PEDIATRIC CARDIOLOGY
advertisement
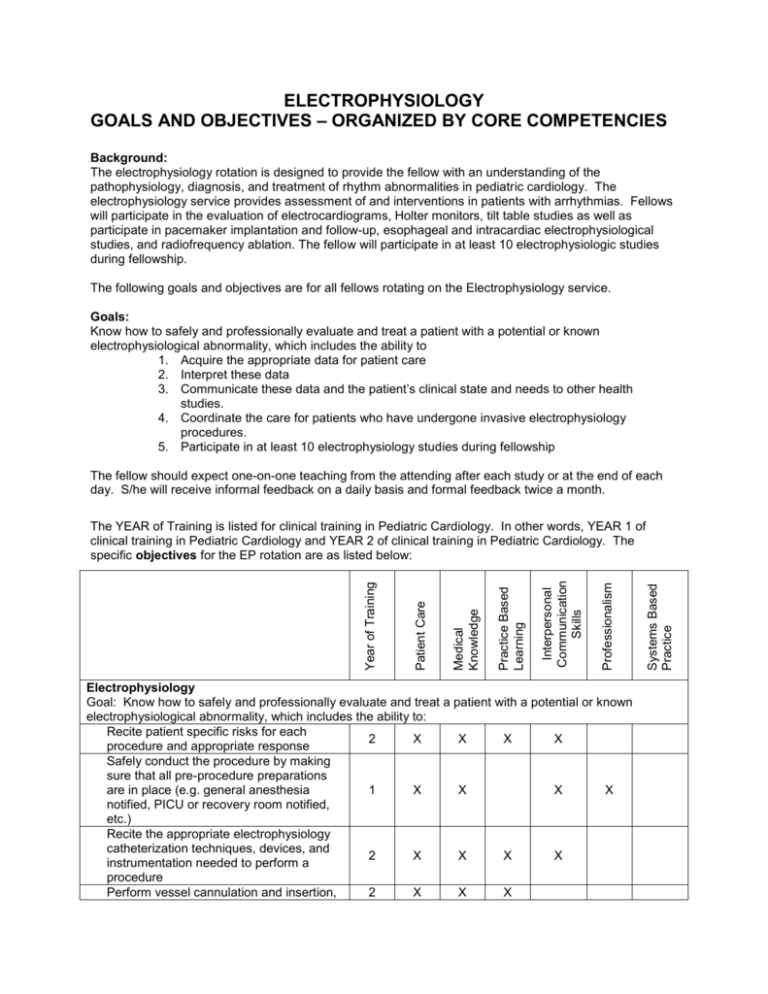
ELECTROPHYSIOLOGY GOALS AND OBJECTIVES – ORGANIZED BY CORE COMPETENCIES Background: The electrophysiology rotation is designed to provide the fellow with an understanding of the pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment of rhythm abnormalities in pediatric cardiology. The electrophysiology service provides assessment of and interventions in patients with arrhythmias. Fellows will participate in the evaluation of electrocardiograms, Holter monitors, tilt table studies as well as participate in pacemaker implantation and follow-up, esophageal and intracardiac electrophysiological studies, and radiofrequency ablation. The fellow will participate in at least 10 electrophysiologic studies during fellowship. The following goals and objectives are for all fellows rotating on the Electrophysiology service. Goals: Know how to safely and professionally evaluate and treat a patient with a potential or known electrophysiological abnormality, which includes the ability to 1. Acquire the appropriate data for patient care 2. Interpret these data 3. Communicate these data and the patient’s clinical state and needs to other health studies. 4. Coordinate the care for patients who have undergone invasive electrophysiology procedures. 5. Participate in at least 10 electrophysiology studies during fellowship The fellow should expect one-on-one teaching from the attending after each study or at the end of each day. S/he will receive informal feedback on a daily basis and formal feedback twice a month. Electrophysiology Goal: Know how to safely and professionally evaluate and treat a patient with a potential or known electrophysiological abnormality, which includes the ability to: Recite patient specific risks for each 2 X X X X procedure and appropriate response Safely conduct the procedure by making sure that all pre-procedure preparations are in place (e.g. general anesthesia 1 X X X X notified, PICU or recovery room notified, etc.) Recite the appropriate electrophysiology catheterization techniques, devices, and 2 X X X X instrumentation needed to perform a procedure Perform vessel cannulation and insertion, 2 X X X Systems Based Practice Professionalism Interpersonal Communication Skills Practice Based Learning Medical Knowledge Patient Care Year of Training The YEAR of Training is listed for clinical training in Pediatric Cardiology. In other words, YEAR 1 of clinical training in Pediatric Cardiology and YEAR 2 of clinical training in Pediatric Cardiology. The specific objectives for the EP rotation are as listed below: 1 X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X 2 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X X Systems Based Practice X Professionalism Interpersonal Communication Skills X Practice Based Learning 1 Medical Knowledge Patient Care Interpret rhythm strips showing all forms of AV block and SAN block, atrial flutter; atrial fibrillation; long R-P SVT; short R-P SVT; wide complex tachycardia; paced patients having failure to capture, over sensing, and undersensing; early beats; bradycardia; pauses; and bigeminal rhythms Recite indications for referring patient for catheter ablation of arrhythmias Coordinate the care for patients that have undergone invasive electrophysiological study Compose a plan for an electrophysiology procedure by performing pre-procedure evaluation consisting of history and physical examination and review of all past medical data and past procedure data (previous study reports, ECHO, Holter, Treadmill, EKGs, etc) Relate this plan to the electrophysiology attending prior to the procedure Participate in obtaining consent with the attending for all invasive electrophysiology ablation (published indications) Interpret temporary epicardial wire Year of Training positioning and removal of catheters Characterize the anatomy underlying the arrhythmia studied in the electrophysiological procedure Communicate and provide appropriate post-procedure care Relate how to supervise and perform adenosine termination of SVT Interpret normal ECG’s by age at the end of the first rotation and ECG’s in the presence of common congenital heart defects, myocarditis, ischemia, pericarditis, electrolyte disorders, common metabolic disorders; preexcitation; antiarrhythmic drug effect; channelopathies, and bundle branch block by the end of the 2nd rotation Interpret transtelephonic ECG’s X X X X X X X 2 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 2 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X X 1 X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X X 1 X X X X X X X Systems Based Practice X Professionalism Interpersonal Communication Skills X Practice Based Learning Patient Care 2 Medical Knowledge Year of Training electrograms in post-operative patients, including rhythms showing junctional tachycardia, various forms of AV block, atrial flutter, and non-conducted PAC’s at the end of the first rotation Interpret all Holters and Treadmill Exercise Tests Apply the pharmacokinetics of procainamide, disopyramide, quinidine, mexiletine, lidocaine, flecainide, propranolol, metoprolol, atenolol, amiodarone, sotalol, verapamil, diltiazem, adenosine, digoxin, and dofetilide in their clinical use Interpret chest roentgenograms of patients with implanted devices Participate in electrical mapping and radiofrequency ablation Interrogate, interpret, and perform simple programming of implanted devices manufactured by Medtronic, Guidant, and St. Jude proficiently under supervision Order event recorders; unattached, attached, and implanted appropriately Discuss the causes and treatment of syncope Recognize possible etiologies of and screen for risk of sudden death Describe the indications for implantation of pacemakers and ICDs Identify indications for and perform cardioversion and defibrillation Discuss the most common arrhythmias in patients following congenital heart surgery Discuss performance of head-up tilt table testing Describe the conduction system anatomy and common variants Identify indications for pacemaker use and recite theory and function Discuss exercise physiology and protocol rationale, risks of exercise testing for patient groups and appropriate response Communicate compassionately and Professionalism Systems Based Practice Interpersonal Communication Skills X X X 1 X X X X X X 1 X X X X X X Practice Based Learning Patient Care 1 Medical Knowledge Year of Training effectively with patients and parents Utilize medical literature and apply to patient care Utilize health system to optimize patient care Coordinate care for patients; achieved in part by: o Writing preliminary procedure note o Writing post-procedure orders o relating the results of the study and status of the patient to those to whom care will be transferred, which will include other fellows and the residents o assisting on all invasive E.P. cases (except during clinic times) and participate as appropriate based on complexity of case o Monitoring patient recovery following the procedure by doing a postcatheterization evaluation on the day of the procedure before leaving the hospital o Communicating important findings/management changes to referring physician promptly o writing follow-up notes in patient chart o Coordinating follow-up care with referring physician and other health care professionals o Making a discharge plan o reviewing with the attending their interpretations of rhythm strips, Holters, Treadmill Exercise Tests, and epicardial electrograms and placing the interpretations in the medical record before leaving the hospital o Completing a draft of the procedure note and conclusions by the end of the day on which procedure is performed