sliding-filament theory of muscular contraction
advertisement

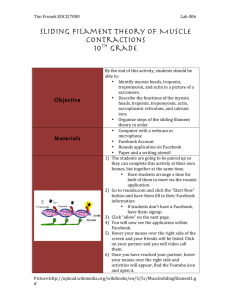
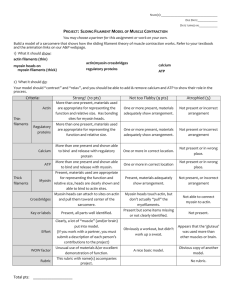
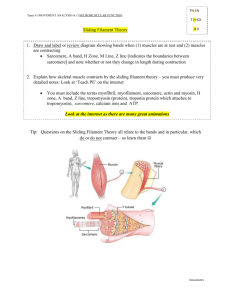
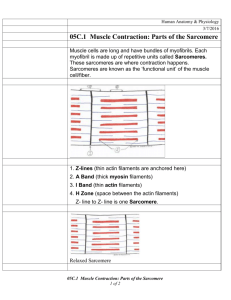
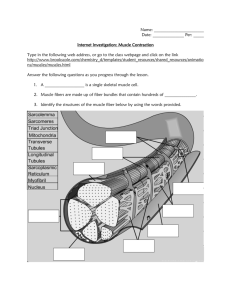
SLIDING-FILAMENT THEORY OF MUSCULAR CONTRACTION The sliding filament theory states that “the ACTIN filaments at each end of the sarcomere slide INWARD on MYOSIN filaments, pulling the Z-lines toward the center of the sarcomere and thus shortening the muscle fiber” As ACTIN filaments slide over MYOSIN filaments the H-zone and the I-band of the Sarcomere shrink The flexion of MYOSIN crossbridges as they pull on the actin filaments is responsible for the movement of the ACTIN filaments This action causes only a very small displacement Very rapid repeated flexions must occur in many crossbridges throughout the entire muscle for measurable movement to occur before crossbridges can flex they must first attach to the actin filament when the sarcoplasmic reticulum releases calcium ions, they bind with troponin, a protein situated at regular intervals along the actin filament this causes a shift in another protein tropomyosin, which runs along the length of the ACTIN filament in the groove of the double helix the MYOSIN crossbridge attaches much more rapidly to the ACTIN filament allowing flexion to occur TYPES OF MUSCLE ACTION Concentric actions Occur when tension developed in crossbridges is enough to overcome any resistance to shortening Isometric Contraction Occur when the tension in the crossbridges equals the resistance to shortening and muscle length remains the same Eccentric Contractions Occur when the tension developed in the crossbridges is less then the resistance and the muscle lengthens despite contact between the MYOSIN crossbridge heads and ACTIN filaments Understanding the Process- Stimulus to Contraction Using a visual representation DESCRIBE YOUR UNDERSTANDING of the process we go through in order to contract a muscle cell. Use the following terms in your description and illustrations: Stimulus Brain Spinal Cord Motor Neuron Axon Motor Endplate Neuromuscular junction Ach-Acetylcholine Ca+ Myofibril Sarcomere Z-line A-band I-band H-zone M-line Actin Filament Myosin Filament Troponin Tropomyosin Binding Sites