Unit 6 Study Guide Below are some key questions to help guide you in

Unit 6 Study Guide
Below are some key questions to help guide you in your preparation for the Unit 6 Exam. Look over each of the questions and ask yourself: Do I know this? Do I need some help with this question? Where can I go to get answers for this topic? Use your notes, quizzes, labs, and textbook to help you find these answers. I
would also suggest trying the Chapter Assessments in your textbook as another way to test your knowledge. Good luck!
Chapter 13
1.
What are valence electrons and why are they important to understand?
2.
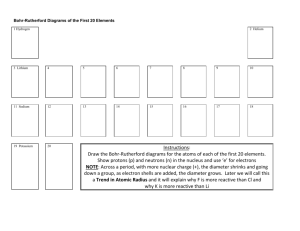
Be able to draw dot diagrams for any of the first 20 elements on the Periodic Table.
3.
What is an orbital? What are the four orbitals (and their shapes) that electrons occupy around a nucleus? How many electrons can each hold?
4.
What is the order in which orbitals will be filled by electrons from Hydrogen to Barium?
5.
Be able to do electron configurations for any of the first 56 elements on the Periodic Table
(short and long version).
6.
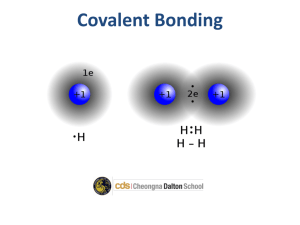
Compare and contrast the differences among covalent, ionic, and metallic bonds. Include properties, characteristics, and examples for each.
7.
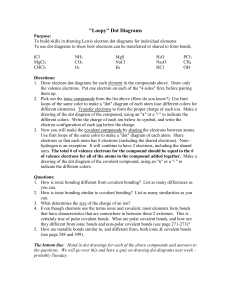
Be able to draw dot diagrams for the following covalently bonded molecules: H
2
, H
CO
2
, and N
2
2
O, CH
4
, PCl
8.
Be able to draw dot diagrams for the following ionically bonded compounds: NaCl, MgO, K
2
S,
3
BeBr
2
9.
Be able to draw dot diagrams for the following Polyatomic ions: OH -‐ , SO
42-‐
, NH
4
10.
Be able to identify the oxidation states (numbers) of the main groups of the periodic table and the multiple oxidation states of some of the designated transition metals.
11.
Be able to determine if a molecule is ionic or covalent.
12.
Be able to write the chemical formulas for the following ionic compounds: Beryllium Bromide,
Calcium Chloride, Iron (III) Oxide, Copper (II) Sulfide, Aluminum Sulfate, Sodium Hydroxide,
Magnesium Carbonate.
13.
Be able to write the chemical formulas for the following covalent molecules: nitrogen
trihydride, dinitrogen trioxide, tetracarbon decahydride
14.
Be able to write the names for the following: MgBr
2
, K
2
S, CaCO
3
, K
3
PO
4
, NH
4
Cl, CH
15.
What are the four elements associated with organic chemistry?
4
, PCl
3
16.
What are the four molecules that exist in all living things? What is the function of each? Where might they be found?
17.
Provide an example of a polymer and a monomer for each of the molecules listed in question
#16.
When you have looked over these questions, spend some time looking over pp. 330-332 and quiz yourself or a friend on the questions that pertain to the topics addressed above.
Chapter 14
1.
What are four examples of evidence that would indicate that a chemical reaction has taken place? Which one of these is sometimes misleading?
2.
What is a chemical equation? What goes on the left of the equation? The right?
3.
What is important to note about the properties of the reactants and the products when a chemical reaction occurs?
4.
What is the Law of Conservation of Matter? Why is it important to understand when balancing equations?
5.
Be able to balance the following equations:
____ Na
3
PO
4
+ ____ KOH
____ NaOH + ____ K
3
PO
4
____ P
4
+ ____ O
2
____ P
2
O
3
____ CH
4
+ ____ O
2
____ CO
2
+ ____ H
2
O
____ AgNO
3
+ ____ Cu
____ Cu(NO
3
)
2
+ ____ Ag
____ MgCl
2
____ Mg + ____ Cl
2
6.
What are the five types of chemical reactions? Identify the type of reaction for each of the examples in #5.
When you have looked over these questions, spend some time looking over pp. 360-362
(sections 14.1 and 14.2 only) and quiz yourself or a friend on the questions that pertain to the topics addressed above.