Seventh Grade Mid-Term Study Guide ANSWERS I. Nature of

Seventh Grade Mid-Term Study Guide ANSWERS
I. Nature of Science- Ch NOS, 1
A. What is science?
Investigation and exploration of natural events and of the new info in that
results from those investigations
B. Define Scientific Inquiry – process that uses a variety of skills and tools to answer questions or to test about the natural world.
– Formulating an investigable question
– Planning an investigation to answer the question
– The collection of appropriate data
– Drawing a conclusion based on the data
– Communicating the results of the investigation
C. Define Scientific Theory – Theories are well tested scientific beliefs. They are believed to be true but could change if new information were to be obtained.
D. Define Scientific Law – a rule that describes a pattern in nature
E. Can scientific theories be changed? Why or why not? yes, if new evidence to support the theory is discovered the theory can be “updated”
F. Why do you use a control group? So you have something to compare your results to
G. Describe the difference between a dependent and an independent variable?
-independent variable is the factor changed by the investigator, “I” change it.
-dependent variable is the factor investigator observes or measures during an experiment
H. Why is it important to use models in science? Scientists may use a variety of models such as physical or computer to simulate things that are too dangerous, expensive, big or small.
I.
What are the standard steps, in order, of the scientific method? ask a question, form a hypothesis, test hypothesis, analyze results, draw conclusions, communicate results
J. Why is it important for scientists to be able to replicate the data from other scientists?
They use this info in their own research and also to verify other scientists’ investigations
How do they communicate their information to other scientists? Scientific articles, speak at conferences, exchange info on internet
K. What is an experiment? a test, especially a scientific one, carried out in order to discover whether a theory is correct or what the results of a particular course of action would be
II. Earth Science- Ch’s 2, 4, 5, 6
A. What are convection currents?
Less dense (hotter) material rises upward towards the crust. As it cools and becomes more dense (cooler) the material sinks back down into the mantle.
In which layer of the Earth do you find convection currents?
Convection currents occur in earth’s mantle.
How do convection currents help with the rock cycle?
As the less dense material moves toward the crust and brings with it igneous and metamorphic rock. This rock then is turned into sediment through erosion and weathering.
The sedimentary rock returns to the crust and through subsidence is pulled into the mantle where it becomes metamorphic and igneous rock again.
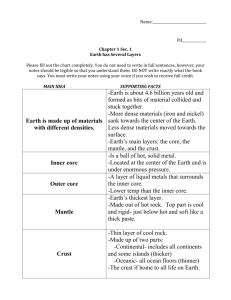
B. What are the layers of the Earth? Give a description of each.
Crust – brittle, rocky slow moving plates, mantle – liquid rock, outer core – solid metal, inner core – liquid metal
C. Explain how density affects the layers of Earth.
The densest materials are in the inner most layer and the least dense materials are on the surface. The two middle layers have intermediate densities. The core is the densest layer, then mantle, and the crust is the least dense.
D. Describe the 3 types of rock and the processes they go through in order to change into other types of rock.
Metamorphic rock-two types: foliate and non-foliated; formed by heat and pressure deep within Earth. The rocks do not melt.
Igneous rock-2 types: intrusive and extrusive; molten lava from within Earth’s core or out of
Earth’s crust cools and hardens.
Sedimentary rock-three types : detrital, chemical, organic; forms in layers from broken rock, shells, plants, and other materials
E. What role does heat play in the rock cycle?
Heat from Earth’s interior is responsible for melting rock and allowing it to form different crystal structures as it cools.
F. What is the Law of Superposition and what does it state about rock layers?
The rock layer on the bottom is likely the oldest, while the top layer is most likely the youngest
G. How does earthquake data support the theory of plate tectonics?
it shows that movement occurs around tectonic plate boundaries
H. What happens at a fault?
A break where one block of rock moves toward, away from, or past another. This causes earthquakes to occur.
I. Describe the Theory of Plate Tectonics. What scientist proposed that the continents changed position over time?
Plate tectonics states that Earth’s surface is made of rigid slabs of rock, or plates, that move with respect to each other.
Wegner
J. Describe the process that occurs at a mid-ocean ridge.
The seafloor spreads, the mantle below melts and magma forms. Because magma is less dense than the solid mantle it rises through cracks in the crust along the mid-ocean ridge. As the process continues the older crust moves away from the ridge.
What is created at mid-ocean ridges?
New crust is created as the plates separate.
What theory was proven by the discovery of the mid-ocean ridge?
Theory of Plate Tectonics
K. What do both volcanic eruptions and fissures have in common?
Both allow magma to reach the earth’s surface
L. Where do most earthquakes occur?
Most earthquakes occur on plate boundaries, especially at the Ring of Fire around the Pacific coastline