Modeling EC-Coupling and Contraction
advertisement
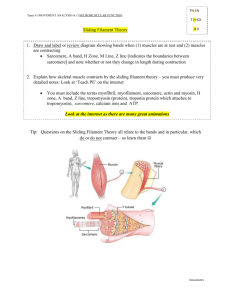
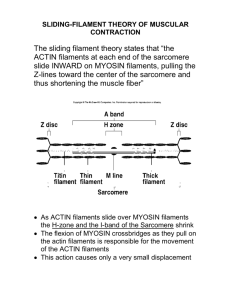
Bioeng 6460 Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity Modeling of EC-Coupling and Contraction Frank B. Sachse fs@cvrti.utah.edu CVRTI Overview • Quiz • Excitation-Contraction Coupling • Anatomy • Cross Bridge Binding • Coupling • Experimental Studies • Outline of Experiment CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 2 Phases of Sarcomere Calcium Handling Begin of contraction Ca release Triggering Relaxation Ca uptake Filling A: Actin M: Myosin Z: Z-Disc SL: Sarcolemma TTS: Transversal tubules SPR: Sarcoplasmic Reticulum Ca2+ Release Ca2+ Uptake CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 3 Calcium Handling and EC-Coupling Transversal Tubule Cell Membrane S a rc op R e ti c l a s m i c u lu m Troponin Mi NCX: ATP: RyR: PLB: CVRTI h toc on io dr n Sodium-calcium exchanger Ionic pump driven by ATP-hydrolysis Calcium channel (ryanodine receptor) Phospholamban (Bers, Nature Insight Review Articles, 2002, modified) Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 4 Quiz: Role of Mitochondria Work in pairs of 2 Time 5 min Mitochondria take part of the cellular calcium handling. Why were they not considered in electrophysiological models? CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 5 Sarcomeres in Cardiac Muscle (Fawcett & McNutt 69) Sarcoplasmic reticulum Terminal cisternae Z-Disc Mitochondrion Transversal tubuli Sarcoplasmic reticulum Dyad CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 6 Sarcomeres in Skeletal Muscle (Fawcett & McNutt 69) Sarcolemma Transversal tubules I-Band Sarcoplasmic reticulum A-Band Terminal cisternae Z-Disc Triad CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 7 Electron Micrograph of Sarcomere in Striated Muscle A - anisotrop I - isotrop (Modified from Lodish et al., Molecular Cell Biology, 2004) CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 8 Myofilaments (Modified from Lodish et al., Molecular Cell Biology, 2004) CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 9 Proteins of Sarcomere 2 !m CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 10 EC-Coupling: Involved Proteins 2 µm Actin Myosin Actin TnC TnI Actin TnT Tm Head-to-tail overlap CVRTI Tn: Troponin Tm: Tropomyosin A: Actin Z: Z-Disk (adapted from Gordon et al. 2001) Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 11 Force Development: Sliding Filament Theory Cellular force development by sliding myofilaments (Huxley 1957), i.e. actin and myosin, located in sarcomere Attachment of myosin heads to actin Detachment Filament sliding Spanning of myosin heads CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 12 Force Development: Sliding Filament Theory http://www.sci.sdsu.edu/movies/actin_myosin.html CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 13 Actin-Myosin Interaction A ADP Pi Actin Adenosine diphosphate Phosphate M ATP Myosin Adenosine triphosphate (Bers, Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Cardiac Contractile Force, 1991, modified) CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 14 EC-Coupling Rest small Ca2+ Stimulus Contraction Ca2+ release from SR High concentration of intracellular Ca2+ high Ca2+ Force development Contraction of sarcomere/cell CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 15 Contraction of Myocyte by Electrical Stimulation Microscopic imaging of isolated ventricular cell from guinea pig http://www-ang.kfunigraz.ac.at/˜schaffer CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 16 Measurement of Force Development in Single Cell Myocyte glued between glass plates Force transmission to measurement system Stimulator Fluid at body temperature Mechanical Fixation (variable strain) Glass plates Measured force per myocyte: 0.15-6.0 µN CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 17 Measurement Techniques Permeabilization of sarcolemma/skinning of myocytes by saponin or Triton X-100 Direct control of intracellular concentrations of ions, drugs etc. [ ] [ Ca2+ = Ca2+ i ] o ! Transillumination of myocyte or muscle strands with laser light Diffraction pattern ~ sarcomere length CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 18 Sarcomere Length Measurement via Laser Diffraction (Figures from Lecarpentier et al., Real-Time Kinetics of Sarcomere Relaxation by Laser Diffraction, AJP, 1985) More information: http://muscle.ucsd.edu/musintro/diffraction.shtml CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 19 Mathematical Modeling of Myofilament Sliding (Huxley) f A+ M " A#M g Number of bzgl. myosins notungekoppeltem bound to actin Myosin A + M: Anzahl von Actin Number of myosins bound actin gekoppelt) A # M: Anzahl Querbrücken (Actin /to Myosin f,g: Ratenkonstanten fürbinding Bindung Ablösung Rate constants for andbzw. unbinding d [A # M] = f(Max[A # M] # [A # M]) # g[A # M] dt Max[A # M]: Maximale Anzahl of anmyosin Querbrücken Maximal number proteins bound to actin filament CVRTI Bioeng 6460: Electrophysiology and Bioelectricity - Page 20