Covalent Bonding
advertisement
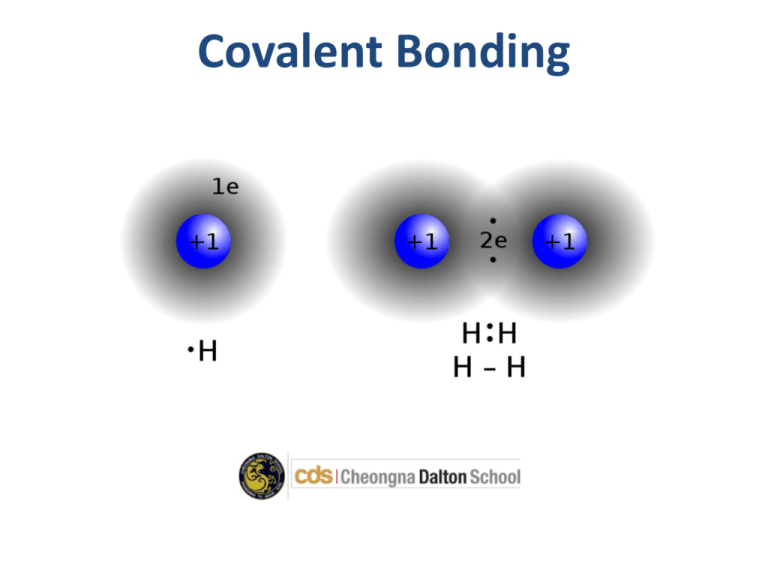
Covalent Bonding Goal of the class • To learn how covalent bonds are formed between atoms • Question of the day: What do Lewis dot structures show? • Previous Answer: Ionic bonds are formed when one atom takes the electron(s) of another atom and are then attracted. Covalent Bonding • Non metals combine together by sharing electrons. • The shared pair of electrons holds the two atoms together. – It's called a covalent bond. • The group of atoms bonded together in this way is called a molecule. Examples of Covalent Molecules • Hydrogen (H2) • Water (H2O) • Ammonia (NH3) • Methane (CH4) Properties • Covalent compounds are usually gases or liquids with low melting points or boiling points. • They don't conduct electricity. Dot and Cross Diagrams • Dot and cross models show how a pair of electrons forms a covalent bond. • Notice that in the diagrams only the electrons in the outer shell of each atom are shown. • All atoms want a full valence shell – octet rule Dot and Cross Diagrams Practice • Draw a dot and cross diagram for water (H2O) • Again for methane (CH4) Lewis Dot Structures • Lewis dot structures are an easy and helpful way to diagram valence electrons • The electrons must be arranged like this: Be C O Ne Lewis Dot Structures Double and Triple Bonds • Some compounds are formed when two elements share more than one electron with each other. • These form double or triple bonds • Much stronger than single bonds Questions • Draw a Lewis dot diagram hydrogen cyanide (HCN) Vocabulary • Covalent bonding – A type of chemical bond where two atoms are connected to each other by sharing pairs of electrons • Octet – a group of eight things Homework • Please read Chemical Interactions textbook pages 57-61 • Please complete Chemical Interactions workbook page 18.






