The Kidney - TeachLine
advertisement

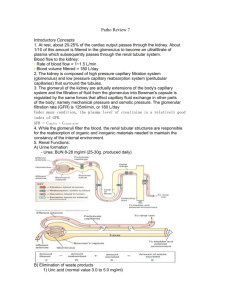
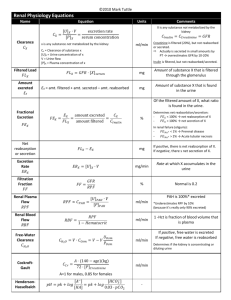
The Kidneys Practical questions Functions of the kidneys • Regulation of water and inorganic ion balance. • Removal of metabolic waste products from the blood and their excretion in the urine. • Removal of foreign chemicals from the blood and their excretion in the urine. • Gluconeogenesis. • Production of hormones/enzymes (Renin, Erythropoietin…) 3 main renal processes 1. Glomerular filtration. ()סינון 2. Tubular secretion. ()הפרשה 3. Tubular reabsorption. ()ספיגה מחדש excretion = filtration - reabsorbtion + secretion Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR) • The volume of fluid filtered from the glomerulus into Bowman’s space per unit time. • Affected by: – – Net filtration pressure. Permeability of the corpuscular membrane. – Surface area available for filtration. • Regulated by nerve and hormones. • In a 70Kg person: GFR of ~180L/day. Filtered Load • The total amount of substance (S) filtered into Bowman’s space per time unit. • Filtered Load of S = GFR x [S]P Example: GFR = 180L/day [Na+]P = 3.5g/L What is the Na+ filtered load? GFR x [Na+]P = 180L/day x 3.5g/L = 630g/day Filtered Load (continue) • Once the filtered load is known, it can be compared to the amount excreted. • Indication of net tubular reabsorption or net secretion. Example: Na+ filtered load = 630g/day Na+ excreted = 3.2g/day % reabsorbed = 99.5% Renal clearance • The volume of plasma completely cleared of a specific substance (S) per unit time. Mass of S excreted / time [S]P (example: if the mass of urea excreted in the urine is 5 g/hour, and the plasma concentration of urea is 5 g/L, then the urea clearance is 1 L/h) • A useful way of quantifying renal function. Renal clearance Renal clearance = GFR (Inulin, Creatinine) Renal clearance > GFR No net reabsorption, secretion, metabolism Net secretion (K+, H+…) Renal clearance < GFR (Glucose, Amino-acids…) Net reabsorption Kidney function assessment Urine and blood test of a 65 years old male gives the following results: – Amount of urine collected over 24 hours: 4.32 L – Plasma creatinine: 0.03 mg/mL – Urine creatinine: 0.3 mg/mL – Plasma K+: 0.005 mmol/mL – Urine K+: 0.120 mmol/mL What is this man’s GFR? Assessing GFR Urine volume per day: 4.32L Plasma creatinine: 0.03 mg/mL Urine creatinine: 0.3 mg/mL + Plasma K : 0.005 mmol/mL + Urine K : 0.120 mmol/mL Mass of Cr excreted / time [Cr ]U × V / t = CCr = [Cr ]P [Cr ]P CCr = renal clearance of Creatinine (L/day) [Cr]U = Creatinine concentration in the urine V/t = the volume of urine collected per time unit [Cr]P = Creatinine concentration in the plasma 0.3mg / mL × 4.32 L / day CCr = = 43.2 L / day 0.03mg / mL So, his GFR is 4 times lower than normal (180 L/ day)… What is the renal clearance of K+? CK + Urine volume per day: 4.32L Plasma creatinine: 0.03 mg/mL Urine creatinine: 0.3 mg/mL + Plasma K : 0.005 mmol/mL + Urine K : 0.120 mmol/mL 0.120mmol / mL × 4.32 L / day = = 103.7 L / day 0.005mmol / mL CK+ > GFR K+ is net secreted Urine volume per day: 4.32L Plasma creatinine: 0.03 mg/mL Urine creatinine: 0.3 mg/mL + Plasma K : 0.005 mmol/mL + Urine K : 0.120 mmol/mL What is the renal secretion rate of K+ in this patient? K+ excretion = K+ filtered - K+ reabsorbed + K+ secreted Computing the difference between how much is excreted and how much is filtered gives net secretion rate How much K+ is filtered? Filtered Load = GFR × [K ]P = + 43200mL/day × 0.005mmol / mL = 216mmol / day What is the renal reabsorption rate of K+ in this patient? (continue) Urine volume per day: 4.32L Plasma creatinine: 0.03 mg/mL Urine creatinine: 0.3 mg/mL + Plasma K : 0.005 mmol/mL + Urine K : 0.120 mmol/mL K+ excretion = K+ filtered - K+ reabsorbed + K+ secreted K+ secreted = K+ excreted 0.120 mmol/mL x 4320 mL/day = 518 mmol/day K+ filtered 216 mmol/day = 302 mmol/day 58% of the total K+ excretion is by secretion K+ in the Kidney Reabsorption: • Not regulated • In the proximal tube and thick ascending tube of the loop of Henle • Absorption of 90% of K+. Secretion: • Coupled to Na+ reabsorption. • Via K+ channels in the apical membrane of the cortical collecting duct. • Regulated by the activity of the of the Na/K ATPase and by aldosterone activity. Another example A patient complains about a general feeling of sickness (nausa, fatigue, frequent urination…). You decide to check his kidneys function. You are about to do blood and urine test and you decide to use Inulin as a way to assess GFR. Test results [In]P = 0.5 mg/mL V (per min) = 1.1 mL [In]U = 60 mg/mL [Glu]P = 0.4 mg/mL [Glu]U = 1.5 mg/mL Assessing GFR [In]P = 0.5 mg/mL V (per min) = 1.1 mL [In]U = 60 mg/mL [Glu]P = 0.4 mg/mL [Glu]U = 1.5 mg/mL Mass of In excreted / time [ In]U × V / t CIn = = [ In]P [ In]P 60mg / mL × 1.1mL / min CIn = = 132mL / min = 190 L / day 0.5mg / mL So his GFR is 190 L/day – normal, more or less What about his glucose level? What is the glucose renal clearance? [In]P = 0.5 mg/mL V (per min) = 1.1 mL [In]U = 60 mg/mL [Glu]P = 0.4 mg/mL [Glu]U = 1.5 mg/mL CGlu Mass of Glu excreted / time [Glu ]U × V / t = = [Glu ]P [Glu ]P CGlu 1.5mg / mL × 1.1mL / min = = 4.125mL / min = 5.9 L / day 0.4mg / mL CGlu << GFR Glucose is net reabsorbed What is the glucose reabsorption rate? [In]P = 0.5 mg/mL V (per min) = 1.1 mL [In]U = 60 mg/mL [Glu]P = 0.4 mg/mL [Glu]U = 1.5 mg/mL Glu excretion = Glu filtered - Glu reabsorbed + Glu secreted What is the glucose filtration load? Filtered Load = GFR × [Glu]P = 132mL/min × 0.4mg / mL = 53mg / min 1.5 mg/mL x 1.1 mL/min = 53 mg/min - Glu reabsorbed 1.7 mg/min = 53 mg/min - Glu reabsorbed Glu reabsorbed = 51.3 mg/min (97% of the glucose that was filtered) Glucose reabsorption in the kidney Proximal convoluted tubule Proximal straight tubule