Seasons and Earth's Distance to the Sun Environmental Science
advertisement

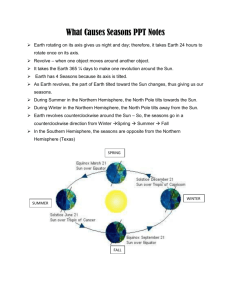
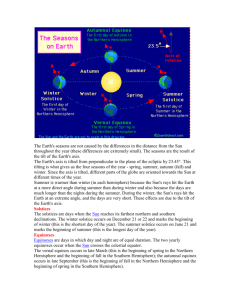
Seasons and Earth’s Distance to the Sun Environmental Science Name: _______________________________________________ Period: _____ Date: ______________ Essential question: How do we have seasons on Earth? What do you think? Many people believe that Earth is closer to the Sun in the summer and that is why it is hotter. And, likewise, they think Earth is farthest from the Sun in the winter. Although this idea makes sense, it is incorrect. It is true that Earth’s orbit is not a perfect circle. It is a elliptical ( Kepler’s 1st law). Yes! The orbit of Earth around the Sun is elliptical or oval shaped. During part of the year, Earth is closer to the Sun, called Perihelion, than at other times. However, in the Northern Hemisphere, we are having winter when Earth is closest to the Sun and summer when it is farthest away! Compared with how far away the Sun is, this change in Earth's distance throughout the year does not make much difference to our weather. Earth’s tilt on its axis and its revolution around the barycenter of the Solar System causes seasons. Not the distance! Earth's axis is an imaginary pole going right through the center of Earth from "top" to "bottom." Earth spins or rotate around this pole, making one complete turn each day. That is why we have day and night, and why every part of Earth's surface gets some of each. Earth has seasons because its axis doesn't stand up straight. Long, long ago, when Earth was young, it is thought that something big hit Earth and knocked it off-kilter. So instead of rotating with its axis straight up and down, it leans over a bit. By the way, that big thing that hit Earth is called Theia. It also blasted a big hole the surface. That big hit sent a huge amount of dust and rubble into orbit. Most scientists think that rubble, in time, became our Moon. http://spaceplace.nasa.gov/seasons/ Remember! We have season because of Earth’s tilt and its revolution around the barycenter of the Solar system and not the distance to the Sun. The uneven distribution of sunlight is the main reason why we have season. This happens because Earth is tilted at 23.5 degrees on its axis. When the Northern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun it is winter and Summer in Australia, which is in the Southern hemisphere. It is summer in June in the Northern Hemisphere because the Sun's rays hit that part of Earth more directly than at any other time of the year. It is winter in December in the Northern Hemisphere, because that is when it is the South Pole's turn to be tilted toward the Sun. http://vnatsci.ltu.edu/s_schneider/astro/wbstla2k/mytalk/seasons.shtml http://www.pa.msu.edu/sciencet/ask_st/110691.html Clarifying questions: 1. What do many people believe about seasons and the distance of Earth to the Sun? Is this correct? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 2. What is the shape of Earth’s orbit? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 3. What does it mean by Perihelion? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 4. What kind of season do we have in the Northern hemisphere when Earth is farthest from the Sun? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 5. Does Earth’s distance to the sun throughout the year has any effect with our seasons? Why? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 6. What is Earth’s axis? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 7. Why do we have day and night? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 8. Why is Earth tilted? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 9. What do you call the thing that hit Earth and caused it to tilt? _____________________________________________________________________________________ 10. How did the moon form? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 11. What cause Earth’s seasons? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 12. What is season in the Northern hemisphere when it is tilted away from the Sun? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 13. What is season in the Northern hemisphere when it is tilted towards the Sun? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 14. What is the season when the Sun's rays hit that part of Earth more directly? _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 15. Why is it winter in December-January-February? Think! _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Completion: Get the answers from the charts on the front page. 16. The Northern hemisphere points towards the Sun, causing ____________days and __________ direct sunlight. The Northern hemisphere points away the Sun, causing ____________ days and _________ direct sunlight. 17. Write the dates of the following: Get the answers from the charts on the front page. a. Autumnal equinox ________________________________________________ b. Winter solstice ____________________________________________________ c. Vernal equinox ____________________________________________________ d. Summer solstice ___________________________________________________ Remember: Spring: Time Forward 1 Hour; Fall: Time Backward 1 Hour Spring forward, Fall back During DST, clocks are turned forward an hour, effectively moving an hour of daylight from the morning to the evening. United States European Union Year DST Begins at 2 a.m. DST Ends at 2 a.m. Summertime period begins at 1 a.m. UT Summertime period ends at 1 a.m. UT 2009 March 8 November 1 March 29 October 25 2010 March 14 November 7 March 28 October 31 2011 March 13 November 6 March 27 October 30 2012 March 11 November 4 March 25 October 28 2013 March 10 November 3 March 31 October 27 2014 March 9 November 2 March 30 October 26 2015 March 8 November 1 March 29 October 25 March 13 November 6 March 27 October 30 2016 US calculator valid 1976-2099; EU 1996-2099. Change with up/down key.