SEASONS - Aarohi Life Education
advertisement

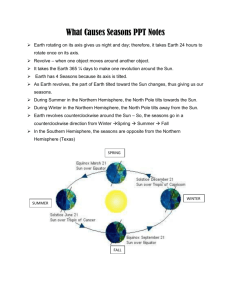
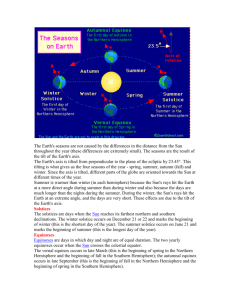
SEASONS In some places, such as deserts or rainforests, the weather is much the same all year round. However in other places, for example northern Europe, we expect a certain kind of weather at certain times of the year. In winter, the days may often be cold or stormy, while summer days can be warm and sunny. When the weather changes regularly throughout the year like this, the changes are known asseasons. Some places have just two seasons, a wet one and a dry one, other places have four: spring, summer, autumn and winter. Seasons occur because the Earth is tilted at an angle on its axis. As the Earth moves around the sun during the year, different parts of the Earth are tilted towards the sun at different times. In the Northern Hemisphere, when the North Pole tilts away from the sun, the sun is low in the sky and days are short, bringing the season we call winter. When the North Pole tilts towards the sun though, more light and heat reaches the Northern Hemisphere as the sun is high in the sky and days are long. This change brings what we know as summer. Between these two seasons are spring and autumn, where the region becomes gradually warmer and colder as it tilts towards or away from the sun respectively These movements of the Earth all contribute to give the four seasons we experience in Great Britain and the rest of the Northern Hemisphere. However, because of the way the seasons work, the opposite sides of the equator experience opposite seasons as the Earth moves round the sun each year. For example winter happens in Europe and the United States when it is summer on the opposite side of the world, in Australia.