What Abiotic and Biotic Factors Characterize Biomes?
advertisement

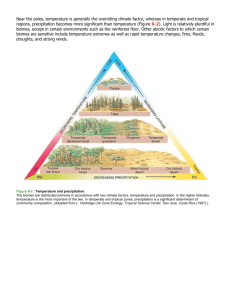
What Abiotic and Biotic Factors Characterize Biomes? Abiotic Factors Biotic Factors -Proximity to mountain ranges ­Animal Life -Proximity to oceans ­Plant Life -Soil Type -Climate Oct 4­9:23 PM Boreal Forest Average Precipitation: 30-84 cm per year Average Temperature: -54-21 Degrees Celsius Plant Species:Broad band of dense conical shaped trees Have wax-covered needle-like leaves that prevent excessive loss of water Example: Evergreens Animal Species: Staying warm is major challenge Many species have feathers or fur Small extremities Examples: birds, beavers, deer, mountain lions Characteristics: Long, cold winters and summers are mild Sometimes referred to as the Taiga Tundra Average precipitation: 15-25 cm per year (low) Temperature range: -34-12 degrees Celsius (very cold) Plant species: Adapted due to nutrient poor soil. Seed dispersal by wind, avoid damage by laying low to the ground Some species have nitrogen fixing bacteria in the roots Contains short shrubs and grasses Animal species: Many animal species migrate due to long harsh winters Examples: Polar bears, caribou, birds Soil: Nutrient poor, permafrost-permanently frozen subsoil Characteristics: Cold temperatures, harsh winters, short growing season Oct 4­9:53 M Temperature Forest Average Precipitation: 75-100 cm per year Average Temperature: -30-30 Degrees Celsius Plant Species:Coniferous trees Deciduous trees lose leaves and are dormant in the summer time Examples: Oak, birch, and maple trees Animal Species:Adapted to constantly changing seasons (migration/hibernation) Camouflage for animals that do not hibernate Examples: squirrels, rabbits, skunks, birds, deer Characteristics: Well-defined seasons, summers are hot, winters are cold Oct 4­10:05 PM Temperate Woodland and Shrubland Average precipitation: 38–100 cm per year Temperature range: 10°C–40°C Plant Life: Mixed shrubs and evergreens Dense, low plants that contain flammable oils make fire a constant threat Some plants need fire to germinate seeds Animal Life: Animals tend to be browsers Characteristics: Summers are very hot and dry, winters are cool and wet Oct 4­10:36 PM Oct 4­10:30 PM 1 Temperate Grassland Desert Average precipitation: 2–26 cm per year Average precipitation: 50–89 cm per year Temperature range: ­40°C–38°C Plant Life: Grassland Plants Periodic fires and grazing by herbivores maintained plant communities Animal Life: Camouflage and burrowing are two common protective adaptations Characteristics: Open, exposed environments causes predation to be constant threat for smaller animals Oct 5­9:48 AM Tropical Savanna Temperature range: high: 20°C–49°C; low: ­18°C–10°C Plant Life: Many plants store water in their tissues Minimized leaf surface area cuts down water loss Specialized photosynthesis in some plants, called C4 Animal Life:Animals receive water from the plants they eat Large or elongated ears are supplied with many blood vessels, aides in the lose of body heat and regulate body temperature Characteristics: Varying temperature ranges from day to night Oct 5­9:57 AM Tropical Seasonal Forest Average precipitation: 50–130 cm per year • Average precipitation: >200 cm per year Temperature range: 20°C–30°C Plant Life: • Temperature range: 20°C–25°C Animal Life:Many animals migrate during the dry season • Characteristics: rainfall is seasonal • Plant Species: Adaptations for little amounts of precipitation Characteristics: Receives more seasonal rain than desert, but less than tropical rainforest Frequent fires, compacted soil Action from large animals prevent some areas from turning into dry forest Oct 5­10:05 AM • Animal Species: Many of the animals will migrate in search of food and water Oct 5­4:30 PM Tropical Rain Forest Average precipitation: 200–1000 cm per year Temperature range: 24°C–27°C Abiotic factors: humid all year; hot and wet What other information can we add to this slide? Many groups presented on Tropical Rain Forest List abiotic and biotic characteristics for this section on your notes sheets May 20­4:33 AM Oct 5­4:40 PM 2 Sep 30­9:48 AM 3