Chemistry Solutions Worksheet: Molarity, Dilution, Molality
advertisement
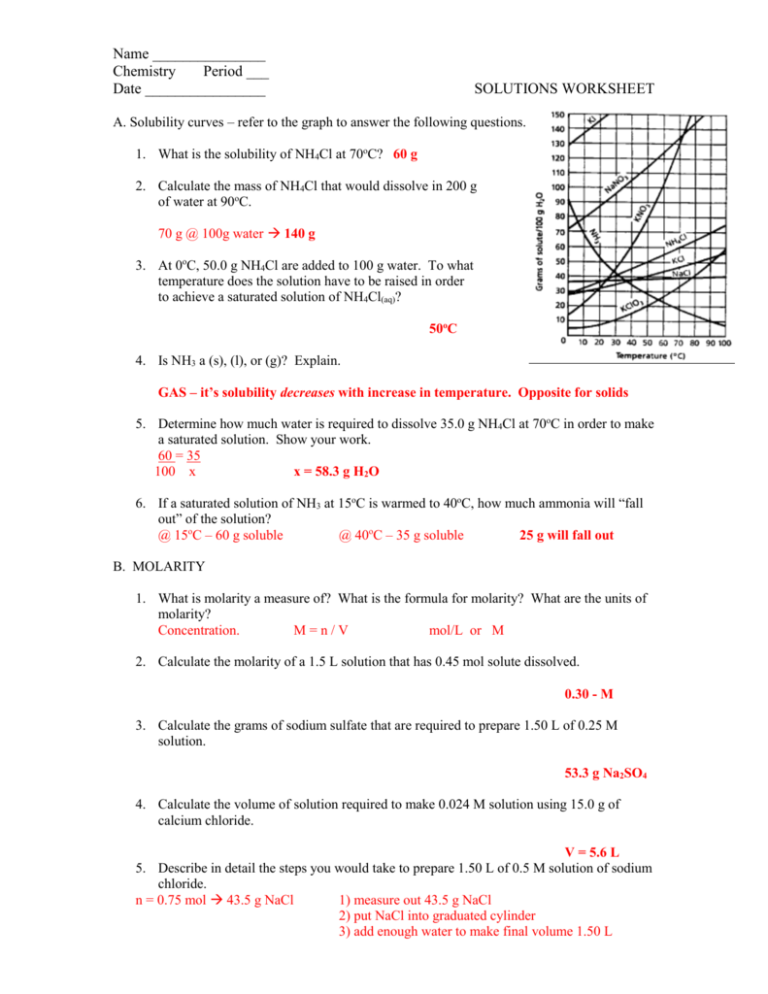
Name _______________ Chemistry Period ___ Date ________________ SOLUTIONS WORKSHEET A. Solubility curves – refer to the graph to answer the following questions. 1. What is the solubility of NH4Cl at 70oC? 60 g 2. Calculate the mass of NH4Cl that would dissolve in 200 g of water at 90oC. 70 g @ 100g water 140 g 3. At 0oC, 50.0 g NH4Cl are added to 100 g water. To what temperature does the solution have to be raised in order to achieve a saturated solution of NH4Cl(aq)? 50oC 4. Is NH3 a (s), (l), or (g)? Explain. GAS – it’s solubility decreases with increase in temperature. Opposite for solids 5. Determine how much water is required to dissolve 35.0 g NH4Cl at 70oC in order to make a saturated solution. Show your work. 60 = 35 100 x x = 58.3 g H2O 6. If a saturated solution of NH3 at 15oC is warmed to 40oC, how much ammonia will “fall out” of the solution? @ 15oC – 60 g soluble @ 40oC – 35 g soluble 25 g will fall out B. MOLARITY 1. What is molarity a measure of? What is the formula for molarity? What are the units of molarity? Concentration. M=n/V mol/L or M 2. Calculate the molarity of a 1.5 L solution that has 0.45 mol solute dissolved. 0.30 - M 3. Calculate the grams of sodium sulfate that are required to prepare 1.50 L of 0.25 M solution. 53.3 g Na2SO4 4. Calculate the volume of solution required to make 0.024 M solution using 15.0 g of calcium chloride. V = 5.6 L 5. Describe in detail the steps you would take to prepare 1.50 L of 0.5 M solution of sodium chloride. n = 0.75 mol 43.5 g NaCl 1) measure out 43.5 g NaCl 2) put NaCl into graduated cylinder 3) add enough water to make final volume 1.50 L C. DILUTION 1. Define dilute and concentrated. Dilute – little solute compared to a lot of solvent Concentrated - a lot of solute compared to little solvent 2. Calculate the volume of 12 M HCl(aq) needed to make 300 ml of 1.5 M HCl(aq). V = 37.5 ml 3. Calculate the new molarity that results when 25.2 ml of 15 M HNO3 is diluted to a final volume of 1.0 L. M = 0.378 M D. MOLALITY & FREEZING POINT DEPRESSION 1. What is molality a measure of? What is the formula for molality? What are the units of molality? Moles of solute per kilogram of solvent. m = n/m mol/kg or m 2. Calculate the molality of a solution made from 0.50 g CO2 in 652 g water. 0.017 m 3. Calculate the mass of glucose needed to make a 0.238 m solution in 1000 g water. 43 g C6H12O6 4. What is meant by freezing point depression? What is the formula? The freezing point of a solution is lower than the pure solvent (formula not needed for test) 5. Determine the temperature at which the following solution will freeze: 50.0 g sucrose (C12H22O11) in 200 g water m = 0.73 mol/kg T = -1.36oC 6. Determine the temperature at which the following solution will freeze: 0.328 mol naphthalene in 250 g benzene m = 1.312 mol/kg SOLVENT benzene water T = -0.93oC FREEZING POINT (oC) 5.5 0.0 kf 4.90 1.86











