Science 8 Unit A Topic 7 Notes Fluid Pressure
advertisement

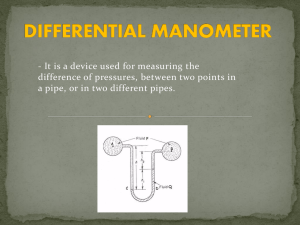
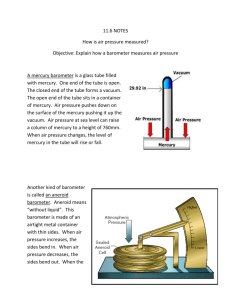
Topic 7: Fluid Pressure The force acting perpendicular to a certain surface area continuous physical force exerted on or against an object by something in contact with it. Pressure (P)= Force (F) Area (a) Force(F) is measured in Newton's (N) Area (a) is measured in square meters (m2) Pressure (P) is measured in (N/m2) ◦ This is also called a Pascal (Pa) ◦ 1000 Pa = 1 kilopascal (kPa) When gases are compressed, they exert a force back We can use this property in vehicle shocks ◦ Vehicle shocks ◦ Car tires (the tubes) ◦ Air bags Earth’s atmosphere is approx. 160 km thick Gravity keeps the envelope of air around Earth Just as water pressure changes with depth, air pressure changes with altitude ◦ The higher the altitude, the less air particles pressing against your body ◦ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QeAp3CuGjk8 ◦ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=7_yf-iRf8Vc Barometer ◦ Early barometer’s were made with Mercury Still used in many weather station’s today ◦ They are made from a thin glass tube that is sealed at one end and open at the other and completely filled with mercury ◦ The tube is then inverted (turned upside down) in a pool of mercury This allows no air to enter the system Mercury falls to the lower level due to gravity Leaves a vacuum at the top As air pushes down on the mercury in the pol which in turn pushes the mercury up the tube until it equalizes with the pressure of gravity Air pressure is 760 mm/Hg at sea level https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VqKkAJd arZ8 If in a closed container, the air pressure is lower inside then on the outside the container will buckle ◦ The pressures do not balance therefore creating an unbalanced force ◦ Ex. Juice box