Measuring Pressure
advertisement
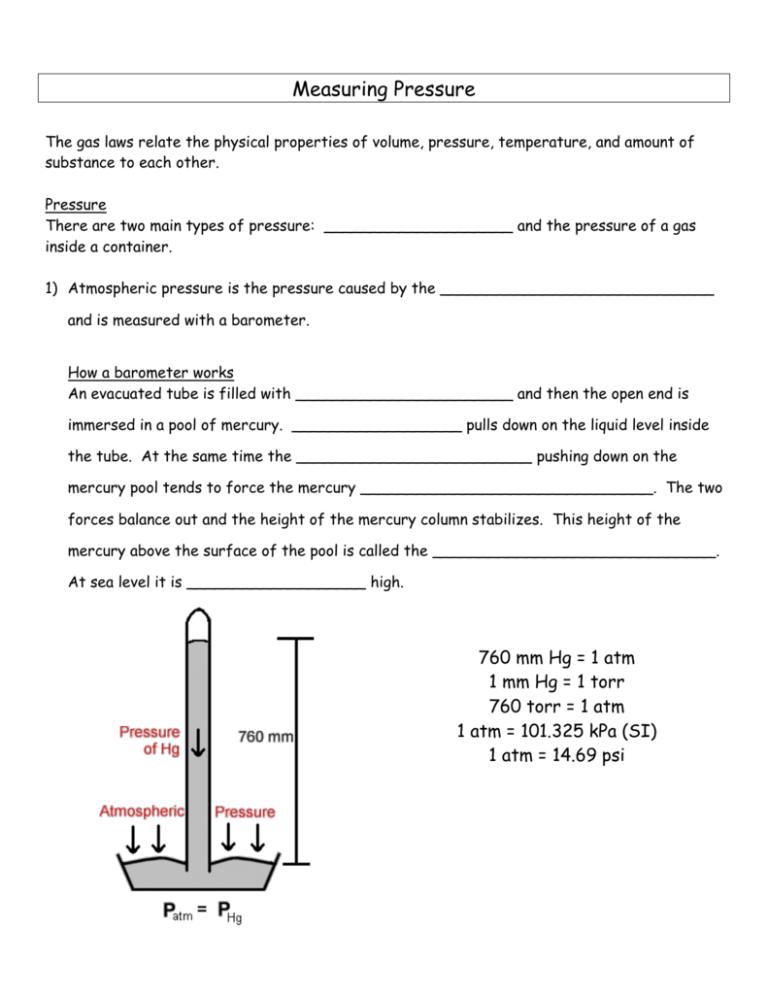
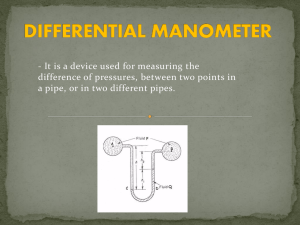
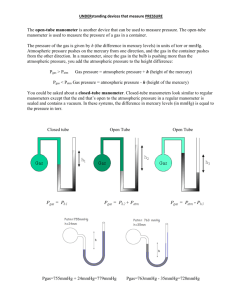
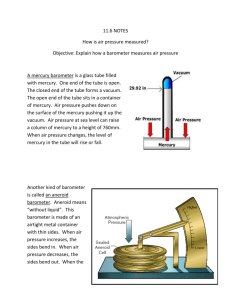
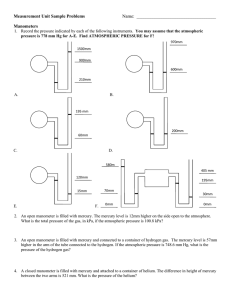
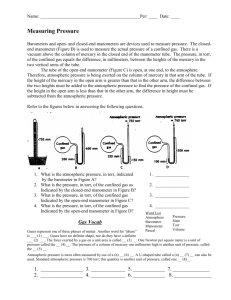
Measuring Pressure The gas laws relate the physical properties of volume, pressure, temperature, and amount of substance to each other. Pressure There are two main types of pressure: ____________________ and the pressure of a gas inside a container. 1) Atmospheric pressure is the pressure caused by the _____________________________ and is measured with a barometer. How a barometer works An evacuated tube is filled with _______________________ and then the open end is immersed in a pool of mercury. __________________ pulls down on the liquid level inside the tube. At the same time the _________________________ pushing down on the mercury pool tends to force the mercury _______________________________. The two forces balance out and the height of the mercury column stabilizes. This height of the mercury above the surface of the pool is called the ______________________________. At sea level it is ___________________ high. 760 mm Hg = 1 atm 1 mm Hg = 1 torr 760 torr = 1 atm 1 atm = 101.325 kPa (SI) 1 atm = 14.69 psi Notice that _______________________ is used in barometers rather than other liquids because it is so ___________________. This means that the mercury will not rise too high. At the same temperature, the ratio of _________________ of the liquid columns is _____________________ proportional to the ratio of the liquids’ __________________. Example: The barometer reading in Mrs. Darling’s classroom on September 4, 2008 was 104.1 kPa. a) Convert this measurement into mm Hg. b) If Mrs. Darling’s barometer used ethanol (d = 0.80 g/mL) instead of mercury (d = 13.6 g/mL), how high would the column of ethanol be? 2) The pressure of a gas inside a container is measured with a ________________________. How a manometer works As with the barometer, the pressure of a gas is balanced against a column of ___________. There are two types of manometers: _______________________________ and ________________________________. In open tube manometers you are essentially comparing the pressure of the gas inside the container to _________________________ ____________________________. In the diagram below, the first manometer shows a gas with a pressure ____________________ atmospheric and the second manometer shows a gas with a pressure ______________________ atmospheric. Example: Calculate the pressure of a gas if barometric pressure is 748.2 torr and the mercury in the arm open to the atmosphere is 7.8 mm higher than the other arm. In closed tube manometers you are essentially comparing the pressure of the gas inside the container to a _______________________. This type of manometer is generally used for measuring low gas pressures and there is no need to correct for atmospheric pressure. Example: A scientists heats a solid sample of CaCO3 and collects the CO2 formed in an evacuated, closed- end manometer. At room temperature the change in height of mercury is 313.2 mm Hg. Calculate the pressure of the CO2 in atmospheres.