Social Studies Chapter 2
advertisement

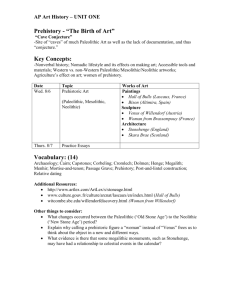
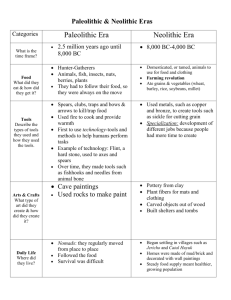
Social Studies Chapter 2 Prehistoric People 8000B.C- 3000 B.C. Text Pages 32-40 1. - Prehistory – the human experience prior to written records or documentation. This period began when people appeared and ended when writing developed. - Civilization was the advancement of culture. - Migrate: to move. - Bands: groups of about 30 members. - Home Territory: The area where bands gathered food. 2. Why did early people move out of Africa and into other parts of the world 900,000 years ago? - The climate became colder, ice sheets grew, and land bridges were created. Rain increased and changed desserts to grasslands. 3. How did tools change in the Paleolithic Age? - Tools changed from sticks and stones to sharpened tools. 4. What do you think was the most important advancement made by early people? Explain. - The ability to use fire - The ability to communicate with one and other. Objective: To be able to describe early human or prehistoric culture. Challenge: To learn about early human culture without using available written documentation of any kind. - Science of Archeology. When does the discovery of fire have value? - The need to apply the discovery - Ability to control fire. (Helps with humans survival) Paleolithic Period - Was extremely cold and food was scarce. - Paleolithic Humans lived 3.5 million years ago – 10,000 years ago. - They had stones to use as tools. - There are no written records of this time. - Many believe that they lived in the grasslands of Eastern Southern Africa. - They were unable to grow food. - Food was hunted for, the big game hunters (Wooly Mammoth) - People would gather fruits and vegetables. - People hunted in groups or Bands. A band would have about thirty members. If the food supply was good the band might have forty to fifty members. - Survival was the goal. - Hunt and Gather. 1. Define: Domesticated: To be tamed Population: The number of people Specialization: the development of occupations 2. What two important discoveries changed people from food gathers to food producers? The two major discoveries were farming and herding. 3. What were the results of the increased food supply during the Neolithic Age? The population increased and specialization/ the development of occupations. 4. What two roles did village chiefs play? They were rulers and priests. 5. How did learning to produce food lead early civilizations to develop villages? People had to learn to produce food before they could settle in villages because farming provided a steady food supply and people no longer needed to hunt and gather food in nomadic bands.