Short Story Notetaking Outline
advertisement

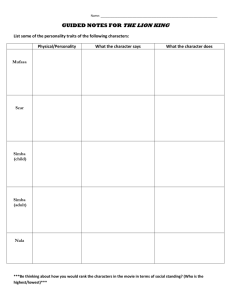
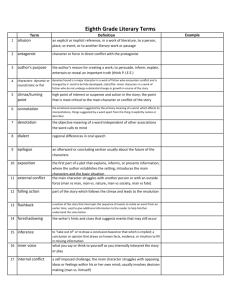
Short Story Unit Miller 2011-2012 English I Genre ►A category of literature ►Example: short story, poetry, or drama Short Story Definition ►a fictional, prose, narrative of 12,000 words or less ►Fictional: not true ►Prose: written in sentences and paragraphs ►Narrative: tells a story Plot ►The sequence of events (action) in a narrative ► Plotline Model Flashbacks and Foreshadowing A scene that interrupts the action of a story to tell about events that happened at an earlier time ► Flashback: In the Lion King, during Simba’s fight with Scar, Simba is hanging over the edge of the cliff and the movie uses a flashback to revert to the scene where Mufasa was hanging in a similar way. ► Example: Flashbacks and Foreshadowing ► Foreshadowing- Clues that hint at actions that are to follow in the story Horror movies – any time a blonde screams at the beginning, she’ll be dead before the end of movie ► Example: Figures of Speech ► literary devices used by an author ► simile- A comparison between two unlike things using “like” or “as.” ► Example: You eat like a pig. ► metaphor- A comparison between two unlike things without using like or as. ► Example: You’re such a pig. Figures of Speech ► imagery- language that appeals to the five senses-taste, touch, sight, smell, hearing ► Example: mouth-watering chocolate; slick and glistening streets Figures of Speech ► irony- A contrast between what is stated and what is really meant, or between what is expected to happen and what actually happens ► Example: Calling a 6’6’’ guy “shorty” / A guy gives up drinking, then he’s killed when a beer truck hits him. Theme ►the message or messages the author is trying to show the reader Point of View ►the position from which the story is told to the reader ►First person- the narrator is a character in the story ►Innocent eye- 1st person- when the narrator is a child in the story ►Example: The Wonder Years; A Christmas Story; Malcolm in the Middle Point of View ► Third person- the narrator is outside the story ► Omniscient- all knowing; the narrator is outside the story and tells the reader everything ► Example: The beginning of Beauty and the Beast starts with a hand opening a book and stating, “Once upon a time…” ► Limited Omniscient- narrator tells most of the story Types of Conflict ► Internal- a person is in conflict within himself (character vs. self) Simba’s inner struggle to get over his guilt and decide whether or not to face his past by returning to the pride. ► Example: Types of Conflict ► External- conflict arises from the outside ► character vs. character- conflict between two characters ► Example: Simba versus Scar ► character vs. nature- conflict between character and nature ► Example: Survivor; The Amazing Race Types of Conflict ► character vs. society- conflict between character and society ► Example: In Beauty and the Beast, the Beast struggles to fit into society despite his looks. ► character vs. supernatural- conflict between ghosts, etc ► Example: Aliens; Terminator Character Types Character’s personality does not change throughout the story static- Example: Throughout the movie, Finding Nemo, Nemo remains courageous and adventurous. Character Types dynamic- Character undergoes a change in attitude or personality Example: In Finding Nemo, Marlin (Nemo’s dad) changes as he learns to not let fear control his life. Character Types ►stereotype- the character represents an entire group of people ► Example: The show/movie Clueless has the “ditzy blonde” stereotype. Characterization ► the way the author presents the character to the reader ► direct-the author states in the text what the character is like ► Example: Henry is not intelligent. Characterization ► indirect- the character states what he or she is feeling ► Example: “Boy, Henry you’re not too smart.” ► inferred- the reader has to arrive at the conclusion by interpreting the character’s actions ► Example: Henry forgot to do his homework every day. Aspects of A Character physical- characteristics such as height, weight, hair, and eye color Example: Belle from Beauty and the Beast has brown hair, thin, dainty-like ► psychological-what is going on in the character’s mind and how he thinks, acts, and behaves ► Example: Belle is smart, kind, compassionate, open-minded Aspects of A Character ► sociological- where a character actually fits into society ► Example: Beast from Beauty and the Beast is ostracized/shunned by society because of his looks Aspects of A Character Central character in a work of literature (not necessarily a hero or “good guy”) ► PROTAGONIST- ► Example: Simba ► ANTAGONIST- protagonist ► Example: Scar Character who opposes the Levels of Understanding ► literal level- what the story is about- the plot line/surface level level- the author’s message(s) and understanding ► interpretative ► applied level- how do those messages apply to your own personal life and to our society Tone and Atmosphere the author’s attitude toward his subject ► Tone- ► Atmosphere- mood ► Example: scary, happy, sad, etc. World Views ► How the author feels toward life and existence ► Romantic- positive; good, capable of change, happy endings, etc (Disney) World Views ► Realistic- no emotions, facts only, no “good” or “bad” (Newspaper) ► Naturalistic- negative, people are not good; man is trapped in a mechanized society and can’t help himself Epiphany ►a sudden understanding of something you didn’t understand before (AHA! Moment)