European Exploration and Colonization PDF
advertisement
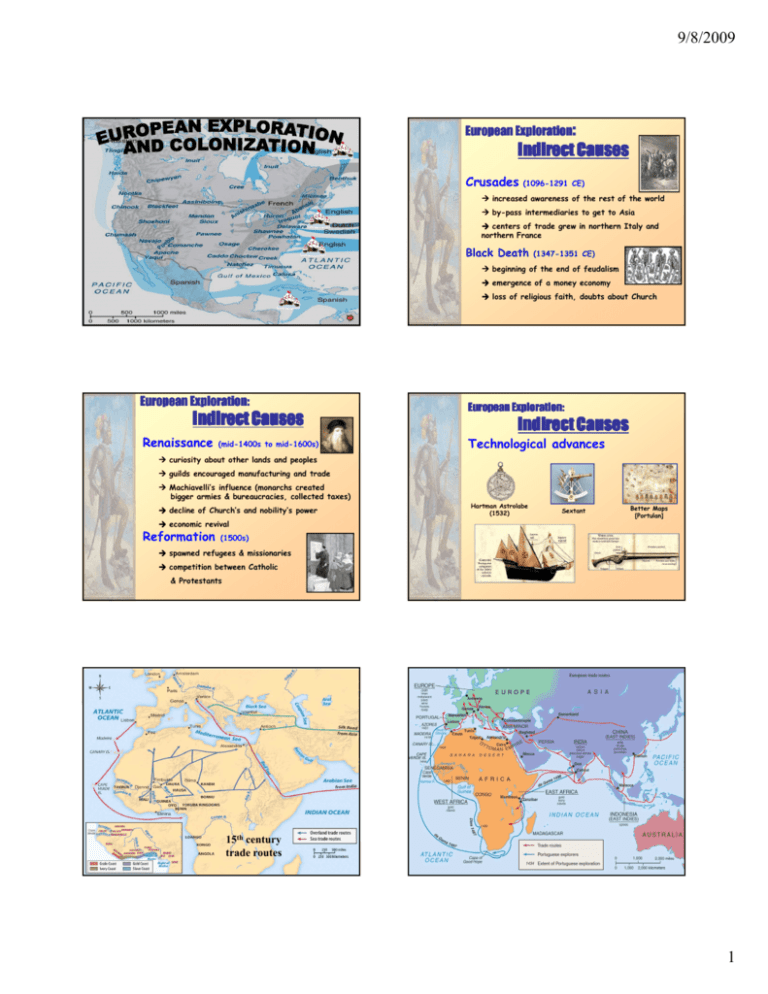
9/8/2009 European Exploration: Indirect Causes Crusades (1096-1291 CE) increased awareness of the rest of the world by-pass intermediaries to get to Asia centers of trade grew in northern Italy and northern France Black Death (1347-1351 CE) beginning of the end of feudalism emergence of a money economy loss of religious faith, doubts about Church European movement European Exploration: Indirect Causes Renaissance (mid-1400s to mid-1600s) European Exploration: Indirect Causes Technological advances curiosity about other lands and peoples guilds encouraged manufacturing and trade Machiavelli’s influence (monarchs created bigger armies & bureaucracies, collected taxes) decline of Church’s and nobility’s power Hartman Astrolabe (1532) Sextant Better Maps [Portulan] economic revival Reformation (1500s) spawned refugees & missionaries competition between Catholic & Protestants European trade routes 15th century trade routes 1 9/8/2009 European Exploration: A Map of the Known World, pre-- 1492 pre Direct Causes • Political: Become a world power through gaining wealth and land. (GLORY) • Economic: Search for new trade routes with direct access to Asian/African luxury goods would enrich individuals and their nations (GOLD) • Religious: spread Christianity and weaken Middle Eastern Muslims. (GOD) *** The 3 motives reinforce each other *** explorers 2 9/8/2009 F/I War 1750 EFFECTS •Europeans reach and settle Americas •Expanded knowledge of world geography •Growth of trade, mercantilism and capitalism •Indian conflicts over land and impact of disease on Indian populations •Introduction of the institution of slavery •Columbian Exchange Columbian Exchange or the transfer of goods involved 3 continents, Americas, Europe and Africa * Squash * Turkey * Cocoa * Peanut * Avocado * Pumpkin * Pineapple * Tomato * Peppers * Tobacco * Cassava * Vanilla * Sweet Potatoes * Quinine * POTATO * MAIZE * Syphillis EuropeanColonization Colonization European • Once the New World is discovered, four European countries begin competing for control of North America and the world…. * Olive * Coffee Beans * Banana * Onion * Turnip * Honeybee * Grape * Peach * Sugar Cane * Citrus Fruits * Pear * Wheat * Cattle * Sheep * Pig * Flu * Typhus * Measles * Diptheria * Whooping Cough * Rice * Barley * Oats * HORSE * Smallpox * Malaria • Spain • France • The Netherland • England Path of Conquest & Colonization Explorers • Spanish first to pursue colonization • Start in Caribbean, then Central and South America—most important was conquest of Aztecs by Cortez (1521) and Incas by Pizzaro (1531) • First permanent colonies in what will become United States are founded by Spain – St. Augustine (Florida) is founded (1565) to protect Spanish treasure fleets European Colonial Empire Permanent Settlers 3 9/8/2009 Columbus’ Four Voyages Explorers Sailing From Hispaniola • Ponce de Leon • est. colony at Puerto Rico • sailed north looking for Fountain of Youth • discovered Florida for Spain (1508) • de Coronado • went north from Mexico, up Colorado River, saw Grand Canyon (1540) • de Soto • through Florida into Carolinas and west to the Mississippi River (1541) First Spanish Conquests: The Aztecs First Spanish Conquests: The Incas Cortes conquered Aztec Empire (1519) Pizarro conquered Incan Empire (1532) vs. vs. Montezuma II Hernando Cortés Francisco Pizarro Atahualpa 4 9/8/2009 Treasures from the Americas! The Colonial Class System Peninsulares Spanish ancestory Creoles Spanish and Black mixture. Mestizos Spanish and Indian mixture Mulattos White American and Black mixture Native Indians 1. Spanish practice of securing an adequate and cheap labor supply = FEUDALISM Black Slaves The Influence of the Colonial Catholic Church – “granted” to deserving subjects of the King 2. Conquistador controlled Indian populations – required Indians to pay tribute from their lands – Indians often rendered personal services as well Our Lady of Guadalupe Guadalajara Cathedral 3. In return the conquistador was obligated to – protect his wards – instruct them in the Christian faith – defend their right to live off the land Spanish Mission Father Bartolomé de Las Casas •Believed Native Americans had been treated harshly by the Spanish. •Indians could be educated and converted to Christianized. •Believed Indian culture was advanced as European but in different ways. Eventually decimated Indian population. With support of de Las Casas the King restricted the system with the New Laws (1542) Missionaries put in charge of settlements, not conquistadors (1573) religious conversions continued under new cultural assimilation system forced labor 5 9/8/2009 The Spanish Empire by the 1600’s • Overworked Native population • King Philip II spent too much on religious wars • Lack of industrial development • High costs of empire huge area, distant outposts, “sea dogs” plundered • Defeat of the Spanish Armada (1588) by England French Explorers • French settle Quebec (1608) & Montreal (1642) and what would become Canada – drawn by fishing & whaling Newfoundland – took control of St. Lawrence River & access to interior – developed fur trade with help of “courier de bois” • Cartier reached St. Lawrence River claimed Eastern Canada for France (1535) • Samuel de Champlain “Father of New France” est. Quebec (1st permanent French colony) est. settlements and explored Maine, Montreal & Nova Scotia - 1608 French Explorers • Marquette Jesuit missionary assigned to Quebec mastered several Native languages ventured down much of Mississippi River, charting its course (1673) • De La Salle charted much of the Great Lakes (1679) claimed Louisiana and MI River Basin for France (1682-84) 6 9/8/2009 Why didn’t France dominate North America? Alliance with Hurons pitted them against other tribes Fur traders discouraged immigration (deforestation) Natives Natives skeptical of Jesuits Louis XIV’s large military drafts French peasants had stronger land rights Huguenots barred from New France • Commercial focus fur & slave trades Dutch West India Co. • Sparse settlements Fort Orange New Netherland Connecticut River Delaware River • Allied with Iroquois Dutch Exploration & Settlement • Henry Hudson • searched for Northwest Passage • claimed Hudson River • settlers established New Netherlands • New Amsterdam (est. 1609) • part of the Dutch global trade system • culturally & linguistically diverse • autocratic business-oriented 7








