Introduction to Physics
AP
Chemistry
The Gas Laws
Basics on Gases composition of the atmosphere: ~78% N
2
, ~21% O
2 properties of gases: expand to fill container compressible form homogeneous mixtures
-due to gas particles being…
1) far apart
2) in constant, random motion vapors: gases of substances that are normally liquids or solids e.g., gasoline vapors
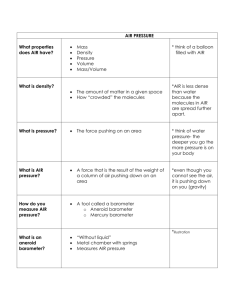
Equation for pressure:
P
F
A
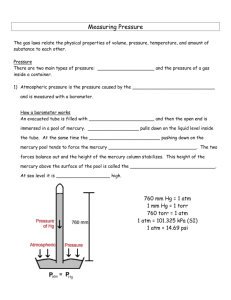
1 atm…
= 760 mm Hg
= 760 torr
= 101.325 kPa
= 1.01325 bar
(1 bar = 10 5 Pa)
F N
A m 2
P N/m 2 = Pa
At a depth of 350 m (1150 ft), the hull pressure on a submarine is 3.4 x 10 6 Pa (36 tons/ft 2 ).
BAROMETER vacuum air pressure mercury (Hg) mercury barometer
Close-up of an early mercury barometer, showing how the mercury column is supported by atmospheric pressure.
An aneroid barometer contains a small, pressure-sensitive metal box that has been evacuated of air. The box is prevented from collapsing by being connected to a spring that is also attached to the dial on the barometer. When the air pressure on the walls of the box changes, the box
“flexes,” which moves the spring and the dial.
OPEN END
MANOMETER air pressure
CLOSED END
MANOMETER sealed end confined gas
Hg height difference
SMALL + HEIGHT = BIG P gas
= HEIGHT
The Gas Laws
Boyle’s law:
PV = constant
(when T is constant)
V
P
Robert Boyle
(1627 –1691)
V
1/P
Charles’s law:
V/T = constant
(when P is constant)
V
Jacques Charles
(1746 –1823)
**T in K
(0.00 K = –273.15
o C)
T
GayLussac’s law:
P/T = constant
(when V is constant)
P
Joseph Louis
Gay-Lussac
(1778 –1850)
T
Avogadro’s hypothesis:
Equal volumes of gas at the same temperature and pressure have the same number of particles. e.g., 22.4 L of ANY GAS at STP contains
6.02 x 10 23 particles
Avogadro’s law:
Volume of a gas is proportional to the number of moles of gas.
(1876 –1956) i.e., V
n
Combined Gas law: merges Boyle’s, Charles’s, and GayLussac’s laws into one equation.
P
1
V
1
T
1
P
2
V
T
2
2
**NOTE:
For all gas law calculations, use the absolute temperature (in K).
Other Equations and Constants
Ideal Gas law:
P V = n R T
R = 8.314 L-kPa/mol-K
= 0.08206 L-atm/mol-K
Conditions of standard temp. and pressure (STP):
0 o C (273.15 K) 1 atm
Equations for gas density:
D
P
R T
= molar mass of gas
P
1
T
1
D
1
P
2
T
2
D
2 same gas; two sets of conditions