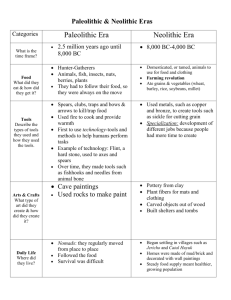
Paleolithic Stuff

Paleolithic Stuff
• Key Concept 1.1 Big Geography and the
Peopling of the Earth
• 1.1.I. Archaeological evidence indicates that during the Paleolithic era, huntingforaging bands of humans gradually migrated from their origin in East Africa to
Eurasia, Australia, and the Americas, adapting their technology and cultures to new climate regions
1.1. Big Geography
• “Big Geography” – focus on global nature of _____ ______
• Through the PP, humans migrated from
Africa to ______, ______, and the ______.
• Early humans were creative in adapting to different geo settings
• Use of modern hunter-forager societies help us infer that the earlier bands were relatively _______.
• 1.1.I. hunting-foraging bands of humans gradually migrated, adapting their ____ and
____ to new climate regions
• A. use of fire in new ways:
– 1.
– 2.
– 3.
• B. developed a wider range of tools specially adapted to different environments from tropics to tundra
• C. economic structures focused on small kinship groups, made what was needed to survive; some groups were not self-sufficient and exchanged ____, ____, and _____
Comparison: Which of the following is
NOT a true statement concerning the
Paleolithic period?
• a. It was the period when mankind settled all regions of the earth except Australia and the
Americas.
• b. It was a period when mankind adapted to live in every environmental niche from the frigid arctic, to rainforests, to mountains, to deserts.
• c. It was a period of slow technological development.
• d. It encompassed well over 90 percent of the time that human beings have inhabited the earth.
• A
Answer
Change: When Paleolithic humans settled down into the first permanent settlements,
• a. their continued reliance on a gatherer-hunter lifestyle meant that the settlement communities remained roughly the same size as before they settled down.
• b. they maintained the same egalitarian social organizations that they possessed before they settled down.
• c. they were able to accumulate and store more goods.
• d. they no longer needed a clearly defined leader to direct their yearly migratory movements.
• C
Answer
Comparison: Members of gathererhunter societies
• a. typically have less leisure time than members of agricultural or industrial societies.
• b. have been referred to as “the original affluent society” not because they had so much but because they wanted or needed so little.
• c. typically have longer life spans than members of agricultural or industrial societies.
• d. do not intentionally or unintentionally alter their environments.
• B
Answer
Which of the following do you find the most attractive feature of Paleolithic society?
• a. Egalitarian social structure
• b. Relations between genders
• c. Gathering and hunting lifestyle
• d. Variety of lifestyles that one could partake in
Which of the following do you think would most improve our knowledge of
Paleolithic man?
• a. A more precise chronological sequence for the spread of mankind across the planet
• b. A better understanding of their religious beliefs
• c. If more hunter-gatherer societies existed today
• d. A better understanding of the origins of our species
Would you like living in a
Paleolithic society?
• a. Yes
• b. No