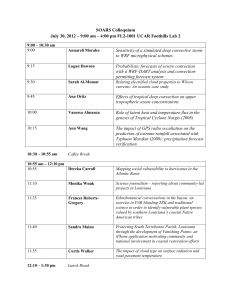
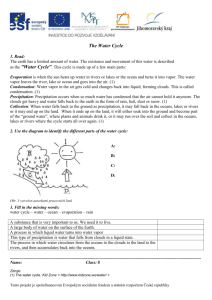
Meteorology Review Answers
advertisement

Meteorology Review Answers Completion 1. warm 2. low 3. air masses 4. temperature, precipitation 5. summer, winter 6. dry adiabatic 7. cooler 8. inward 9. global warming 10. nitrogen, oxygen 11. Northern 12. mesocyclone 13. summer 14. carbon dioxide 15. cloud seed (or condensation nuclei) 16. polar, tropical 17. fog 18. temperature control 19. precipitation 20. cooler, milder 21. balances 22. reflection 23. right 24. polar 25. occlusion 26. 100 27. heat 28. rising 29. higher, lower 30. rotation 31. decrease 32. La Niña 33. poles, equator 34. form, height 35. front 36. continental, maritime 37. hurricanes 38. continental polar 39. stratosphere 40. conduction 41. ice cap 42. evaporation 43. air pollutants 44. radiation 45. temperature profile 46. one million 47. counterclockwise 48. precipitation Short Answer 49. a whirling tropical cyclone that produces winds of at least 119 kilometers per hour 50. the windward side 51. friction causes a net flow of air inward around a cyclone and outward around an anticyclone 52. the height of the column decreases 53. heating of land and water, altitude, geographic position, cloud cover, and ocean currents 54. orographic lifting, frontal wedging, convergence, and localized convective lifting 55. the rate of movement of the front and the steepness of its slope 56. continental tropical 57. latent heat of condensation 58. warm, moist, unstable maritime tropical air seldom penetrates this region 59. subtropical high, polar high, equatorial low, and subpolar low 60. the state of the atmosphere at any given time and place 61. tiny bits of particulate matter that serve as surfaces for water-vapor condensation 62. centers of low pressure 63. when air is compressed, it warms, and when it is allowed to expand, it cools 64. the pressure exerted by the weight of air above 65. the stronger the wind, the greater the deflection of the Coriolis effect 66. source region and overall temperature 67. increases in greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide have caused global temperatures to rise 68. eye wall 69. the ratio of air’s actual water-vapor content compared with the amount of water vapor air can hold at that temperature and pressure 70. the natural warming of both Earth’s lower atmosphere and surface 71. the general term for the amount of water vapor in air 72. by adding or removing water vapor or by changing temperature 73. higher elevations are generally wetter than lower elevations 74. land heats more rapidly and cools down more rapidly than does water 75. a semiarid climate is a marginal and more humid variant of an arid climate 76. the development of a front, occurring when two air masses with different temperatures encounter each other moving in two different directions 77. temperature and precipitation 78. there are no landmasses to interrupt that particular pressure belt 79. tundra climate and ice cap climate 80. the temperature profile in the lower atmosphere 81. pressure differences, the Coriolis effect, and friction 82. prevailing westerlies 83. stationary fronts are shown by blue triangles on one side of the front and red semicircles on the other side 84. 0 to 4 percent 85. the method and place of formation 86. global winds move warm air toward the poles and cool air toward the equator 87. it may be reflected, transmitted, or absorbed 88. the energy transferred from one object to another because of temperature differences 89. centers of high pressure 90. when it is in a liquid state below 0ºC 91. seasons occur because Earth’s axis is tilted and its position relative to the sun continually changes as it travels along its orbit 92. Volcanic ash, dust, and aerosols in the air increase the amount of solar radiation that is reflected back into space 93. Fujita tornado intensity scale 94. light to moderate 95. air temperature, humidity, type and amount of precipitation, air pressure, and the speed and direction of the wind 96. climate refers to weather patterns that have been observed over many years 97. when the air mass moves over a new surface 98. an mP air mass is wet and cold