Section III

SECTION III
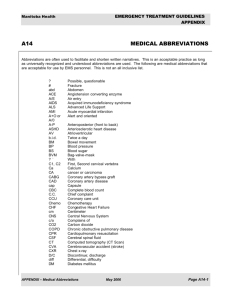
COMMON MEDICAL ABBREVIATIONS
COMMON MEDICAL ABBREVIATIONS
To discuss a therapeutic regimen with a physician you must speak his language. The terminology that will confront you in the patient care areas is different from that to which you have previously been exposed. A typical conversation you might hear at the patient's bedside would go something like, " I hear an S-2 and S-4 with no split sounds or opening snap. Since there has been no history of dyspnea and the
ASO was negative, I suspect an ASD or VSD, but we will not know for sure until after the results of the cath." An admission order written by the physician might read "up ad lib, ADA diet (2000 cal), S&A,
MOM 30 ml, hs, pm. Lab tests as follows: CBC, Crit., Amylase, CPK, PBI, Blood Gases, BUN,
Creatinine, LDH, SGOT, SGPT and Lytes." The language of the physician is oriented toward disease, diagnostic tests and treatment.
The most commonly encountered abbreviations and terminology will be helpful to you as a
Ant
ANA
ASCVD
ASD
ASHD
ASO
A.S.T.
AV
BBB
BBT
BE
BJ reference source. If you are not familiar with a term that is used, you should consult a medical dictionary or ask the physician.
Abbreviations
Abbreviation
ABE
ABS
ADA
AF ad lib
A/G
AHCA
AMA
AK
A.L.T.
Amb
Explanation
Acute bacterial endocarditis
Admitting blood sugar
American Dietetic Association
Acid Fast
As desired
Albumin-globulin ratio
Agency for Healthcare Administration
Against Medical Advice
Above knee amputation
Alanine Aminotransferase (formerly called SGPT)
Ambulant
Anterior
Antinuclear antibody arteriosclerotic vascular disease ( arteriosclerosis )
Atrial septum defect
Arteriosclerotic heart disease
Antistreptolysin 0
Aspartate Aminotransferase (formerly SCOT)
Atrioventricular
BKA
BM
BMR
BP
BRP
BS
Bundle branch block or blood brain barrier
Basal body temperature
Barium enema
Bone and joint
Below knee amputation
Bowel movement
Basal Metabolic rate
Blood pressure
Bathroom privileges
Breath sounds or bowel sounds
III.1
CHF
CHO chr c/o
CNS
COLD
CONG
COPD
CPK
CSF
CST
CT
CV
CVA
CVD
CVP
D/C
D and C
Derm diff
DM
BSA
BSP
BUN
BW
Bx
Ca
Cal
C and S
CBC
CC
Ceph Floc
CFT
DOA
DOE
DTR
DQA
DX
ECG
ECT
EEG
EENT
EKG eg
EMG
EPS
ER
Body surface area
Bromsulphalein
Blood urea nitrogen
Body weight
Biopsy
Carcinoma
Calorie
Culture and sensitivity
Complete blood count
Chief complaint
Cephalin Flocculation
Complement fixation test
Congestive heart failure
Carbohydrate
Chronic
Complains of
Central nervous system
Chronic obstructive lung disease
Congenital
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
Creatinine phosphokinase
Cerebrospinal fluid
Convulsive shock therapy
Circulation time
Cardiovascular
Cerebrovascular accident
Cardiovascular disease
Central venous pressure
Discontinue
Dilation and curettage
Dermatology
Differential blood count
Diabetes mellitus
Dead on arrival
Dyspnea on exertion
Deep tendon reflex
Division of Quality Assurance
Diagnosis
Electrocardiogram
Electroconvulsive therapy
Electroencephalogram
Eye, ear, nose and throat
Electrocardiogram
For example
Electromyography
Extra pyramidal syndrome
Emergency room
III.2
GB
Gc
GFR
GI
G-6-PD
GSW
GTT
GU
GYN
H h
Hb
HCT
HCVD
Hgb
H and P
HPI
HT
HTVD
Hx
ESR
EST
Ext
FBS
F and R
FH
Fld
FRC
FTA
FUO
Fx
ICS
ICU
I and D
I and 0
IM
Imp inf int
Int Med
IOP
IP
IPPB
IV
IVP
IVT
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
Electroshock therapy
Extremities
Fasting blood sugar
Force and rhythm of pulse
Family history
Fluid
Functional residual capacity
Fluorescent treponemal antibody
Fever of undetermined origin
Fracture
Gallbladder
Gonorrhea
Glomerular filtration rate
Gastrointestinal
Glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase
Gun shot wound
Glucose tolerance test
Genitourinary
Gynecology
Hypodermic
Hour
Hemoglobin
Hematocrit
Hypertensive cardiovascular disease
Hemoglobin
History and physical
History of present illness
Height
Hypertensive vascular disease
History
Intercostal space
Intensive care unit
Incision and drainage
Input and output
Intramuscular
Impression
Inferior
Interval
Internal medicine
Intraocular pressure
Intraperitoneal
Intermittent positive pressure breathing
Intravenous
Intravenous pyelogram
Intravenous transfusion
III.3
LDH
LE
LLQ
LMD
LMP
LOA
LUQ
LP
LVH
L and W
MCH
MCV
Med
MH
MI rnm
MOM
MRXI
MS
MSE
MMSE
JVD
K
Kg
KO
KUB
KVO lat
L and A
LBBB
LCM
LBCD
N
NB
Neg
NM
NG
NOS
NPN
NPO
N/S
NSR
NTP
NTG
NYD
Jugular Venous distention
Potassium
Kilogram
Keep open
Kidney, ureter, bladder
Keep vein open
Lateral
Light and accommodation (of pupils)
Left bundle branch block
Left costal margin
Left border cardiac dullness
Lactic acid dehydrogenase
Lupus erythematosus
Left lower quadrant
Local medical doctor
Last menstrual period
Leave of absence
Left upper quadrant
Lumbar puncture
Left ventricular hypertrophy
Living and well
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin
Mean corpuscular volume
Medicine
Menstrual history
Myocardial infarction
Millimeter
Milk of magnesia
May repeat times one
Mitral stenosis or multiple schlerosis or morphine sulfate
Mental status examination
Mini Mental Status Exam
Normal
Newborn
Negative
Neuromusclar
Nasogastric tube
Not Otherwise Specified (used as part of a diagnosis)
Nonprotein nitrogen
Nothing by mouth
Normal saline
Normal sinus rhythm
Normal temperature and pressure
Nitroglyercin
Not yet diagnosed
III.4
OOB
PM
PHC
PMH
PI
PID
PO
Post Op qd qh qod
R
RA
RBBB
RBC
PP
PPD
PPT
PRA
Pre Op
P and R
PRN
Prog
Ps
PSP
Pt
PT
PVC
OB
OB-GYN
Out of bed
OR
OT
P p
PAC
P and A
Para 1
PAT
PBI
PCV
PCO
2
PE
Obstetrics
Obstetrics and gynecology
Operating room
Occupational therapy
Pulse
After
Premature atrial contraction
Percussion and auscultation
Having bom one child
Paroxysmal atrial tachycardia
Protein - bound iodine
Packed Cell Volume
Carbon dioxide partial pressure
Physical examination
Post mortem
Post hospital care
Past medical hospital
Present illness
Pelvic inflammatory disease
By mouth
Post operative
Post partum
Purified protein derivative of tuberculin
Partial prothrombin time
Plasma renin activity before surgery
Pulse and respiration
When necessary
Prognosis
Posterior
Phenosulfonphthalein
Patient
Physical therapy
Premature ventricular contraction
Every day
Every hour
Every other day
Right
Agglutinins or right atrium
Right bundle branch block
Red blood cell
III.5
RHD
RLQ
R/O
ROM
RPF
RR
TP
TPN
TPR
TUR
TV
Tx
URI
UTI sup
Sx
T
T and A
TB
TBW
TCA's
TIBC
VC
VD
VDH
VDRL
ROS
RV
RVH
RUQ
Rx s
S-A
SBE
SC
SGOT
SGPT
SH
Sig
SOB s/p
Sp gr
SR
STAT
STS
Rheumatic heart disease
Right lower quadrant
Rule out
Range of motion exercise
Renal plasma flow
Recovery room
Review of systems
Right ventricle
Right ventricular hypertrophy
Right upper quadrant
Treatment
Without
Sino-atrial
Subacute bacterial endocarditis
Subcutaneous
Serum glutamic oxalacetic transaminase
Serum glutamic pyruvic transaminase
Social history
Let it be labeled
Shortness of breath
Status Post
Specific gravity
Sedimentation rate
At once
Serologic test for syphilis
Superior
Symptoms
Temperature tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy
Tuberculosis
Total body water
Tricyclic antidepressants
Total iron binding capacity
Total protein
Total parenteral nutrition
Temperature, pulse and respiration
Transurethral resection
Trial visit
Treatment
Upper respiratory infection
Urinary tract infection
Vital capacity or vena cava
Venereal disease
Valvular disease of heart
Venereal disease research laboratory
III.6
VF vis
VMA
VP
VS
VSD
WBC
WNL
Wt
Visual field
Namely
Vanilmandelic acid
Venous pressure
Vital signs
Ventricular septal defect
White blood cells
Within normal limits
Weight
III.7
III.8