 6 c. Solution 7 d. Solution 8 d. 22% d. Solution 4 d. 33% Study Guide for Content Mastery Chemistry: Matter and Change • Chapter 15 to the volume needed to calculate molarity. 85.0 mL 1 L/1000 mL 10. Write the expression needed to convert the volume of the solution given in the problem 9. In what unit must the volume of the solution be expressed to calculate molarity? liter 8. In what unit must the amount of the solute be expressed to calculate molarity? mole Molarity moles of solute/liters of solution 7. Write the equation that is used to calculate molarity. 6. What is the volume of the solution? 85.0 mL 5. What is the mass of the solute? 7.54 g An 85.0-mL aqueous solution contains 7.54 g iron(II) chloride (FeCl2). Calculate the molarity of the solution. Read the following problem and then answer the questions. In your textbook, read about molarity and preparing molar solutions. a. Solution 5 4. Which of the following solutions is the most concentrated? a. 0.2% 100.0 100.0 100.0 100.0 H2O Volume (mL) C2H5OH 3. What is the percent by volume of C2H5OH in Solution 5? a. Solution 1 2. Which of the following solutions is the most dilute? a. 0.030% 1. What is the percent by mass of NaCl in solution 1? NaCl Solution Data related to aqueous solutions of sodium chloride (NaCl) and aqueous solutions of ethanol (C2H5OH) are provided in the table below. Use the table to answer the following questions. Circle the letter of the choice that best answers the question. 87 STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY Solution Concentration 15 Date In your textbook, read about expressing concentration and using percent to describe concentration. Section 15.2 CHAPTER Name Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. 15 Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY Date 88 Chemistry: Matter and Change • Chapter 15 Study Guide for Content Mastery mHCl 100 g 0.336 33.6 g HCl mH O 100 g 33.6 66.4 g H2O 2 33.6 g HCl 1 mol HCl/36.46 g HCl 0.922 mol HCl 66.4 g H2O 1 mol H2O/18.02 g H2O 3.68 mol H2O XHCl nHCl/nHCl nH O 0.922 mol/0.922 mol 3.68 mol 0.922 mol/4.60 mol 2 XHCl 0.200 mass. Show all your work. 17. Calculate the mole fraction of HCl in an aqueous solution that contains 33.6% HCl by total number of moles of solute and solvent. Mole fraction is the ratio of the number of moles of solute in a solution to the 16. What is mole fraction? 15.4 g NaBr 1 mol NaBr/102.89 g NaBr 0.150 mol NaBr 125 g H2O 1 Kg/1000 g 0.125 kg H2O Molality moles of solute/kilograms of solvent 0.150 mol NaBr/0.125 kg H2O 1.20 mol NaBr/kg H2O Molality 1.20m NaBr(aq) of water. Show all your work. 15. Calculate the molality of a solution of 15.4 g sodium bromide (NaBr) dissolved in 125 g 1 liter of solution. of solvent. Molarity is a measure of the number of moles of solute dissolved in Molality is a measure of the number of moles of solute dissolved in 1 kilogram 14. How does molality differ from molarity? Answer the following questions. In your textbook, read about molality and mole fractions. 85 mL H2O 1L/1000 mL 0.085 L H2O 7.54 g FeCl2 1 mol FeCl2/126.75 g FeCl2 0.0595 mol FeCl2 Molarity moles of solute/liters of solution 0.0595 mol FeCl2/0.0850 L H2O Molarity 0.700 mol FeCl2/L H2O 0.700M FeCl2 (aq) 13. Calculate the molarity of the solution. Show all your work. 7.54 g FeCl2 1 mol FeCl2/126.75 g FeCl2 12. Write the expression used to calculate the amount of solute. the molar mass of FeCl2 amount of solute needed to calculate molarity? 11. What quantity must be used to convert the mass of the solute given in the problem to the Section 15.2 continued CHAPTER Name T202 Chemistry: Matter and Change Study Guide for Content Mastery Answer Key Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY Colligative Properties of Solutions 15 Date 1.05 1.03 1.06 1.12 1.0m C2H5OH(aq) 1.0m HCl(aq) 1.0m NaCl(aq) 2.0m NaCl(aq) 102.1 101.0 101.0 100.5 Boiling Point (°C) 7.4 3.7 3.7 1.8 Freezing Point (°C) Column A Column B 10. A colligative property of solutions semipermeable membrane solution side g. pure solvent side f. e. osmosis Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Chemistry: Matter and Change • Chapter 15 9. The side from which more water molecules cross the pass through but not others 8. The barrier with tiny pores that allow some particles to semipermeable membrane from the area of higher solvent concentration to the area of lower solvent concentration d. sugar molecules 89 c. semipermeable membrane 6. The side that exerts osmotic pressure 7. The diffusion of the solvent particles across the b. water molecules a. osmotic pressure 5. Can cross the semipermeable membrane 4. Cannot cross the semipermeable membrane Study Guide for Content Mastery a g c e f b d Suppose that in a simple system, a semipermeable membrane is used to separate a sucrose-water solution from its pure solvent, water. Match the descriptions of the system in Column A with the terms in Column B. Colligative properties are independent of the type of electrolytes in solution. of ions in solution from the 1.0m HCl(aq) and 1.0m NaCl(aq) solutions? 3. What can you conclude about the relationship between colligative properties and the type Colligative properties depend on the number of electrolytes in solution. number of ions in solution from the 1.0m NaCl(aq) and 2.0m NaCl(aq) solutions? 2. What can you conclude about the relationship between colligative properties and the boiling point and freezing point 1. Which properties in the table are colligative properties? Density (g/L) Solution Use the table to answer the following questions. In your textbook, read about electrolytes and colligative properties, vapor pressure lowering, boiling point elevation, and freezing point depression. Section 15.3 CHAPTER Name 10. Colloids demonstrate the Tyndall effect. 9. Stirring an electrolyte into a colloid stabilizes the colloid. polar or charged atomic groups on their surfaces. 8. Dispersed particles in a colloid do not tend to settle out because they have medium with the dispersed particles. 7. Brownian motion results from the collisions of particles of the dispersion 6. In an aerosol, the dispersing medium is a liquid. 5. Whipped cream is an example of a foam. 4. A solid emulsion consists of a liquid dispersed in a solid. 3. A colloid can be separated by filtration. 2. The most abundant substance in a colloid is the dispersion medium. left undisturbed. 90 Chemistry: Matter and Change • Chapter 15 17. Scatter light 16. Lower vapor pressure 15. Pass through standard filter paper 14. Settle out if undisturbed 13. More than 1000 nm in diameter 12. Between 1 nm and 1000 nm in diameter 11. Less than 1 nm in diameter Characteristics of Particles ✔ ✔ ✔ Colloid ✔ ✔ ✔ Solution ✔ ✔ ✔ Study Guide for Content Mastery Suspension The table below lists the characteristics of particles in colloids, solutions, and suspensions. Place a check in the column of each mixture whose particles have a particular characteristic. true false true true false true true false true 1. A solution is a mixture containing particles that settle out of the mixture if For each statement below, write true or false. false Class STUDY GUIDE FOR CONTENT MASTERY Date Heterogeneous Solutions 15 In your textbook, read about suspensions and colloids. Section 15.4 CHAPTER Name