Cells, Photosynthesis, Respiration Practice
advertisement

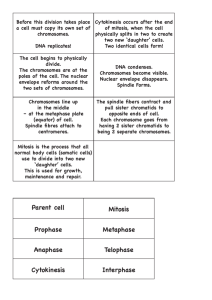
Cells, Photosynthesis, Respiration Practice Questions F 1. What are chromosomes? When do they form? Chromosomes are coiled structures made of DNA and proteins. They form during cell division. Specifically, they form during prophase in mitosis. 2. Identify the chromatids and the centromere of a chromosome. Each chromosome actually consists of two identical copies of DNA because DNA has already replicated. Each copy is called the chromatid of the chromosome. The two copies are called sister chromatids. These sister chromatids are attached to one another at a region around the middle of the chromosome. The region is called the centromere of the chromosome. 3. List the phases of mitosis. Prophase – metaphase – anaphase - telophase 4. What happens during prophase of mitosis? During prophase, chromatin condenses into chromosomes, and the nuclear envelope, or membrane, breaks down. In animal cells, the centrioles near the nucleus begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. As the centrioles move, a spindle starts to form between them. 5. During which phase of mitosis do sister chromatids separate? Anaphase. 6. Describe what happens during cytokinesis in animal cells. During cytokinesis in animal cells, the cytoplasm splits in two and the cell divides. And then, the plasma membrane of the parent cell pinches inward along the cell's equator until two daughter cells form. 7. If a cell skipped metaphase during mitosis, how might this affect the two daughter cells? If this happened, the two daughter cells would not have an identical set of chromosomes. This is because spindle fibers don't attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids. It follows from this that sister chromatids will not separate and go to different daughter cells when the cell divides. 8. Explain how chromosomes are related to chromatin. Why are chromosomes important for mitosis? DNA wraps around protein to make chromatin. Chromatin folds up to make chromosomes. Chromosomes contain the genetic material of a cell. After DNA has replicated during S phase, mitosis begins. During mitosis, DNA condenses and coils into the X-shaped form of a chromosome. This X-shaped chromosome has two identical copies of DNA which are called sister chromatids. These sister chromatids separate and fit into two new daughter cells. This is how chromosomes transfer the genetic material of the parent cell to the new daughter cells. This is why chromosomes are important for mitosis. 9. Explain the significance of the spindle in mitosis. During prophase in mitosis, chromatin condenses into chromosomes and the centrioles begin to separate and move to opposite poles of the cell. As the centrioles move, a spindle starts to form between them. The spindle consists of fibers made of microtubules. During metaphase, spindle fibers attach to the centromere of each pair of sister chromatids. The spindle fibers ensure that sister chromatids will separate and go to different daughter cells when the cell divides. During anaphase, the sister chromatids are pulled apart by the shortening of the spindle fibers. At the end of anaphase, each pole of the cell has a complete set of chromosomes. As stated above, the spindle plays an important role in making sure that the genetic material of the parent cell will equally go to two new daughter cells.