CHAPTER REVIEW
CHAPTER
REVIEW
5
5
REVIEW ANSWERS
Using Key Terms
USING KEY TERMS
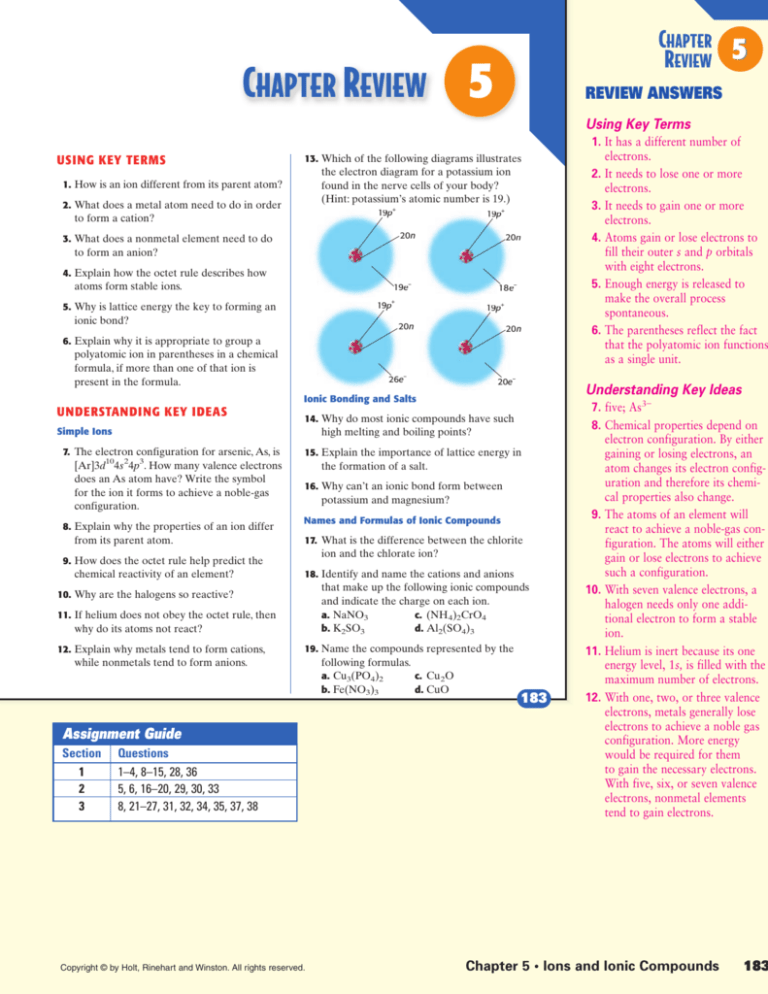
13. Which of the following diagrams illustrates
the electron diagram for a potassium ion
found in the nerve cells of your body?
(Hint: potassium’s atomic number is 19.)
1. How is an ion different from its parent atom?
2. What does a metal atom need to do in order
+
19p
9
to form a cation?
+
19p
9
20n
3. What does a nonmetal element need to do
20n
to form an anion?
4. Explain how the octet rule describes how
atoms form stable ions.
–
18e–
19e
+
19p
9
5. Why is lattice energy the key to forming an
ionic bond?
19p
9 +
20n
20n
6. Explain why it is appropriate to group a
polyatomic ion in parentheses in a chemical
formula, if more than one of that ion is
present in the formula.
UNDERSTANDING KEY IDEAS
26e–
Understanding Key Ideas
Ionic Bonding and Salts
14. Why do most ionic compounds have such
Simple Ions
high melting and boiling points?
7. The electron configuration for arsenic, As, is
[Ar]3d104s 24p3. How many valence electrons
does an As atom have? Write the symbol
for the ion it forms to achieve a noble-gas
configuration.
8. Explain why the properties of an ion differ
from its parent atom.
15. Explain the importance of lattice energy in
the formation of a salt.
16. Why can’t an ionic bond form between
potassium and magnesium?
Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds
17. What is the difference between the chlorite
ion and the chlorate ion?
9. How does the octet rule help predict the
chemical reactivity of an element?
18. Identify and name the cations and anions
that make up the following ionic compounds
and indicate the charge on each ion.
a. NaNO3
c. (NH 4)2CrO4
b. K2SO3
d. Al2(SO4)3
10. Why are the halogens so reactive?
11. If helium does not obey the octet rule, then
why do its atoms not react?
12. Explain why metals tend to form cations,
19. Name the compounds represented by the
while nonmetals tend to form anions.
Assignment Guide
Section
1
2
3
20e–
Questions
1–4, 8–15, 28, 36
5, 6, 16–20, 29, 30, 33
8, 21–27, 31, 32, 34, 35, 37, 38
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
following formulas.
a. Cu3(PO4)2
c. Cu 2O
b. Fe(NO3)3
d. CuO
1. It has a different number of
electrons.
2. It needs to lose one or more
electrons.
3. It needs to gain one or more
electrons.
4. Atoms gain or lose electrons to
fill their outer s and p orbitals
with eight electrons.
5. Enough energy is released to
make the overall process
spontaneous.
6. The parentheses reflect the fact
that the polyatomic ion functions
as a single unit.
183
7. five; As3−
8. Chemical properties depend on
electron configuration. By either
gaining or losing electrons, an
atom changes its electron configuration and therefore its chemical properties also change.
9. The atoms of an element will
react to achieve a noble-gas configuration. The atoms will either
gain or lose electrons to achieve
such a configuration.
10. With seven valence electrons, a
halogen needs only one additional electron to form a stable
ion.
11. Helium is inert because its one
energy level, 1s, is filled with the
maximum number of electrons.
12. With one, two, or three valence
electrons, metals generally lose
electrons to achieve a noble gas
configuration. More energy
would be required for them
to gain the necessary electrons.
With five, six, or seven valence
electrons, nonmetal elements
tend to gain electrons.
Chapter 5 • Ions and Ionic Compounds
183
REVIEW ANSWERS
continued
PROBLEM
SOLVINLG
SKIL
24. Write formulas for the following polyatomic
ions.
a. cyanide
b. sulfate
20. Write formulas for the following
13. b. 18 electrons
14. The electrical attraction between
cations and anions in the crystal
lattice is strong. Therefore, a
high temperature is required
to break down the lattice and
change the solid crystal into
a liquid. Ions still have strong
attractions in the liquid state.
Therefore, an even higher temperature is required to separate
the ions into a gas.
15. Lattice energy provides enough
energy to drive all the endothermic steps, such as the formation
of cations, that are involved in
the formation of a crystal lattice.
16. Both are metals and form
cations. An ionic bond forms
only between ions of opposite
charges.
17. The chlorate ion, ClO−3, contains
three O atoms while the chlorite
ion, ClO−2, contains only two
O atoms.
18. a. sodium (Na+) and nitrate
(NO−3)
b. potassium (K+) and sulfite
(SO23−)
c. ammonium (NH +4) and chromate (CrO24−)
d. aluminum (Al3+) and sulfate
(SO24−)
19. a. copper(II) phosphate
b. iron(III) nitrate
c. copper(I) oxide
d. copper(II) oxide
20. a. Li2SO4
b. Sr(NO3)2
c. NH4CH3COO
d. Ti2(SO4)3
21. barium; Cl −; chromium(III); fluoride; Mn2+; O2−; a. MnCl2;
b. CrF3; c. BaO
22. a. peroxide
b. chromate
c. ammonium
d. carbonate
184
PRACTICE PROBLEMS
ionic compounds.
a. lithium sulfate
b. strontium nitrate
c. ammonium acetate
d. titanium(III) sulfate
25. Determine the number of valence electrons
21. Complete the table below, and then use it to
answer the questions that follow.
Element
Ion
Barium
Ba2+
Name of ion
Chlorine
chloride
Fluorine
F
Oxygen
oxide
Write the formula for the following
substances:
a. manganese chloride
b. chromium(III) fluoride
c. barium oxide
23. Complete the table below.
I
Rb
18 ions?
29. Compound B has lower melting and boiling
points than compound A does. At the same
temperature, compound B vaporizes faster
and to a greater extent than compound A. If
only one of these compounds is ionic, which
one would you expect it to be? Why?
WRITING
SKILLS
30. A number of homes have “hard water,”
22. Name the following polyatomic ions.
2−
+
a. O2
c. NH 4
2−
2−
b. CrO4
d. CO3
Be
27. Why can’t sodium gain a positive charge by
ALTERNATIVE ASSESSMENT
MIXED REVIEW
Ion
26. Why are most metals found in nature as
28. Why are there no rules for naming Group
manganese(II)
S
CRITICAL THINKING
acquiring a proton in its nucleus?
−
Manganese
Atom
in the following atoms.
a. Al
c. Si
b. Rb
d. F
ores and not as pure metals?
Cr3+
Chromium
c. nitrite
d. permanganate
Noble-gas configuration of ion
which, as you learned in the Start-Up
Activity, does not produce as many soap
suds as water that contains fewer ions. Such
homes often have water conditioners that
remove the ions from the water, making it
“softer” and more likely to produce soapsuds.
Research how such water softeners operate
by checking the Internet or by contacting a
company that sells such devices. Design an
experiment to test the effectiveness of the
softener in removing ions from water.
O
CONCEPT MAPPING
Sr
31. Use the following terms to create a concept
F
map: atoms, valence electrons, ions, cations,
anions, and ionic compounds.
184
Chapter 5 • Ions and Ionic Compounds
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
REVIEW ANSWERS
continued
FOCUS ON GRAPHING
Study the graph below, and answer the questions that follow.
For help in interpreting graphs, see Appendix B, “Study Skills for Chemistry.”
The graph shows the changes in potential
energy that occur when an ionic bond forms
between Na(s) and Cl2(g). The reactants, solid
sodium and chlorine gas, start at an initial
energy state that is assigned a value of zero at
25°C and 1 atm of pressure.
Potential Energy in the Formation of NaCl
800
Potential energy (kJ/mol)
600
400
32. In terms of energy, what do the steps from
200
point A to point D have in common?
0
33. What do the steps from point D to point F
have in common?
–200
34. What is occurring between points D and E?
–400
35. Write the word equation to show what hap-
–600
–800
A
B
C
D
E
pens between points B and C when electrons
are removed from 1 mol of sodium atoms.
F
Steps in formation of NaCl (s)
36. Which portion of this graph represents the
lattice energy involved in the formation of an
ionic bond between sodium and chlorine?
37. Calculate the quantity of energy released
when 2.5 mol of NaCl form.
TECHNOLOGY AND LEARNING
38. Graphing Calculator
Calculating the Number of Valence Electrons
The graphing calculator can run a program
that can determine the number of valence
electrons in an atom, given its atomic number.
Go to Appendix C. If you are using a TI-83
Plus, you can download the program
VALENCE and run the application as
directed. If you are using another calculator,
your teacher will provide you with
keystrokes to use. After you have run
the program, answer these questions.
How many valence electrons are there in
the following atoms?
a. Rutherfordium, Rf, atomic number 104
23. S2−; [Ne]3s23p6
Be2+; 1s2
I −; [Kr]4d 105s25p6
Rb+; [Ar]3d 104s24p6
O2−; [He]2s22p6
Sr2+; [Ar]3d 104s24p6
F −; [He]2s22p6
24. a. CN −
b. SO24−
c. NO−2
d. MnO−4
25 a. 3; b. 1; c. 4; d. 7
26. Most metals are active elements
that lose electrons to form ionic
compounds that are found in
ores.
27. Nuclear processes do not occur
in chemical reactions. Chemical
reactions involve the rearrangement of electrons, not protons
or neutrons.
28. Elements in this group do not
normally form ions. They all
have stable outer energy levels.
29. Compound A is probably ionic
because it has the higher melting
and boiling points. In addition,
compound A does not vaporize
as readily. These properties are
the result of strong ionic bonds.
30. Proposals may include using a
water-testing kit to test the levels
of certain ions both before and
after treatment.
Answers continued on p. 187A
b. Gold, Au, atomic number 79
c. Molybdenum, Mo, atomic number 42
d. Indium, In, atomic number 49
185
Chapter Resource File
• Chapter Test
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5 • Ions and Ionic Compounds
185
STANDARDIZED
TEST PREP
5
Question 4 Choice F is the correct
answer because the two elements
are a metal and a nonmetal, a
combination that is likely to form
a salt. Choices H and I are not
likely to form salts because the elements are both metals and Choice
G because both elements are nonmetals.
UNDERSTANDING CONCEPTS
6
Directions (1–4): For each question, write on a
separate sheet of paper the letter of the correct
answer.
1
Question 5 Because metal atoms
generally have easily removed
valence electrons, they tend to
form salts with nonmetals in the
air, water, or soil and are rarely
found as a pure element.
Question 7 The correct answer is
B – sodium chloride dissolves easily in water. Salt does not melt at
the temperature range at which
water is liquid, does not float in
water, and does not tend to react
with oxygen in the air.
Question 8 The correct answer is
F. Salts, such as sodium chloride,
form strong solids because the
ionic bonds between the metal and
the nonmetal are very strong.
Sodium chloride does not melt
during mining because the temperature is too low; it is an ionic compound whose properties do not
resemble those of metals; the hardness is due to the nature of the
bonds, not the temperature of the
mine.
186
STANDARDIZED TEST PREP
READING SKILLS
Which of the following can achieve the same
electron configuration as a noble gas when
the atom forms an ion?
A. argon
C. nickel
B. iron
D. potassium
2
Why is an input of energy needed when
forming NaCl?
F. to change chlorine to a gas
G. to add an electron to the chlorine atom
H. to remove an electron from the sodium
atom
I. to bring together the sodium and the
chloride ions
3
Which of the following is a characteristic of
a salt?
A. bends but does not shatter when struck
sharply
B. has the ability to conduct electric current
in the solid state
C. has the ability to conduct electric current
in the liquid state
D. melts at temperatures that are slightly
higher than room temperature
Directions (7–8): Read the passage below. Then
answer the questions.
In 1980 an oil drilling rig in Lake Peignur in
Louisiana opened a hole from the lake to a salt
mine 1,300 feet below ground. As the lake
water flowed into the mine, it dissolved the salt
pillars that were left behind to hold up the ceiling. When the entire mine collapsed, the resulting whirlpool swallowed a number of barges, a
tugboat, trucks, and a large portion of an island
in the middle of the lake. Eventually, the hole
filled with water from a canal, leaving a much
deeper lake.
4
Which of the following pairs of elements are
most likely to form an ionic bond?
F. Br and Ca
H. Ca and Mg
G. Br and N
I. Ca and Fe
Directions (5–6): For each question, write a short
response.
5
7
What was the most likely cause of the collapse of the salt mine?
A. The salt melted due to the temperature of
the water.
B. Water dissolved the ionic sodium chloride,
leaving no supports.
C. Water is denser than salt, so the salt began
to float, moving the columns.
D. The open hole exposed the salt pillars to
the air and they had a chemical reaction
with oxygen.
8
When there is no water present, the pillars in
a salt mine are capable of holding the weight
of the ceiling because
F. Salt is held together by strong ionic bonds.
G. Salt melts as it is mined and then reforms
to a hard crystal.
H. Salt contains sodium, which gives it the
properties of metal.
I. Salt does not crumble due to the low
temperatures found below ground level.
Explain why only a few metals are found in
nature in their pure form, while most exist
only as ores, which are metal-containing
compounds.
186
Answers
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
D
H
C
F
Metals lose their outer electrons easily to form
ionic compounds with other elements.
6. Elements that have only a few valence electrons
form cations because it takes less energy to lose
electrons. Elements with an outer energy level that
is close to filled form anions.
7. B
8. F
Chapter 5 • Ions and Ionic Compounds
How can you tell from the number of valence
electrons whether an element is more likely
to form a cation or an anion?
9.
10.
11.
12.
C
H
C
2
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
STANDARDIZED
TEST PREP
INTERPRETING GRAPHICS
Directions (9-12): For each question below, record the correct answer on a
separate sheet of paper.
Many transition metals are capable of forming more than one type of stable
ion. The properties of compounds formed by one ion are often very different
from those formed by an ion of the same element having a different charge.
Use the table below to answer questions 9 through 12.
Question 9 The correct answer is
C. Metals in the first two columns
of the periodic table form ions by
losing all of their valence electrons.
Most transition metals only lose
some of the valence electrons.
Answer A is incorrect because
many of the ions on the table
involve loss of only one or two
electrons,. Answer B is incorrect
because all metals form positively
charged ions, so the nature of the
charge is not a difference. Answer
D is incorrect because some transition metals form only one ion.
Stable Ions Formed by the Transition
Elements and Some Other Metals
Group 4
Ti2+
Ti3+
Hf 4+
Group 5
Group 6
Group 7
Group 8
Group 9 Group 10 Group 11 Group 12 Group 13 Group 14
V2+ Cr 2+ Mn2+ Fe2+ Co2+ Ni 2+ Cu+ Zn2+ Ga 2+ Ge 2+
V3+ Cr 3+ Mn3+ Fe3+ Co3+
Cu 2+
Ga 3+
Mo3+ Tc 2+
Pd 2+ Ag+ Cd2+ In+ Sn 2+
In 2+
Ag 2+
In 3+
Re4+
Re5+
Pt 2+ Au+ Hg 2+
Tl+ Pb 2+
2
Pt 4+ Au 3+ Hg 2+ Tl 3+
9
How do the cations formed by transition metals differ from those formed
by metals in the first two columns of the periodic table?
A. Transition metals lose more electrons.
B. All of the transition metal ions have a positive charge.
C. Transition metals generally do not ionize to a noble gas configuration.
D. All of the transition metals are capable of forming several different
ions.
0
Which of these metals forms ions with a noble gas electron configuration?
F. copper
G. germanium
H. hafnium
I. platinum
q
w
Based on the stable ions in the illustration, which of these compounds is
most likely to exist?
A. Fe2O
B. FeO2
C. Hg2O
D. Mo3O2
How many different ionic compounds exist that consist of only iron and
chlorine?
5
Question 10 The correct choice is
H. Hf4! is the only ion on this
chart in which all of the valence
electrons are removed. Choice F is
incorrect because copper loses 1 or
2 of its 11 valence electrons.
Choice G is incorrect because germanium loses two of its 14 valence
electrons. Choice I is incorrect
because platinum loses 2 or 4 of
its 10 valence electrons.
Test
When possible, use
the text in the test to
answer other questions. For example,
use a multiple-choice
answer to “jump
start” your thinking
about another
question.
Question 12 The correct answer
is 2. Chloride ions always have a
charge of -1, so a neutral compound can be formed by the combination of two chloride ions with
Fe(II) or by combination of three
chloride ions with Fe(III).
187
Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.
Chapter 5 • Ions and Ionic Compounds
187








